You are viewing a plain text version of this content. The canonical link for it is here.
Posted to notifications@shardingsphere.apache.org by zh...@apache.org on 2020/07/18 05:32:53 UTC
[shardingsphere-elasticjob] branch master updated: Translate
failover.en.md & misfire.en.md (#1125)
This is an automated email from the ASF dual-hosted git repository.
zhangliang pushed a commit to branch master
in repository https://gitbox.apache.org/repos/asf/shardingsphere-elasticjob.git
The following commit(s) were added to refs/heads/master by this push:
new c145dd3 Translate failover.en.md & misfire.en.md (#1125)
c145dd3 is described below
commit c145dd31964910c352ba951a44a1b703d88bc321
Author: Tboy <gu...@immomo.com>
AuthorDate: Sat Jul 18 13:32:46 2020 +0800
Translate failover.en.md & misfire.en.md (#1125)
---
docs/content/features/failover.en.md | 48 +++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++-
docs/content/features/misfire.en.md | 27 +++++++++++++++++++-
2 files changed, 73 insertions(+), 2 deletions(-)
diff --git a/docs/content/features/failover.en.md b/docs/content/features/failover.en.md
index db2ef99..c6fc5bf 100644
--- a/docs/content/features/failover.en.md
+++ b/docs/content/features/failover.en.md
@@ -5,4 +5,50 @@ weight = 4
chapter = true
+++
-TODO
+ElasticJob will not re-shard during this execution, but wait for the next scheduling before starting the re-sharding process.
+When the server is down during job execution, failover allows the unfinished task to be compensated and executed on another job node.
+
+## Concept
+
+Failover is a temporary compensation execution mechanism for the currently executed job. When the next job is run, the current job allocation will be adjusted through resharding.
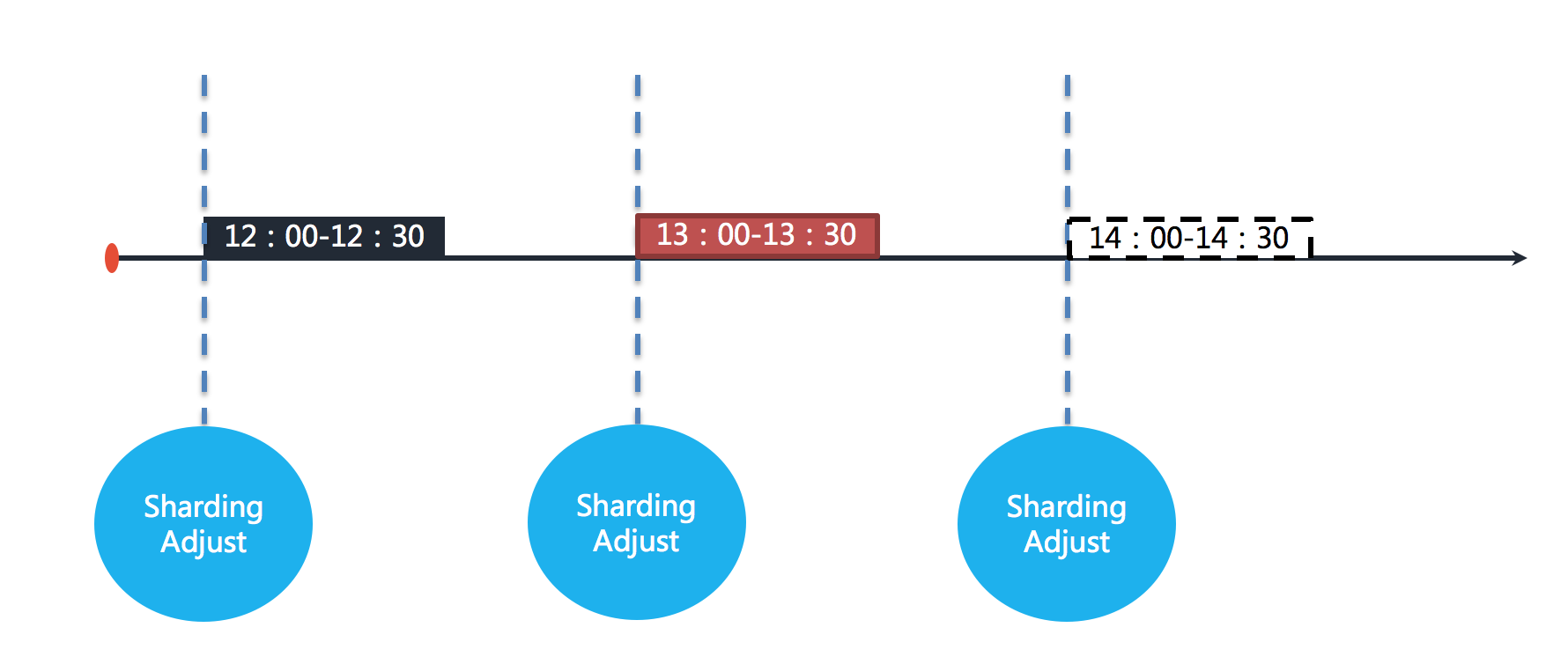
+For example, if the job is executed at an hourly interval, each execution will take 30 minutes. As shown below.
+
+
+
+The figure shows that the jobs are executed at 12:00, 13:00 and 14:00 respectively. The current time point shown in the figure is the job execution at 13:00.
+
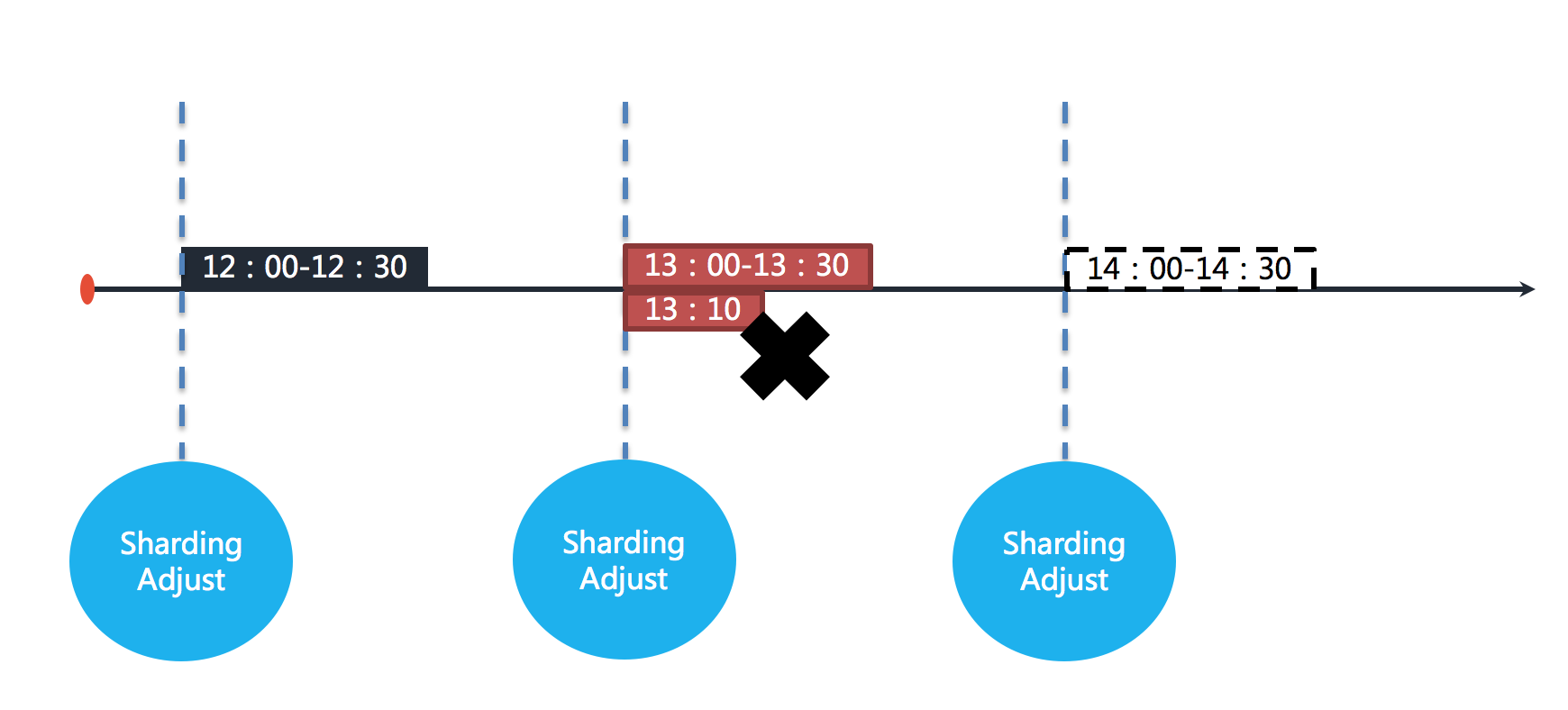
+If one of the shard servers of the job goes down at 13:10, the remaining 20 minutes of the business that should be processed are not executed, and the next job can only be executed at 14:00.
+In other words, if failover is not turned on, there is a 50-minute idle period in this shard. As shown below.
+
+
+
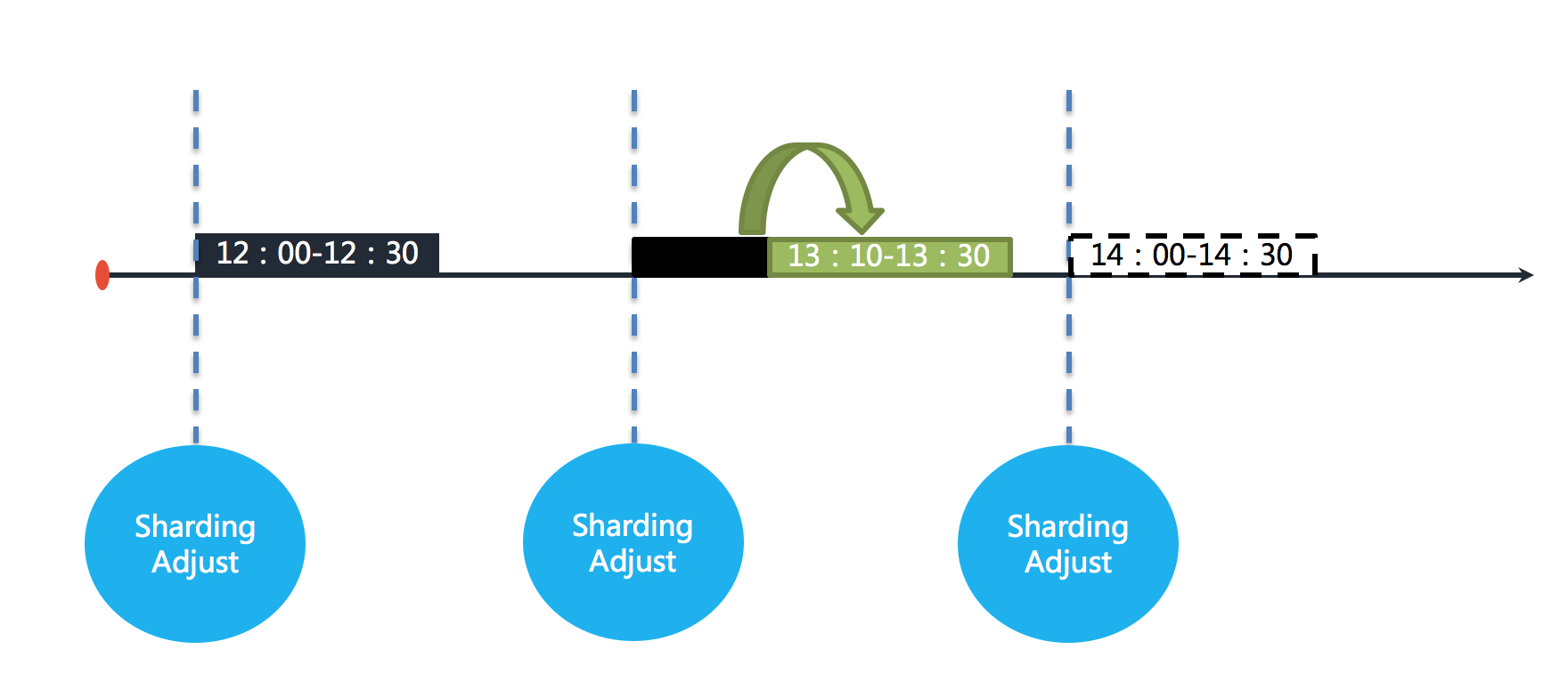
+After the failover is enabled, other ElasticJob servers can compensate for the execution of the sharding job after sensing the down job server. As shown below.
+
+
+
+With sufficient resources, the job can still be executed completely at 13:30.
+
+## Execution mechanism
+
+When the job execution node goes down, the failover process will be triggered. ElasticJob determines the execution timing of the failover according to the different conditions of the distributed job execution when it is triggered。
+
+### Notification execution
+
+When other servers perceive that a failover job needs to be processed, and the job server has completed this task, it will pull the items to be failed over in real time and start compensation execution.
+Also called real-time execution.
+
+### Enquiry execution
+
+After the execution of this task, the job service will inquire about the failover items to be executed from the registry, and if there are any, the compensation execution will start.
+Also called asynchronous execution.
+
+## Scenarios:
+
+With the failover enabled, ElasticJob will monitor the execution status of each shard of the job and write it to the registry for other nodes to perceive.
+
+In a job scenario that takes a long time to run and has a long interval, failover is an effective means to improve the real-time operation of the job;
+For short-interval jobs, a large number of network communications with the registry will be generated, which will affect the performance of the cluster;
+Moreover, short-interval jobs do not necessarily pay attention to the real-time performance of a single job. You can use the re-shard of the next job execution to make all the items execute correctly. Therefore, it is not recommended to enable failover for short-interval jobs.
+
+Another thing to note is that the idempotence of the job itself is a prerequisite to ensure the correctness of failover.
+
diff --git a/docs/content/features/misfire.en.md b/docs/content/features/misfire.en.md
index 6c37ba9..328bd8f 100644
--- a/docs/content/features/misfire.en.md
+++ b/docs/content/features/misfire.en.md
@@ -5,4 +5,29 @@ weight = 5
chapter = true
+++
-TODO
+ElasticJob does not allow jobs to be executed at the same time.
+When the execution time of a job exceeds its running interval, re-executing the missed task can ensure that the job continues to execute the overdue job after completing the last task.
+
+## Concept
+
+The misfire function enables the overdue tasks to be executed immediately after the completion of the previous tasks.
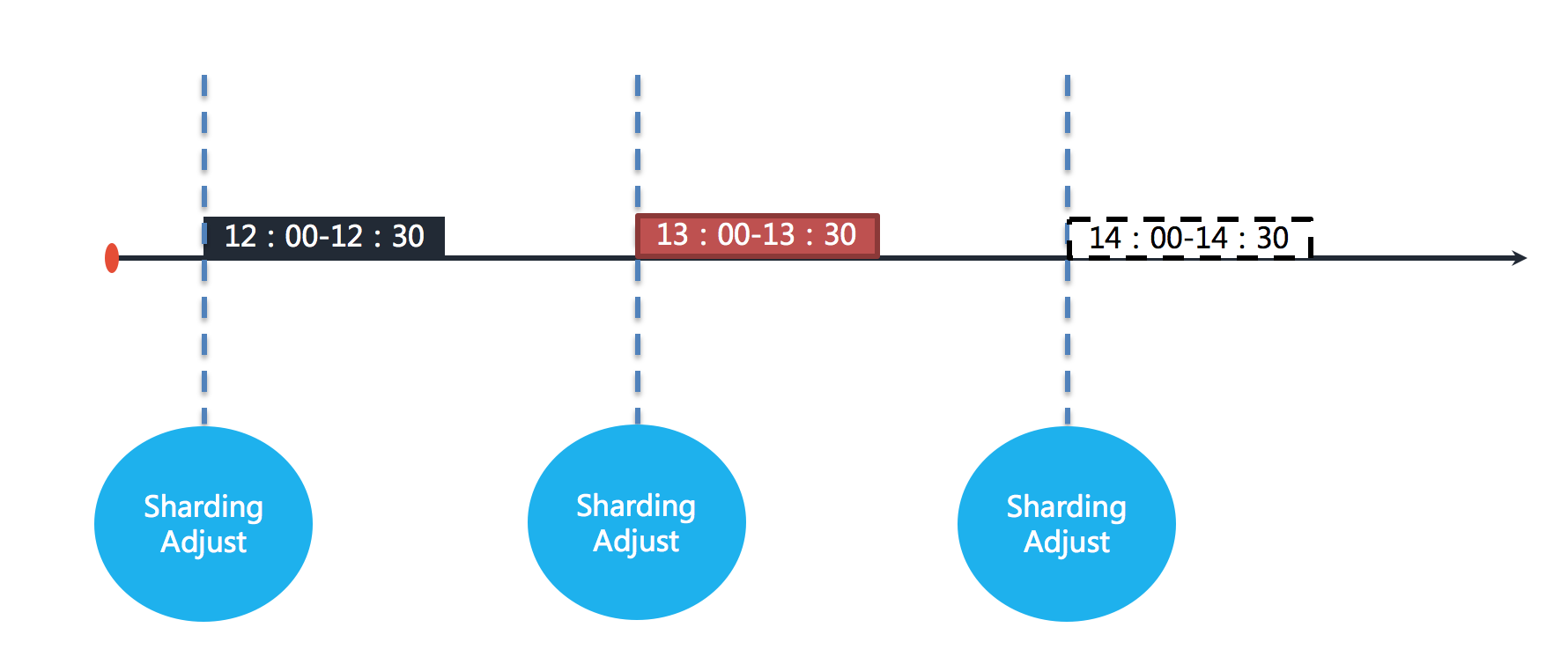
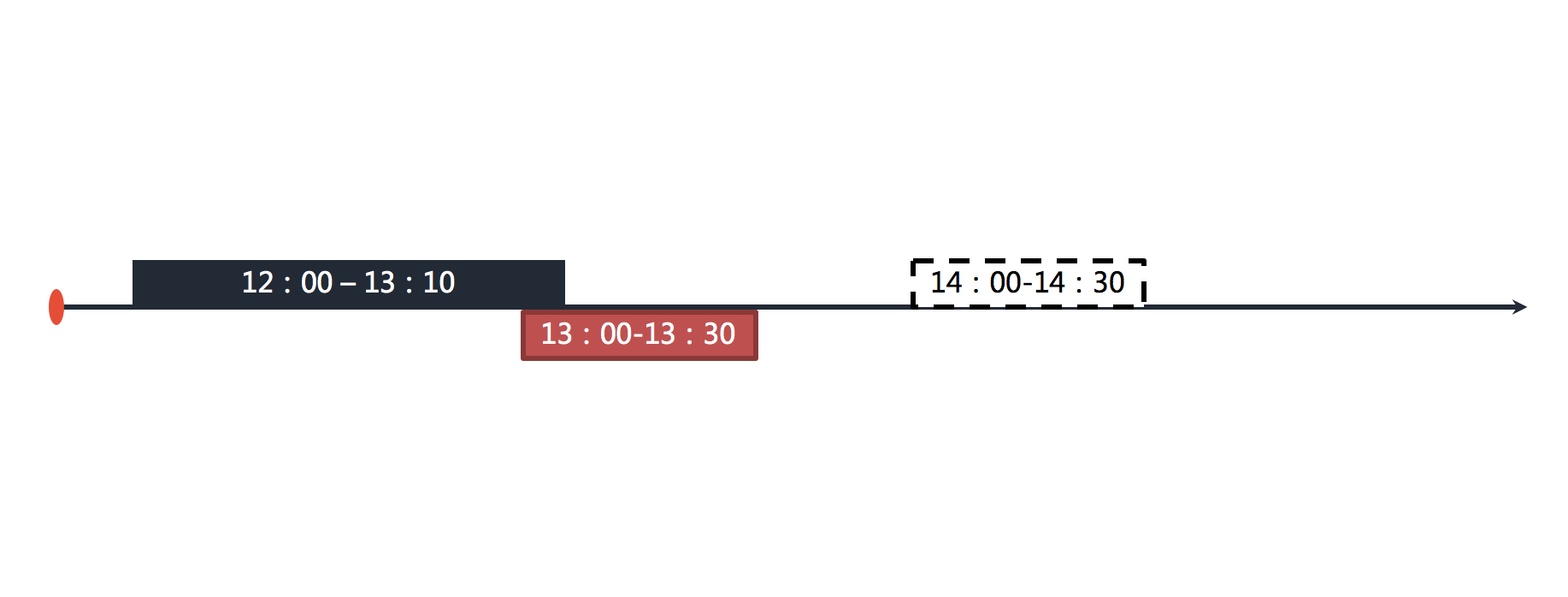
+For example, if the job is executed at an hourly interval, each execution will take 30 minutes. As shown below.
+
+
+
+The figure shows that the jobs are executed at 12:00, 13:00 and 14:00 respectively. The current time point shown in the figure is the job execution at 13:00.
+
+If the job executed at 12:00 is finished at 13:10, then the job that should have been triggered by 13:00 missed the trigger time and needs to wait until the next job trigger at 14:00. As shown below.
+
+
+
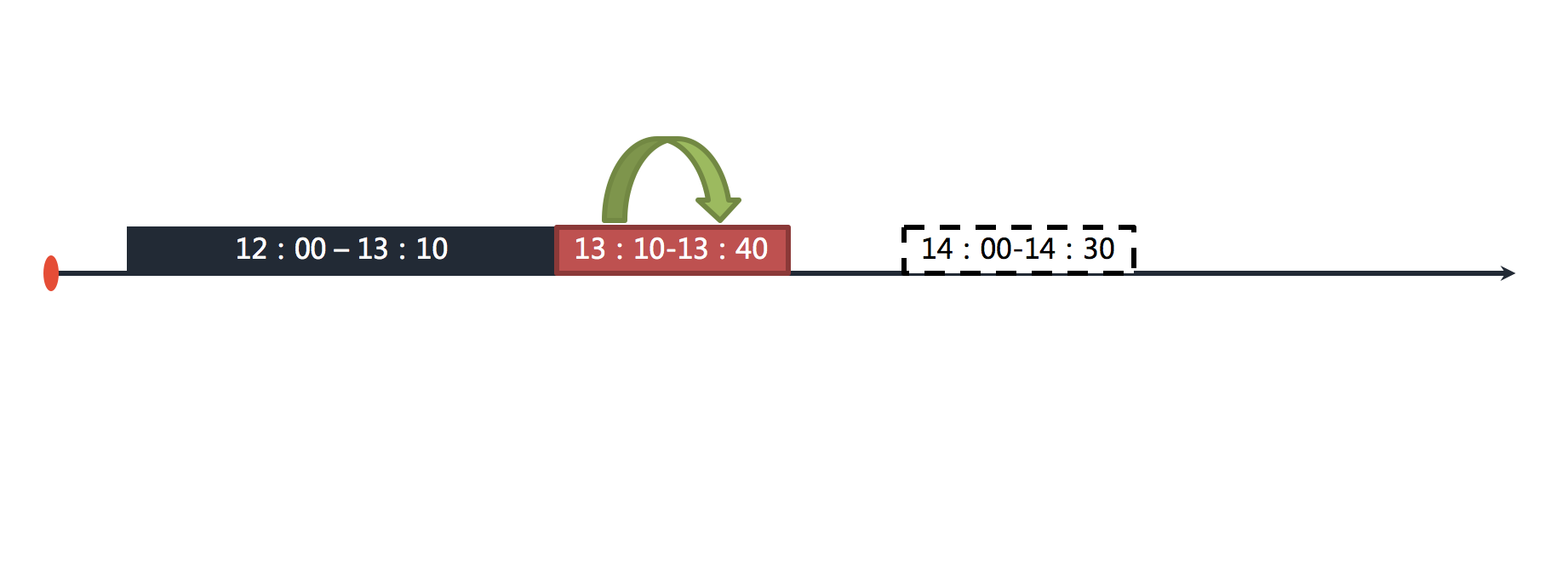
+After the misfire is enabled, ElasticJob will trigger the execution of the missed job immediately after the last job is executed. As shown below.
+
+
+
+Missed jobs between 13:00 and 14:00 will be executed again.
+
+## Scenarios
+
+In a job scenario that takes a long time to run and has a long interval, misfire is an effective means to improve the real-time operation of the job;
+For short-interval jobs that do not necessarily pay attention to the real-time performance of a single job, it is not necessary to turn on the misfire to re-execute.