You are viewing a plain text version of this content. The canonical link for it is here.
Posted to commits@dolphinscheduler.apache.org by li...@apache.org on 2021/06/05 13:35:33 UTC
[dolphinscheduler-website] branch master updated: Translate the
Json_Split (#380)
This is an automated email from the ASF dual-hosted git repository.
lidongdai pushed a commit to branch master
in repository https://gitbox.apache.org/repos/asf/dolphinscheduler-website.git
The following commit(s) were added to refs/heads/master by this push:
new 3a18513 Translate the Json_Split (#380)
3a18513 is described below
commit 3a185130f9880217a5a96c3e389c09c1ff563e7a
Author: QuakeWang <45...@users.noreply.github.com>
AuthorDate: Sat Jun 5 21:35:25 2021 +0800
Translate the Json_Split (#380)
* Create load-balance.md
docs: add en-us load-balance.md
* Delete load-balance.md
* Create Json_Split.md
Translate the Json_Split
* Update json_split.md
update the file
* Update blog.js
update the file
* Update blog.js
update the file
* Update Json_Split.md
Update Json_Split : use process instead of workflow
Co-authored-by: dailidong <da...@gmail.com>
---
blog/en-us/Json_Split.md | 103 +++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
blog/zh-cn/json_split.md | 4 +-
site_config/blog.js | 9 ++++-
3 files changed, 113 insertions(+), 3 deletions(-)
diff --git a/blog/en-us/Json_Split.md b/blog/en-us/Json_Split.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..8d8778c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/blog/en-us/Json_Split.md
@@ -0,0 +1,103 @@
+## Why did we split the big json that holds the tasks and relationships in the DolphinScheduler workflow definition?
+
+### The Background
+
+Currently DolphinScheduler saves tasks and relationships in process as big json to the process_definition_json field in the process_definiton table in the database. If a process is large, for example, with 1000 tasks, the json field becomes very large and needs to be parsed when using the json, which is very performance intensive and the tasks cannot be reused, so the community plans to start a json splitting project. Encouragingly, we have now completed most of this work, so a summary i [...]
+
+### Summarization
+
+The json split project was started on 2021-01-12 and the main development was initially completed by 2021-04-25. The code has been merged into the dev branch. Thanks to lenboo, JinyLeeChina, simon824 and wen-hemin for coding.
+
+The main changes, as well as the contributions, are as follows:
+
+- Code changes 12793 lines
+- 168 files modified/added
+- 145 Commits in total
+- There were 85 PRs
+
+### 拆分方案回顾
+
+
+
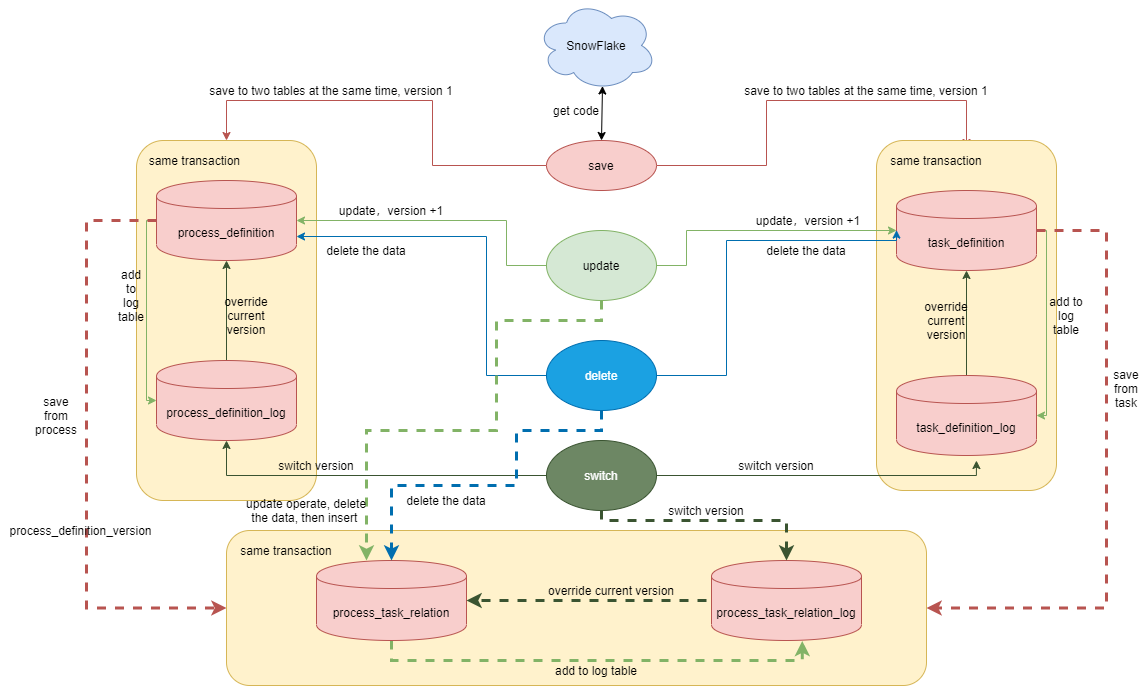
+- [ ] When the api module performs a save operation
+
+1. The process definition is saved to process_definition (main table) and process_definition_log (log table), both tables hold the same data and the process definition version is 1
+2. The task definition table is saved to task_definition (main table) and task_definition_log (log table), also saving the same data, with task definition version 1
+3. process task relationships are stored in the process_task_relation (main table) and process_task_relation_log (log table), which holds the code and version of the process, as tasks are organised through the process and the dag is drawn in terms of the process. The current node of the dag is also known by its post_task_code and post_task_version, the predecessor dependency of this node is identified by pre_task_code and pre_task_version, if there is no dependency, the pre_task_code and [...]
+
+- [ ] When the api module performs an update operation, the process definition and task definition update the main table data directly, and the updated data is inserted into the log table. The main table is deleted and then inserted into the new relationship, and the log table is inserted directly into the new relationship.
+- [ ] When the api module performs a delete operation, the process definition, task definition and relationship table are deleted directly from the master table, leaving the log table data unchanged.
+- [ ] When the api module performs a switch operation, the corresponding version data in the log table is overwritten directly into the main table.
+
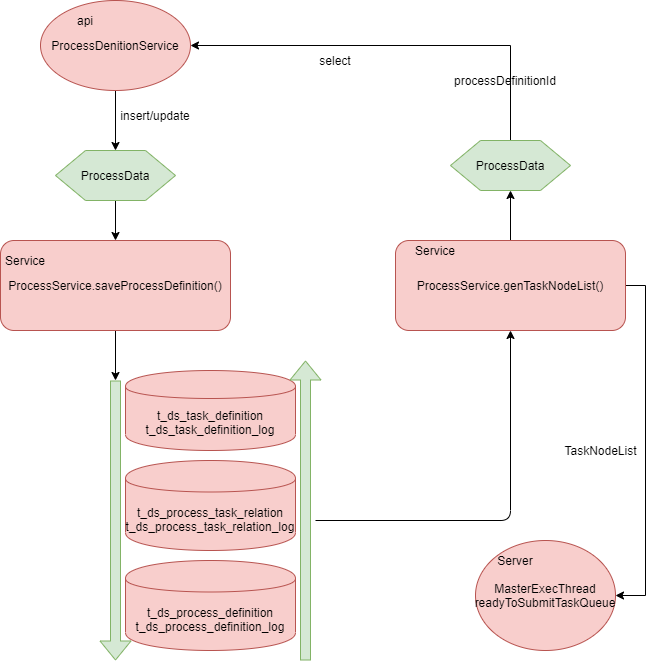
+### Json Access Solutions
+
+
+
+- [ ] In the current phase of the splitting scheme, the api module controller layer remains unchanged and the incoming big json is still mapped to ProcessData objects in the service layer. insert or update operations are done in the public Service module through the ProcessService. saveProcessDefiniton() entry in the public Service module, which saves the database operations in the order of task_definition, process_task_relation, process_definition. When saving, the task is changed if it [...]
+
+- [ ] The data is assembled in the public Service module through the ProcessService.genTaskNodeList() entry, or assembled into a ProcessData object, which in turn generates a json to return
+- [ ] The Server module (Master) also gets the TaskNodeList through the public Service module ProcessService.genTaskNodeList() to generate the dispatch dag, which puts all the information about the current task into the MasterExecThread. readyToSubmitTaskQueue queue in order to generate taskInstance, dispatch to worker
+
+
+
+## Phase 2 Planning
+
+### API / UI module transformation
+
+- [ ] The processDefinition interface requests a back-end replacement for processDefinitonCode via processDefinitionId
+- [ ] Support for separate definition of task, the current task is inserted and modified through the workflow, Phase 2 needs to support separate definition
+- [ ] Frontend and backend controller layer json splitting, Phase 1 has completed the api module service layer to dao json splitting, Phase 2 needs to complete the front-end and controller layer json splitting
+
+### server module retrofit
+
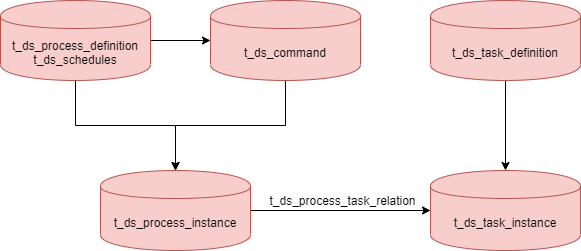
+- [ ] Replace process_definition_id with process_definition_code in t_ds_command and t_ds_error_command、t_ds_schedules
+- [ ] Generating a taskInstance process transformation
+
+The current process_instance is generated from the process_definition and schedules and command tables, while the taskInstance is generated from the MasterExecThread. readyToSubmitTaskQueue queue, and the data in the queue comes from the dag object. At this point, the queue and dag hold all the information about the taskInstance, which is very memory intensive. It can be modified to the following data flow, where the readyToSubmitTaskQueue queue and dag hold the task code and version inf [...]
+
+
+
+---
+
+**Appendix: The snowflake algorithm**
+
+**snowflake:** is an algorithm for generating distributed, drama-wide unique IDs called **snowflake**, which was created by Twitter and used for tweeting IDs.
+
+A Snowflake ID has 64 bits. the first 41 bits are timestamps, representing the number of milliseconds since the selected period. The next 10 bits represent the computer ID to prevent conflicts. The remaining 12 bits represent the serial number of the generated ID on each machine, which allows multiple Snowflake IDs to be created in the same millisecond. snowflakeIDs are generated based on time and can therefore be ordered by time. In addition, the generation time of an ID can be inferred [...]
+
+1. **Structure of the snowflake algorithm:**
+
+ 
+
+ It is divided into 5 main parts.
+
+ 1. is 1 bit: 0, this is meaningless.
+ 2. is 41 bits: this represents the timestamp
+ 3. is 10 bits: the room id, 0000000000, as 0 is passed in at this point.
+ 4. is 12 bits: the serial number, which is the serial number of the ids generated at the same time during the millisecond on a machine in a certain room, 0000 0000 0000.
+
+ Next we will explain the four parts:
+
+**1 bit, which is meaningless:**
+
+Because the first bit in binary is a negative number if it is 1, but the ids we generate are all positive, so the first bit is always 0.
+
+**41 bit: This is a timestamp in milliseconds.**
+
+41 bit can represent as many numbers as 2^41 - 1, i.e. it can identify 2 ^ 41 - 1 milliseconds, which translates into 69 years of time.
+
+**10 bit: Record the work machine ID, which represents this service up to 2 ^ 10 machines, which is 1024 machines.**
+
+But in 10 bits 5 bits represent the machine room id and 5 bits represent the machine id, which means up to 2 ^ 5 machine rooms (32 machine rooms), each of which can represent 2 ^ 5 machines (32 machines), which can be split up as you wish, for example by taking out 4 bits to identify the service number and the other 6 bits as the machine number. This can be combined in any way you like.
+
+**12 bit: This is used to record the different ids generated in the same millisecond.**
+
+12 bit can represent the maximum integer of 2 ^ 12 - 1 = 4096, that is, can be distinguished from 4096 different IDs in the same milliseconds with the numbers of the 12 BIT representative. That is, the maximum number of IDs generated by the same machine in the same milliseconds is 4096
+
+In simple terms, if you have a service that wants to generate a globally unique id, you can send a request to a system that has deployed the SnowFlake algorithm to generate the unique id. The SnowFlake algorithm then receives the request and first generates a 64 bit long id using binary bit manipulation, the first bit of the 64 bits being meaningless. This is followed by 41 bits of the current timestamp (in milliseconds), then 10 bits to set the machine id, and finally the last 12 bits [...]
+
+The characteristics of SnowFlake are:
+
+1. the number of milliseconds is at the high end, the self-incrementing sequence is at the low end, and the entire ID is trended incrementally.
+2. it does not rely on third-party systems such as databases, and is deployed as a service for greater stability and performance in generating IDs.
+3. the bit can be allocated according to your business characteristics, very flexible.
diff --git a/blog/zh-cn/json_split.md b/blog/zh-cn/json_split.md
index 00e2030..eb67b0d 100644
--- a/blog/zh-cn/json_split.md
+++ b/blog/zh-cn/json_split.md
@@ -69,7 +69,7 @@ json split 项目从 2021-01-12 开始启动,到 2021-04-25 初步完成主要
**雪花算法的结构:**
-
+
主要分为 5 个部分:
@@ -102,5 +102,5 @@ SnowFlake 的特点是:
1. 毫秒数在高位,自增序列在低位,整个 ID 都是趋势递增的。
2. 不依赖数据库等第三方系统,以服务的方式部署,稳定性更高,生成 ID 的性能也是非常高的。
-3. 可以根据自身业务特性分配 bi t位,非常灵活。
+3. 可以根据自身业务特性分配 bit 位,非常灵活。
diff --git a/site_config/blog.js b/site_config/blog.js
index 86fe879..f444e4e 100644
--- a/site_config/blog.js
+++ b/site_config/blog.js
@@ -4,6 +4,14 @@ export default {
postsTitle: 'All posts',
list: [
{
+ title: 'Why did we split the big json of DAG in workflow definition?',
+ author: 'JinyLeeChina',
+ translator: 'QuakeWang',
+ dateStr: '2021-06-03',
+ desc: 'The task and relationship in the workflow of Dolphinscheduler is saved as the process_definition_json field that saves the process_definiton table in the database in a large JSON. If a workflow is large, this JSON field has become a result. Very big, you need to analyze JSON when using it, it costs very much, and the task cannot be reused, so the community plan launches the JSON split project.',
+ link: '/en-us/blog/Json_Split.html',
+ },
+ {
title: ' Big Data Workflow Task Scheduling - Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) for Topological Sorting',
author: 'LidongDai',
translator: 'QuakeWang',
@@ -25,7 +33,6 @@ export default {
desc: 'Apache Dolphin Scheduler(Incubating) will organize a meetup in Shanghai 2019.10.26. Welcome to register.',
link: '/en-us/blog/meetup_2019_10_26.html',
},
-
],
},