You are viewing a plain text version of this content. The canonical link for it is here.
Posted to notifications@apisix.apache.org by ju...@apache.org on 2022/04/25 07:51:20 UTC
[apisix-website] branch master updated: docs: add Apache APISIX with TiDB Chinese blog (#1052)
This is an automated email from the ASF dual-hosted git repository.
juzhiyuan pushed a commit to branch master
in repository https://gitbox.apache.org/repos/asf/apisix-website.git
The following commit(s) were added to refs/heads/master by this push:
new 14dc58189c3 docs: add Apache APISIX with TiDB Chinese blog (#1052)
14dc58189c3 is described below
commit 14dc58189c35bfb37e853bcd3f5a98db7b0fba50
Author: Sylvia <39...@users.noreply.github.com>
AuthorDate: Mon Apr 25 15:51:13 2022 +0800
docs: add Apache APISIX with TiDB Chinese blog (#1052)
---
.../blog/2022/04/22/apisix-with-tidb-practice.md | 132 +++++++++++++++++++++
.../2022/04/22/apisix-with-tidb-practice.md | 132 +++++++++++++++++++++
2 files changed, 264 insertions(+)
diff --git a/website/blog/2022/04/22/apisix-with-tidb-practice.md b/website/blog/2022/04/22/apisix-with-tidb-practice.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..3989b2b120b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/website/blog/2022/04/22/apisix-with-tidb-practice.md
@@ -0,0 +1,132 @@
+---
+title: "Best Practices for TiDB-based Apache APISIX High Availability Configuration"
+author: "Chao Zhang"
+authorURL: "https://github.com/tokers"
+authorImageURL: "https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/u/10428333?v=4"
+keywords:
+- API Gateway
+- APISIX
+- TiDB
+- High Availability Configuration
+- TiDB Hackathon
+description: In the TiDB Hackathon 2021, the APISIX team presented the ability of TiDB to interface with Apache APISIX to implement a universal configuration center. In this article, we will bring you some stories behind the project and the future outlook.
+tags: [Technology]
+---
+
+>In the TiDB Hackathon 2021, the APISIX team (team leader: Chao Zhang, team members: Zeping Bai, Zhengsong Tu, Jinghan Chen) presented the ability of TiDB to interface with Apache APISIX to implement a universal configuration center. In this article, we will bring you some stories behind the project and the future outlook, if you are interested in the project, please feel free to participate in the project.
+
+<!--truncate-->
+
+## Project Background
+
+As an important component of microservices architecture, API gateway is the core entry/exit of traffic, used to unify and process business-related requests, which can effectively solve the problems of massive requests and malicious access, and ensure business security and stability.
+
+As an open source cloud-native API gateway, Apache APISIX has three advantages: dynamic, real-time, and high-performance. It provides rich traffic management features such as load balancing, dynamic upstream, grayscale publishing, service fusion, authentication, and observability, helping enterprises to handle API and microservice traffic quickly and securely. Ingress and Service Grid scenarios.
+
+Apache APISIX also supports high customization, Wasm support, and plugin written in Java, Go, Python, and other major computer languages.
+
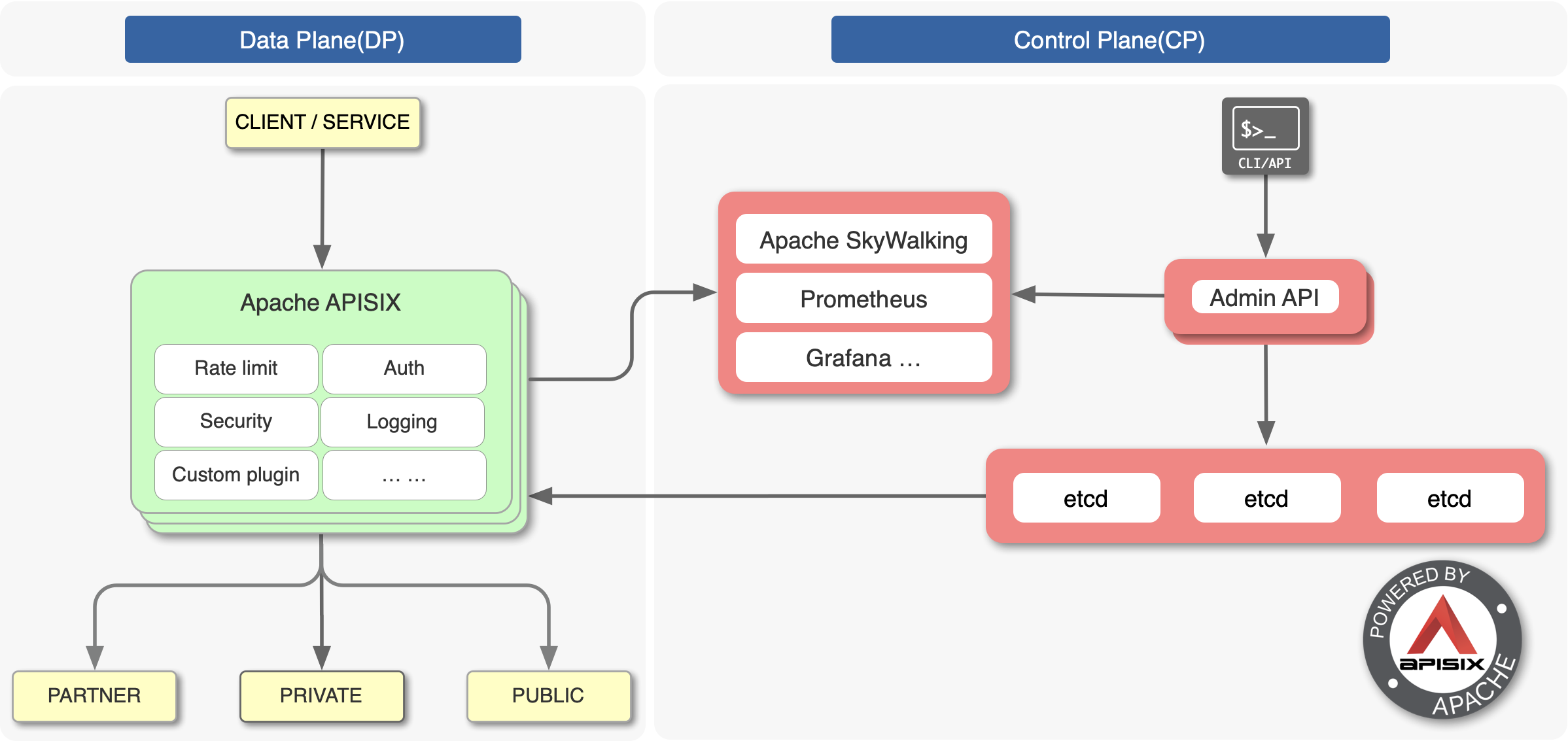
+### Apache APISIX Technical Architecture
+
+Apache APISIX adopts an architecture that separates the data plane from the control plane, receiving and distributing configurations through the configuration center so that the data plane is not affected by the control plane.
+
+
+
+In this architecture, the data plane receives and processes caller requests and dynamically controls request traffic using Lua and NGINX, which can be used to manage the full lifecycle of API requests. The control plane contains the Manager API and the default configuration center etcd, which is used to manage the API gateways. When an administrator accesses and operates the console, the console calls the Manager API to send the configuration to etcd, which takes effect in real time on t [...]
+
+The default configuration center is etcd, which also supports Consul, Nacos, Eureka, etc. etcd naturally supports distributed, high availability, clustering, and has a lot of practice in K8s, etc. APISIX can easily support millisecond configuration updates, thousands of gateway nodes, and the gateway nodes are stateless and can be expanded and reduced at will.
+
+### Limitations of etcd
+
+#### Architectural issues
+
+First of all, etcd is based on BoltDB and has an upper limit. etcd's default storage limit is 2 GB, and if the limit requires more than 2 GB, you can configure the storage with the `-quota-backend-bytes` flag, which can be adjusted up to 8 GB. An etcd cluster with 8 GB of storage is enough to serve one gateway, but if it serves N APISIX clusters at the same time, the capacity may not be enough. but if it serves N APISIX clusters at the same time, it may not have enough capacity and may c [...]
+
+Secondly, etcd is essentially a CP system and cannot host a large number of client connections. Because etcd is distributed consensus through Raft, all read and write requests will be processed by the Leader of Raft, and a large number of client connections may lead to a high load on the whole cluster, which may affect the caller.
+
+#### Scenario issues
+
+In scenarios such as Ingress and Service Mesh, the use of etcd is relatively overloaded, and some users do not want to deploy components other than the control plane and data plane. For example, NGINX Ingress Controller can run with just one image, but APISIX Ingress Controller has an etcd in addition to the Ingress Controller control plane and APISIX data plane. For users, this technical architecture is more expensive to deploy, and they have to ensure the operation and maintenance of etcd.
+
+K8s itself supports storage services, and all configuration information and Endpoints stored in the APISIX backend can be obtained from the K8s API Server. Using etcd in this scenario would make the whole selection more unwieldy.
+
+The same is true for service grids. If you use APISIX in a Service Grid scenario and deploy etcd as well, the whole selection will be heavy. And in a service grid scenario, the number of Pods can be hundreds or even tens of thousands, which is very common. If all the tens of thousands of Pods are connected to etcd, etcd will become the bottleneck of the whole service.
+
+#### Cost issues
+
+First, etcd has high operation and maintenance costs, and some companies do not have dedicated etcd operation and maintenance engineers. At least 3-5 instances are needed to deploy etcd, and after etcd is running successfully, data backups and snapshots need to be done regularly. In order to monitor the operation of etcd and understand the health of etcd in real time, you also need to build an observable system to provide the necessary alerting support. If a company does not have dedicat [...]
+
+Second, some companies or organizations have long-standing middleware or infrastructure, and switching configuration centers can be costly. For these companies or organizations, they often prefer to reuse existing middleware or infrastructure as the configuration center of APISIX, such as TiDB, Consul, and Apache ZooKeeper, so as to converge the technology stack and avoid additional costs.
+
+## Project Motivation
+
+Based on the above considerations, we decided to research a new solution to change the current overloaded technical architecture, provide more flexible options for Apache APISIX users, not bound by etcd, relieve the pressure of etcd operation and maintenance for existing users, reduce operation and maintenance costs, and at the same time expect to give users more and better choices, break through the bottleneck of etcd itself.
+
+Unbinding APISIX from etcd gives users more and more flexible choices, which is actually the charm of open source. If we can remove this layer of restriction and not limit how users can use it, they may create more surprises.
+
+## Project Introduction
+
+### Solution Design
+
+#### How to decouple APISIX and etcd?
+
+The first issue we considered at the beginning of the project design was how to decouple APISIX from etcd, because APISIX's careful code and data structures are closely related to etcd. The Admin API, which is responsible for manipulating the configuration, usually includes the metadata of etcd in the return value.
+
+For example, etcd v3's Revision, etcd v2's createdIndex, modifiedIndex, and even in APISIX's core logic, a route or an Upstream object will carry this metadata.
+
+It would be prohibitively expensive to fundamentally transform APISIX. Modifying such a core area may also affect the existing stability of APISIX, so directly modifying APISIX may not be a good solution.
+
+#### Introducing an additional middle layer
+
+If direct transformation is too costly and risky, can we not consider introducing an extra layer of middle layer? There is a famous saying in the computer world - "there is no problem that cannot be solved by adding a layer". If we were to add a layer, what specific things would this layer be responsible for? What are the things to be done? To summarize, this layer needs to accomplish two more important things.
+
+First, this additional middle tier needs to provide the etcd v3 API and support the etcd gRPC Gateway; currently, APISIX only supports etcd v3. For APISIX, this middle tier is still an etcd, and it must provide the etcd v3 API. Gateway, because APISIX still interacts with etcd via HTTP protocol, and the etcd v3 API is based on gRPC, we need etcd's gRPC Gateway to convert HTTP requests into gRPC requests, so that the whole interaction can proceed smoothly.
+
+Second, this extra middle layer can interface with different storage solutions. We need to figure out how to support TiDB, PostgreSQL, SQLite, and even Consul and Apachce ZooKeeper.
+
+Only when these two things are done can this middle tier interface to different storage solutions and thus bring the full configuration center functionality to APISIX.
+
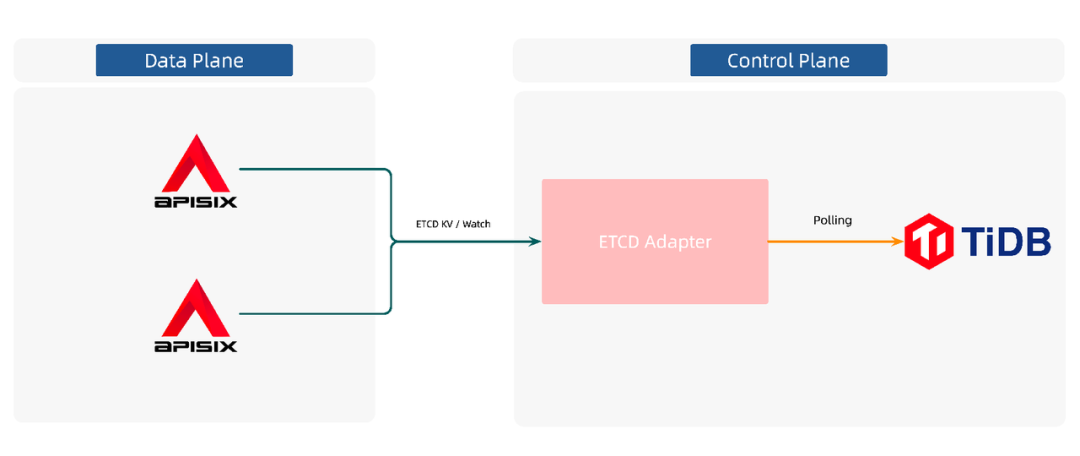
+## Program Implementation
+
+
+
+Once we have this middle tier, how do we integrate TiDB? We actually have a similar project to look at. Although K8s natively supports etcd as a storage solution, Rancher's [K3s](https://github.com/k3s-io/kine) project doesn't use etcd, probably because if K3s is deployed in some embedded environment, etcd has some limitations that make it not well maintained. So, Rancher supports additional components such as PostgreSQL, MySQL, SQLite, and Dqlite through the Kine project, giving K3s use [...]
+
+First, TiDB is compatible with MySQL, and Kine project itself supports MySQL, so we can borrow or refer to some implementations of Kine to help our project better support and interface with TiDB.
+
+Second, Kine completely implements the watch function that etcd needs to support. Because APISIX is based on push mode to sense configuration changes, the latency of configuration changes is usually in millisecond level, which is very low. The watch mechanism is very important because it involves pushing the configuration.
+
+Third, Kine also emulates the MVCC feature of etcd to support Compact, where each change, write, update or delete is a row of data in Kine or TiDB. The primary key for each row of data is etcd's Revision, which is a counter that keeps track of the number of recent changes. In this way, Kine implements multi-version support.
+
+By introducing a similar architecture, Apache APISIX does not have to interact with the real storage center, but with this intermediate layer. As shown above, the APISIX and etcd adapter middle tier goes through etcd's KV API and Watch API. etcd adapter polls TiDB, senses configuration writes, completes the watch operation, and thus pushes the data to APISIX.
+
+## Solution: the etcd adapter
+
+With these thoughts and the reference of the Kine project, we have developed the [etcd adapter](https://github.com/api7/ETCD-adapter) project on the shoulders of giants.
+
+First of all, this project supports TiDB, MySQL and In-Memory B-Tree configuration centers, and soon SQLite and PostgreSQL. If you choose the In-Memory B-tree option, you can directly embed the etcd adapter into the target application. This way there is one less component, which can further improve the overall user experience.
+
+Second, the project supports the etcd v3 API, which currently supports only a subset of the APIs required by APISIX, such as the KV API and the Watch API, while other types of APIs, such as Lease and authentication-based APIs, are not yet fully implemented.
+
+Finally, the project supports the gRPC Gateway, which translates the corresponding gRPC interface into the corresponding Restful interface for APISIX to call.
+
+Although we put the etcd adapter on the control plane, we can also put it on the side of each APISIX as a sidecar. Each of the two options has its own benefits, so you can choose flexibly according to your actual situation.
+
+## Future Plans
+
+We have the following ideas to share with you about the follow-up plan and future direction of this project.
+
+### Provide more configuration center options for Apache APISIX users
+
+We hope that the etcd adapter project will give Apache APISIX users more choices of configuration centers, so that they will not be locked by etcd and can choose solutions according to their actual situation. Consul KV is also based on Raft and has high availability. In addition, you can also consider the more mainstream Apollo or Apache ZooKeeper, which is the counterpart of etcd, and PostgreSQL or other alternatives
+
+### Contribute to the architectural improvement of Apache APISIX Ingress Controller
+
+We hope that the etcd adapter project will help improve the architecture of APISIX Ingress Controller. etcd adapter supports In-Memory B-Tree, which embeds data into memory without the need for physical storage.
+
+In this way, the etcd adapter can become part of the APISIX Ingress Controller, and the Apache Ingress Controller only needs to keep the Ingress Controller control plane and the APISIX data plane components. Since there is no etcd, APISIX can even interact directly with the Ingress Controller to get configuration change data.
+
+In addition, we can also put the Ingress Controller control plane and APISIX data plane in the same image, so that the control plane and data plane can be deployed as one. In the end, we only need one command and one image to run APISIX Ingress Controller in K8s target cluster. If the control plane and data plane are put together, people don't need to deploy an additional etcd and a control plane, which is equivalent to two less components directly and can greatly improve the user experience.
+
+### Donated to the Apache Foundation for incubation as an Apache APISIX subproject
+
+Currently, this [project](https://github.com/api7/etcd-adapter) is sitting in the API7.ai repository. In the future, we hope to continue to polish this project, and when it has been iteratively improved, we will donate it to the Apache Software Foundation to incubate it as a sub-project of Apache APISIX, so as to attract more people from the community to improve this project with us and make the Apache APISIX ecosystem even bigger.
diff --git a/website/i18n/zh/docusaurus-plugin-content-blog/2022/04/22/apisix-with-tidb-practice.md b/website/i18n/zh/docusaurus-plugin-content-blog/2022/04/22/apisix-with-tidb-practice.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..356895d93e1
--- /dev/null
+++ b/website/i18n/zh/docusaurus-plugin-content-blog/2022/04/22/apisix-with-tidb-practice.md
@@ -0,0 +1,132 @@
+---
+title: "基于 TiDB 的 Apache APISIX 高可用配置中心的最佳实践"
+author: "张超"
+authorURL: "https://github.com/tokers"
+authorImageURL: "https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/u/10428333?v=4"
+keywords:
+- API 网关
+- APISIX
+- TiDB
+- 高可用
+- TiDB Hackathon
+description: 在 TiDB Hackathon 2021 的比赛中,APISIX 参赛团队以四人组队方式呈现了 TiDB 与 Apache APISIX 对接实现通用配置中心的能力。本文将为大家带来该项目背后的一些故事以及未来展望。
+tags: [Technology]
+---
+
+> 在 TiDB Hackathon 2021 的比赛中,APISIX 参赛团队以四人组队方式(队长:张超,队员:白泽平、屠正松、陈婧晗)呈现了 TiDB 与 Apache APISIX 对接实现通用配置中心的能力。本文将为大家带来该项目背后的一些故事以及未来展望,如果您对该项目感兴趣,也欢迎随时参与到项目中来。
+
+<!--truncate-->
+
+## 项目背景
+
+API 网关作为微服务架构中的重要组件,是流量的核心出入口,用于统一处理和业务相关的请求,可有效解决海量请求、恶意访问等问题,保障业务安全性与稳定性。
+
+作为开源的云原生 API 网关,Apache APISIX 兼具动态、实时、高性能三大优势,可提供负载均衡、动态上游、灰度发布、服务熔断、鉴权认证、可观测性等丰富的流量管理功能,帮助企业快速、安全地处理 API 和微服务流量,可应用于网关、Kubernetes Ingress 和服务网格等场景。
+
+同时,Apache APISIX 已通过广泛的生态合作建立起丰富的社区生态。Apache APISIX 也支持高度定制化,支持 Wasm,可用 Java、Go、Python 等主流计算机语言编写插件。
+
+### Apache APISIX 技术架构
+
+Apache APISIX 采用了数据平面与控制平面分离的架构方式,通过配置中心接收、下发配置,使得数据平面不会受到控制平面影响。
+
+
+
+在此架构中,数据平面负责接收并处理调用方请求,使用 Lua 与 NGINX 动态控制请求流量,可用于管理 API 请求的全生命周期。控制平面则包含了 Manager API 和默认配置中心 etcd,可用于管理 API 网关。管理员在访问并操作控制台时,控制台将调用 Manager API 下发配置到 etcd,借助 etcd watch 机制,配置将在网关中实时生效。
+
+配置中心默认为 etcd,也支持 Consul、Nacos、Eureka 等。etcd 天然支持分布式、高可用,支持集群,并且在 K8s 等领域有大量的应用实践,使得 APISIX 可以轻松支持毫秒级配置更新、支撑数千网关节点,且网关节点无状态,可任意扩缩容。
+
+### etcd 的局限性
+
+#### 自身架构问题
+
+首先 etcd 基于 BoltDB,容量具有上限 。etcd 的默认存储上限为 2 GB,如果上限要求超过 2 GB,则可以通过 `--quota-backend-bytes` 参数配置存储,最大可调整至 8 GB。一个 etcd 集群如果有 8 GB 的存储量,则足以服务一个网关,但如果同时服务 N 个 APISIX 集群,容量可能不够用,有可能会带来一些麻烦。
+
+其次,etcd 本质上是一个 CP 系统,无法承载大量的客户端连接。因为 etcd 是通过 Raft 来实现分布式共识,所有的读写请求都会经由 Raft 的 Leader 进行处理,大量的客户端连接可能会导致整个集群的负载偏高,有可能会影响到调用者。
+
+#### 场景配合问题
+
+在 Ingress 和 Service Mesh 等场景,使用 etcd 相对来说有点过重,有些用户不希望部署除控制面和数据面以外的组件。比如 NGINX Ingress Controller 只需一个镜像就可以跑起来,但 APISIX Ingress Controller 除了 Ingress Controller 控制面和 APISIX 数据面,还有一个 etcd。对用户来说,这种技术架构的部署成本更高,还要保证 etcd 的运维。
+
+而且本质上,etcd 是一个冗余组件,完全可以去掉。K8s 本身支持存储服务,所有的配置信息、存储在 APISIX 后端的 Endpoints 信息都可以从 K8s 的 API Server 获取。在这种场景使用 etcd 会造成整个选型更加笨重。
+
+服务网格也是同理。在服务网格场景使用 APISIX,如果还要部署 etcd,整个选型就会偏重。而且在服务网格场景,Pod 的数量可能成百上千甚至上万,这种情况很常见。如果上万个 Pod 全部连到 etcd,etcd 会成为整个服务的瓶颈。
+
+#### 成本问题
+
+第一,etcd 的运维成本较高,有些公司没有专门的 etcd 运维工程师。部署 etcd 至少需要 3-5 个实例,etcd 成功运行后,还需要定期做数据备份,创建快照。为了监控 etcd 的运行情况,实时了解 etcd 的健康状况,还需要搭建可观测性系统,提供必要的告警支持。如果一个公司没有专门的 etcd 运维工程师,可能无法做好 etcd 的运维工作。
+
+第二,有些公司或组织有长期使用的中间件或基础设施,切换配置中心会带来一定的成本。对这些公司或组织来说,他们往往更希望复⽤已有的中间件或基础设施作为 APISIX 的配置中⼼,⽐如 TiDB、Consul、Apache ZooKeeper,从而收敛技术栈,避免带来额外的成本。
+
+## 项目动机
+
+基于以上考虑,我们决定研究新的方案,改变现在过重的技术架构,为 Apache APISIX 的用户提供更灵活的选择,不被 etcd 绑定,缓解现有用户的 etcd 运维压力,降低运维成本,同时期望给到用户更多、更优的选择,突破 etcd 的自身瓶颈。
+
+解除 APISIX 和 etcd 的强关联,让用户拥有更多、更灵活的选择,其实也是开源的魅力所在。如果能够解除这一层限制,不限制用户如何用,用户可能会创造出更多惊喜。
+
+## 项目介绍
+
+### 方案设计
+
+#### 如何解耦 APISIX 和 etcd?
+
+方案设计之初,我们考虑的第一个问题是如何实现 APISIX 与 etcd 的解耦,因为 APISIX 的核⼼代码、数据结构与 etcd 关系密切。负责操作配置的 Admin API 通常会在返回值里带上 etcd 的元数据。
+
+比如 etcd v3 的 Revision、etcd v2 的 createdIndex、modifiedIndex,甚至在 APISIX 的核心逻辑里,某个路由或者某个 Upstream 对象也会带上这些元数据。
+
+如果从根本上改造 APISIX,成本会过高。在如此核心的地方进行改造可能也会影响 APISIX 现有的稳定性,因此直接修改 APISIX 可能并不是一个很好的方案。
+
+#### 破局:引入额外的中间层
+
+如果直接改造成本太高且风险太大,那么我们是不是可以考虑引入一层额外的中间层?在计算机界有一句名言——“没有什么问题是加一层解决不了的”。如果要加入一层,这一层具体要负责什么事情?做什么事情?总结下来,这一层需要完成两个比较重要的事情。
+
+第一,这个额外的中间层需提供 etcd v3 API 并⽀持 etcd gRPC Gateway。目前,APISIX 只支持 etcd v3。对 APISIX 来说,这个中间层依然是一个 etcd,它必须提供 etcd v3 的 API。除了提供 v3 的 API,它还要支持 etcd 的 gRPC Gateway,因为 APISIX 现在还是通过 HTTP 协议和 etcd 交互,而 etcd v3 API 是基于 gRPC,我们需要 etcd 的 gRPC Gateway 把 HTTP 的请求转成 gRPC 请求,从而使得整个交互能够顺利进行下去。
+
+第二,这个额外的中间层能对接各种不同的存储方案。我们要想清楚如何支持 TiDB、PostgreSQL,SQLite,甚至是 Consul、Apachce ZooKeeper 这些不同的方案。
+
+只有做到了这两点,这个中间层才能对接不同的存储方案,从而给 APISIX 带来完整的配置中心的功能。
+
+## 方案实施
+
+
+
+有了这个中间层后,我们要怎么集成 TiDB 呢?其实我们有一个类似的项目可以参考。虽然 K8s 原生支持使用 etcd 作为存储方案,但 Rancher 的 [K3s](https://github.com/k3s-io/kine) 项目并没用 etcd,可能是因为如果 K3s 部署在某些嵌入式环境中,etcd 的一些限制使其没有办法很好地运维。于是,Rancher 通过 Kine 这个项目,支持了一些额外的组件,比如 PostgreSQL、MySQL、SQLite、 Dqlite,使得 K3s 的用户可以灵活选择其他存储方案。概括来说,Kine 这个项目有以下几点值得我们借鉴。
+
+第一,TiDB 兼容 MySQL,而 Kine 项目本身又支持 MySQL。我们可以借鉴或者参考 Kine 的一些实现,从而帮助我们这个项目更好地支持和对接 TiDB。
+
+第二, Kine 完整地实现了 etcd 需要支持的 watch 功能。因为 APISIX 是基于推模式来感知配置的变更,配置变更的时延通常在毫秒级别,时延非常低。而 watch 功能正好涉及到配置的推送,所以 watch 机制相当重要。
+
+第三,Kine 还模拟了 etcd 的 MVCC 特性,支持 Compact。每一次的变更、写入、更新或者删除在 Kine 或 TiDB 里就是一行数据。每行数据的主键就是 etcd 的 Revision,也就是计数器,记录最新变更的次数。通过这种方式,Kine 实现了多版本的支持。
+
+通过引入类似架构,Apache APISIX 不用和真正的存储中心进行交互,而是和这个中间层(etcd adapter)进行交互。如上图,APISIX 和 etcd adapter 会走 etcd 的 KV API 和 Watch API,etcd adapter 会轮询 TiDB,感知配置的写入,完成 watch 操作,从而把数据推给 APISIX。
+
+## 方案效果:etcd adapter 的诞生
+
+有了这些思考以及 Kine 这个项目的参考,我们站在巨人的肩膀上开发出了 [etcd adapter](https://github.com/api7/ETCD-adapter) 项目。
+
+首先,这个项目支持了 TiDB、MySQL 以及 In-Memory B-Tree 等多种配置中心,不久后,也会支持 SQLite 和 PostgreSQL。其中,In-Memory B 树和 APISIX Ingress Controller 架构过重有关。如果选择 In-Memory 的 B 树选型,用户可以直接把 etcd adapter 内嵌到目标程序里面。这种方式少了一个组件,可以进一步提升整体的用户体验。
+
+其次,这个项目支持了 etcd v3 的 API。目前,这个项目只支持了 APISIX 所需的 API 子集,比如 KV API 和 Watch API。至于其他类型的 API,比如 Lease、偏认证类的 API 还没有全部实现。
+
+最后,这个项目⽀持了 gRPC Gateway。它会把对应的 gRPC 接口翻译成对应的 Restful 接口,供 APISIX 调用。
+
+虽然我们把 etcd adapter 放在了控制面,但我们也可以把它放在每个 APISIX 边上,作为一个 Sidecar 存在。两种方案各有好处,用户可以根据自己的实际情况灵活选择。
+
+## 未来计划
+
+关于这个项目的后续计划和未来方向,我们有以下几点想法分享给大家。
+
+### 为 Apache APISIX 的⽤户提供更多的配置中心选择
+
+我们希望 etcd adapter 项目能让 Apache APISIX 的用户有更多的配置中心选择,不被 etcd 锁定,用户可以根据自己的实际情况选择解决方案。如果公司的运维、开发的技术栈更偏向于 Consul,就可以使用 Consul。Consul KV 也是基于 Raft,可用性很高。除此以外,也可以考虑比较主流的 Apollo 或者和 etcd 对标的 Apache ZooKeeper,还有 PostgreSQL 或者其他备选方案。
+
+### 为 Apache APISIX Ingress Controller 的架构改良助力
+
+我们希望 etcd adapter 项目能为 APISIX Ingress Controller 的架构改良助力。etcd adapter 支持了 In-Memory B-Tree,In-Memory B-Tree 可以把数据嵌入到内存里,而不需要实际地存储。
+
+如此一来,etcd adapter 可以成为 APISIX Ingress Controller 的一部分,Apache Ingress Controller 只需保留 Ingress Controller 控制面和 APISIX 数据面两个组件。因为没有使用 etcd,APISIX 甚至可以和 Ingress Controller 直接交互,获取配置变更数据。
+
+除此以外,我们还可以把 Ingress Controller 控制面和 APISIX 数据面放在同一个镜像里,实现控制面与数据面的⼀体化部署。最终只需要一条命令、一个镜像,就可以在 K8s 目标集群中把 APISIX Ingress Controller 运行起来。如果控制面、数据面放在一起,用户就不需要额外部署一个 etcd 和一个控制面,相当于直接少了两个组件,可以极大地提升用户体验。
+
+### 捐赠给 Apache 基金会,作为 Apache APISIX 子项目进行孵化
+
+目前,这个[项目](https://github.com/api7/etcd-adapter)放在 API7.ai 仓库里。未来,我们期望持续打磨这个项目,待项目迭代地比较完善后,会把它捐赠给 Apache 软件基金会,作为 Apache APISIX 的子项目进行孵化,从而吸引到更多社区的有志之士,和我们一起完善这个项目,让 Apache APISIX 的生态更加庞大。