You are viewing a plain text version of this content. The canonical link for it is here.
Posted to notifications@shardingsphere.apache.org by zh...@apache.org on 2020/07/18 16:45:12 UTC
[shardingsphere-elasticjob] branch master updated: Translate
docs/content/features/elastic.en.md (#1148)
This is an automated email from the ASF dual-hosted git repository.
zhangliang pushed a commit to branch master
in repository https://gitbox.apache.org/repos/asf/shardingsphere-elasticjob.git
The following commit(s) were added to refs/heads/master by this push:
new 5f2865c Translate docs/content/features/elastic.en.md (#1148)
5f2865c is described below
commit 5f2865c98fda994b3200c92ede2f8e75900024af
Author: kezhenxu94 <ke...@apache.org>
AuthorDate: Sun Jul 19 00:45:04 2020 +0800
Translate docs/content/features/elastic.en.md (#1148)
---
docs/content/features/elastic.en.md | 48 ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++-
1 file changed, 47 insertions(+), 1 deletion(-)
diff --git a/docs/content/features/elastic.en.md b/docs/content/features/elastic.en.md
index 5c93f54..55daf11 100644
--- a/docs/content/features/elastic.en.md
+++ b/docs/content/features/elastic.en.md
@@ -5,4 +5,50 @@ weight = 2
chapter = true
+++
-TODO
+Elastic schedule is the most important feature in ElasticJob, which acts as a job processing system that enables the horizontal scaling of jobs by sharding, it's also the origin of the project name "ElasticJob".
+
+## Sharding
+
+A concept in ElasticJob to split the job, enabling the job to be executed in distributed environment, where every single server only executes one of the slice that is assigned to it.
+ElasticJob is aware of the number of servers in an almost-real-time manner, with the increment/decrement number of the servers, it re-assigns the job slices to the distributed servers, maximizing the efficiency as the increment of resources.
+
+To execute the job in distributed servers, a job will be divided into multiple individual job items, one or some of which will be executed by the distributed servers.
+
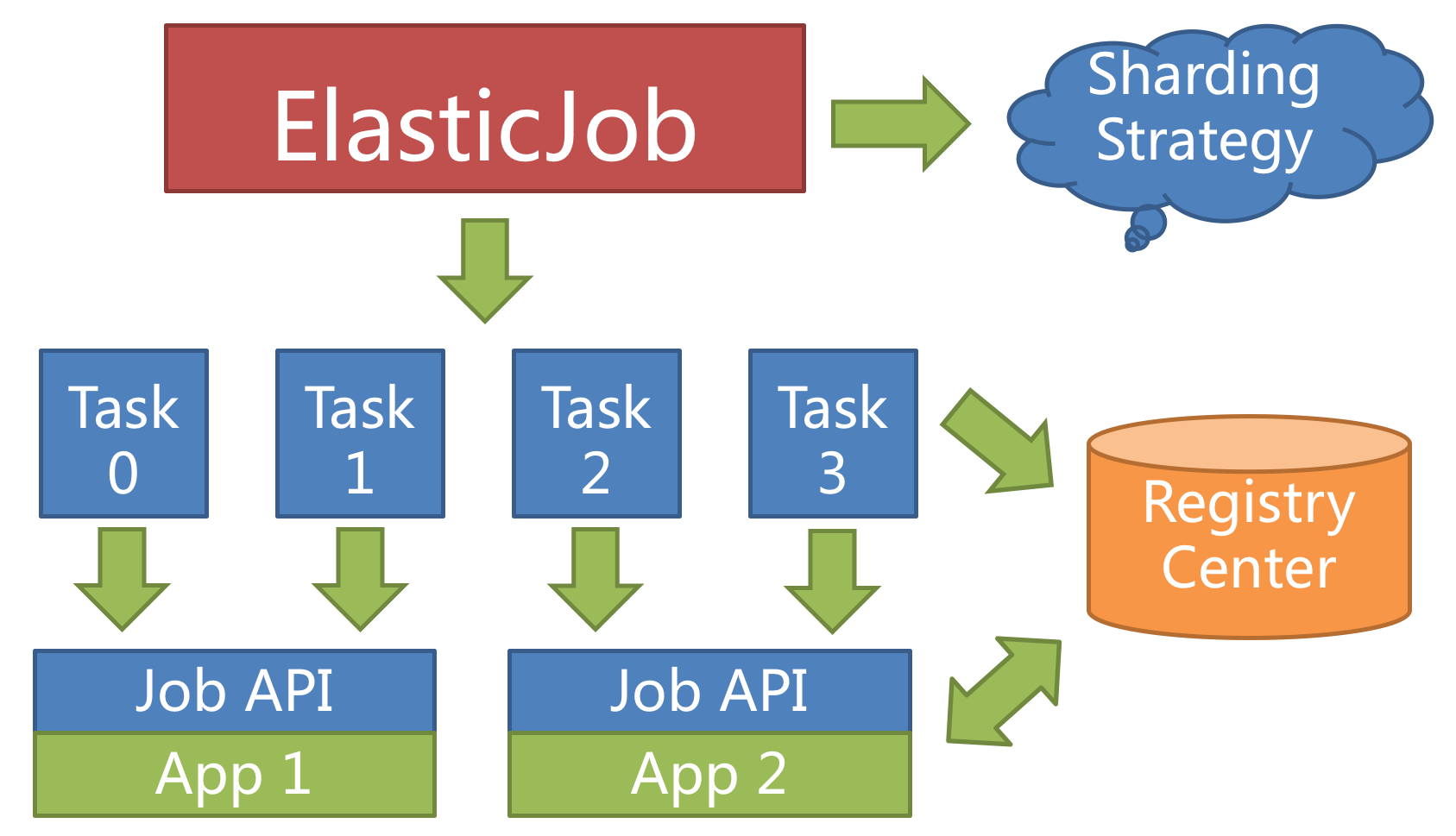
+For example, if a job is divided into 4 slices, and there're two servers to execute the job, then each server is assigned 2 slices, undertaking 50% of the workload, as follows.
+
+
+
+### Sharding Item
+
+ElasticJob doesn't directly provide the abilities to process the data, instead, it assigns the sharding items to the job servers, where the developers should process the sharding items and their business logic themselves.
+The sharding item is numeric type, in the range of [0, size(slices) - 1].
+
+### Customized sharding options
+
+Customized sharding options can build a relationship with the sharding items, converting the sharding items' numbers to more readable business codes.
+
+For example, to horizontally split the databases according to the regions, database A stores data from Beijing, database B stores data from Shanghai and database C stores data from Guangzhou.
+If we configure only by the sharding items' numbers, the developers need the knowledge that 0 represents Beijing, 1 represents Shanghai and 2 represents Guangzhou.
+Customized sharding options make the codes more readable, if we have customized options `0=Beijing,1=Shanghai,2=Guangzhou`, we can simply use `Beijing`, `Shanghai`, `Guangzhou` in the codes.
+
+## Maximize the usage of resources
+
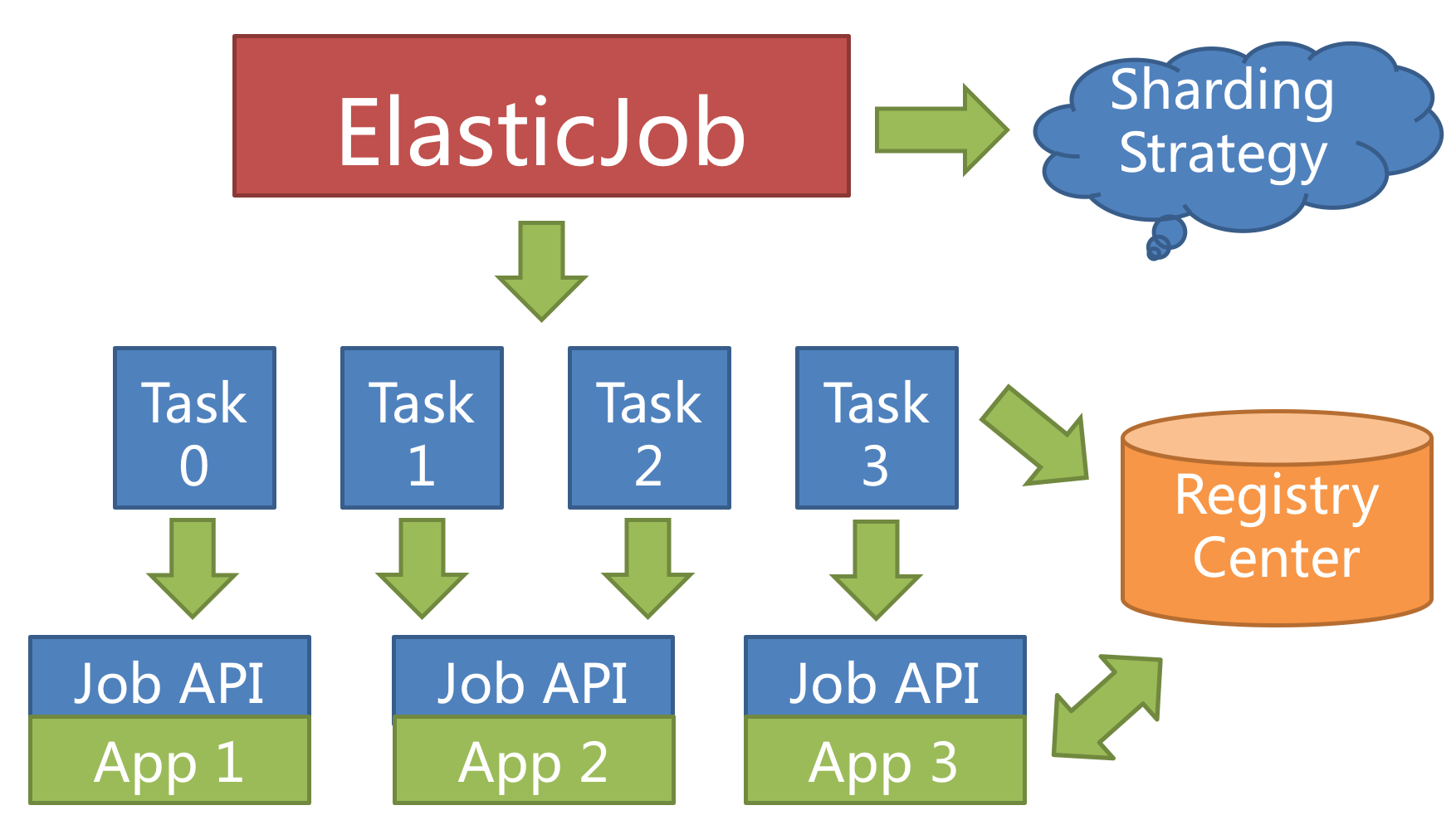
+ElasticJob provides a flexible way to maximize the throughput of the jobs.
+When new job server joins, ElasticJob will be aware of it from the registry, and will re-shard in the next scheduling process, the new server will undertake some of the job slices, as follows.
+
+
+
+Configuring a larger number of sharding items than the number of servers, or better, a multiplier of the number of servers, makes it more reasonably for the job to leverage the resources, and assign the sharding items dynamically.
+
+For example, we have 10 sharding items and there're 3 servers, the number of sharding items are server A = 0,1,2; server B = 3,4,5; server C = 6,7,8,9.
+If the server C is down, then server A = 0,1,2,3,4 and B = 5,6,7,8,9, maximizing the throughput without losing any sharding item.
+
+## High Availability
+
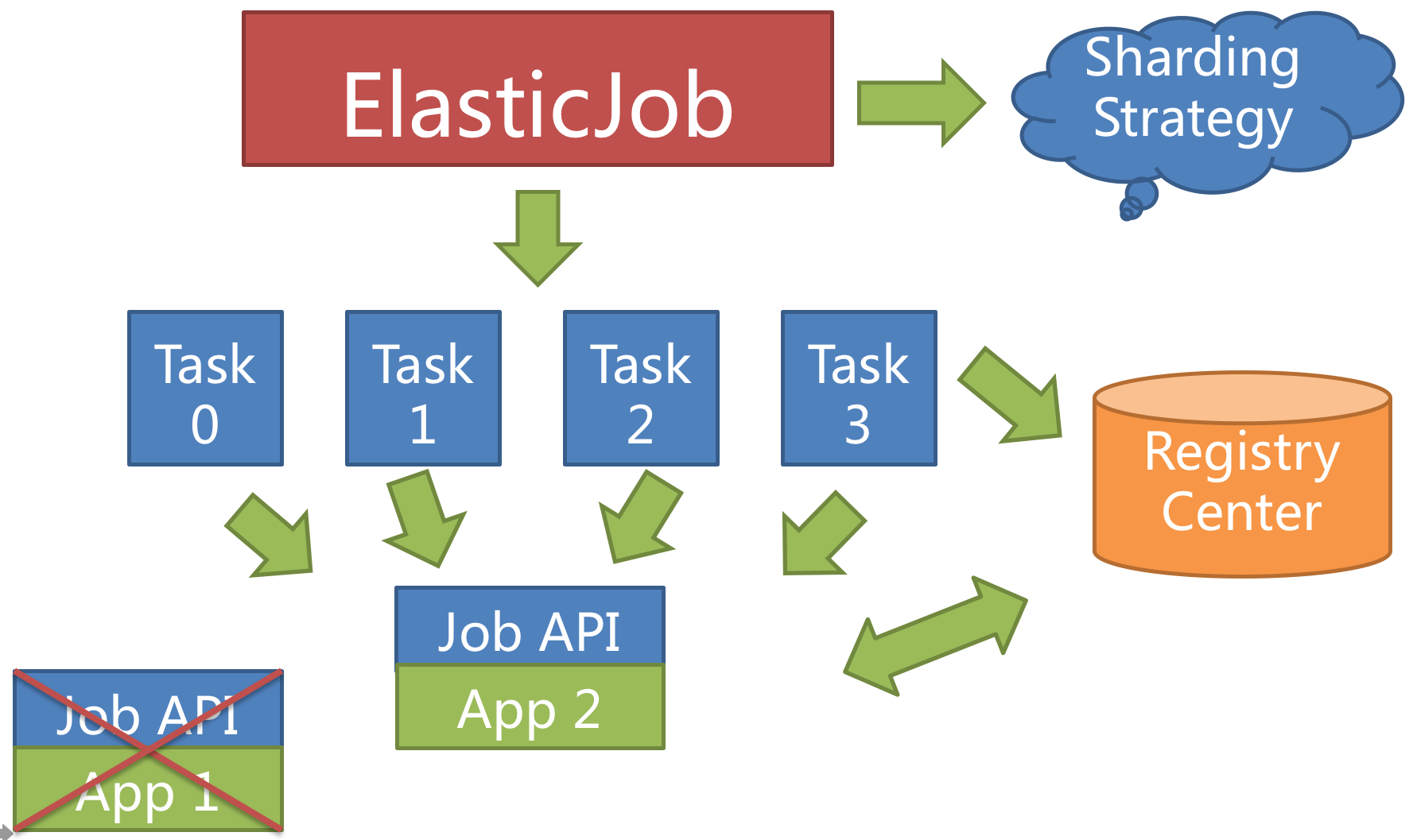
+When a server is down when executing a sharding item, the registry is also aware of that and the sharding item will be transferred to another living server, thus achieve the goal of high availability.
+The unfinished job from a crashed server will be transferred and executed continuously, as follows.
+
+
+
+Setting the total number of sharding items to 1 and more than 1 servers to execute the jobs makes the job run in the mode of `1` master and `n` slaves.
+Once the servers that are executing jobs are down, the idle servers will take over the jobs and execute them in the next scheduling, or better, if the failover option is enabled, the idle servers can take over the failed jobs immediately.