You are viewing a plain text version of this content. The canonical link for it is here.
Posted to notifications@apisix.apache.org by GitBox <gi...@apache.org> on 2022/10/27 08:50:23 UTC
[GitHub] [apisix-website] Boburmirzo opened a new pull request, #1380: docs: Add new blog post 10 usecases of an API Gateway
Boburmirzo opened a new pull request, #1380:
URL: https://github.com/apache/apisix-website/pull/1380
Fixes: #[Add issue number here]
Changes:
A new blog post about the 10 most use cases of an API Gateway in API-Led architecture
Screenshots of the change:
A draft version of the content can be found on dev.to
https://dev.to/bobur/10-most-use-cases-of-an-api-gateway-in-api-led-architecture-3md9-temp-slug-4413613?preview=57dce358a48ae0224e2f3a3f6beae69e9bf277a6ad8272e7acc6bf161cdcb48546803e4ac3eee0afb14bd89dd1701de32059379a4638c379650cde5f
--
This is an automated message from the Apache Git Service.
To respond to the message, please log on to GitHub and use the
URL above to go to the specific comment.
To unsubscribe, e-mail: notifications-unsubscribe@apisix.apache.org
For queries about this service, please contact Infrastructure at:
users@infra.apache.org
[GitHub] [apisix-website] nfrankel commented on a diff in pull request #1380: docs: Add new blog post 10 usecases of an API Gateway
Posted by GitBox <gi...@apache.org>.
nfrankel commented on code in PR #1380:
URL: https://github.com/apache/apisix-website/pull/1380#discussion_r1006672354
##########
blog/en/blog/2022/10/27/ten-use-cases-api-gateway.md:
##########
@@ -0,0 +1,180 @@
+---
+title: "10 most use cases of an API Gateway in API-Led architecture"
+authors:
+ - name: Bobur Umurzokov
+ title: Author
+ url: https://github.com/Boburmirzo
+ image_url: https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/u/14247607
+keywords:
+- API Gateway
+- Apache APISIX
+- API
+- Architecture
+- Use-cases
+- Microservices
+description: This post elaborates on the 10 most common usages of an API Gateway such as Apache APISIX in architecting API-Led Connectivity.
+tags: [Case Studies]
+image: https://static.apiseven.com/2022/10/27/635a40e58b27a.png
+---
+
+> This post elaborates on the **10 most common usages** of an _API Gateway_ such as [Apache APISIX](https://apisix.apache.org/) in architecting [API-Led Connectivity](https://blogs.mulesoft.com/learn-apis/api-led-connectivity/what-is-api-led-connectivity/). We understand different solutions where you can make use of the API Gateway capabilities to design reliable, high-performance, and simple APIs for other developers.
+
+<!--truncate-->
+
+Here is the summary of 10 patterns that uses the API Gateway (but not all):
+
+1. API Resource routing.
+2. API Content-based routing.
+3. API Geo-routing.
+4. API Aggregator.
+5. API Centralized Authentication.
+6. API Format Conversion.
+7. API Observability.
+8. API Caching.
+9. API Fault handling.
+10. Sidecar API Gateway.
+
+## API-Led Architecture
+
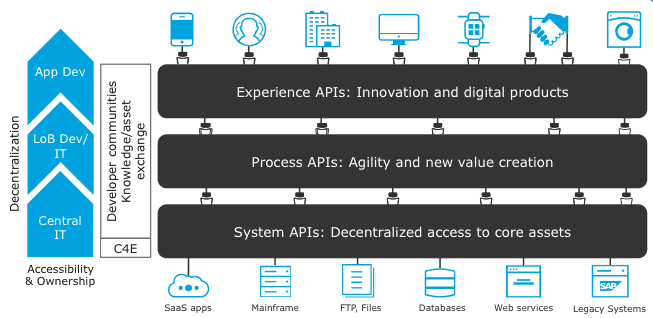
+First of all, let’s revise once again these 3 terms like: **API Gateway**, **API-Led architecture**, and **API-Led Connectivity**.
+
+[API Gateway](https://wikitech.wikimedia.org/wiki/API_Gateway) is a _pattern_ formed by adding a layer between the client and the server that acts as a reverse proxy forwarding request from the client to the server. It allows all clients to access the services they want to access with a single API Gateway layer.
+
+[API-led](https://dzone.com/articles/mulesoft-api-led-connectivity-architectural-and-de) is an _architectural approach_ that puts APIs at the heart of communications between applications and the business capabilities they need to access, in order to consistently deliver seamless functionality across all digital channels.
+
+
+
+**API-led connectivity** refers to _the technique_ of using reusable and well-designed APIs to link data and applications which in turn it is based on **API-Led architecture**. It’s _a modern approach_ that looks at the best ways of reusing APIs to boost your innovation and move quickly in the market. At the most basic level, API-led architecture should address things like:
+
+- Securing APIs from unauthorized access and significant security threats.
+- Ensuring that consuming applications can always find the right API endpoint.
+- Throttling and/or limiting the number of calls made to an API to ensure continuous availability.
+- Supporting capabilities such as API design, testing, continuous integration, life cycle management, monitoring, and operations, to name a few.
+- Error handling and preventing error propagation across the stack.
+- Real-time monitoring of APIs with rich analytics and insight.
+- An approach for implementing scalable and flexible business capabilities, for example, in support of microservices architectures.
+
+Let’s describe in subsequent sections each usage of an API Gateway to address common requirements/challenges that arise when adopting API-led architectures.
+
+---
+
+## API resource routing
+
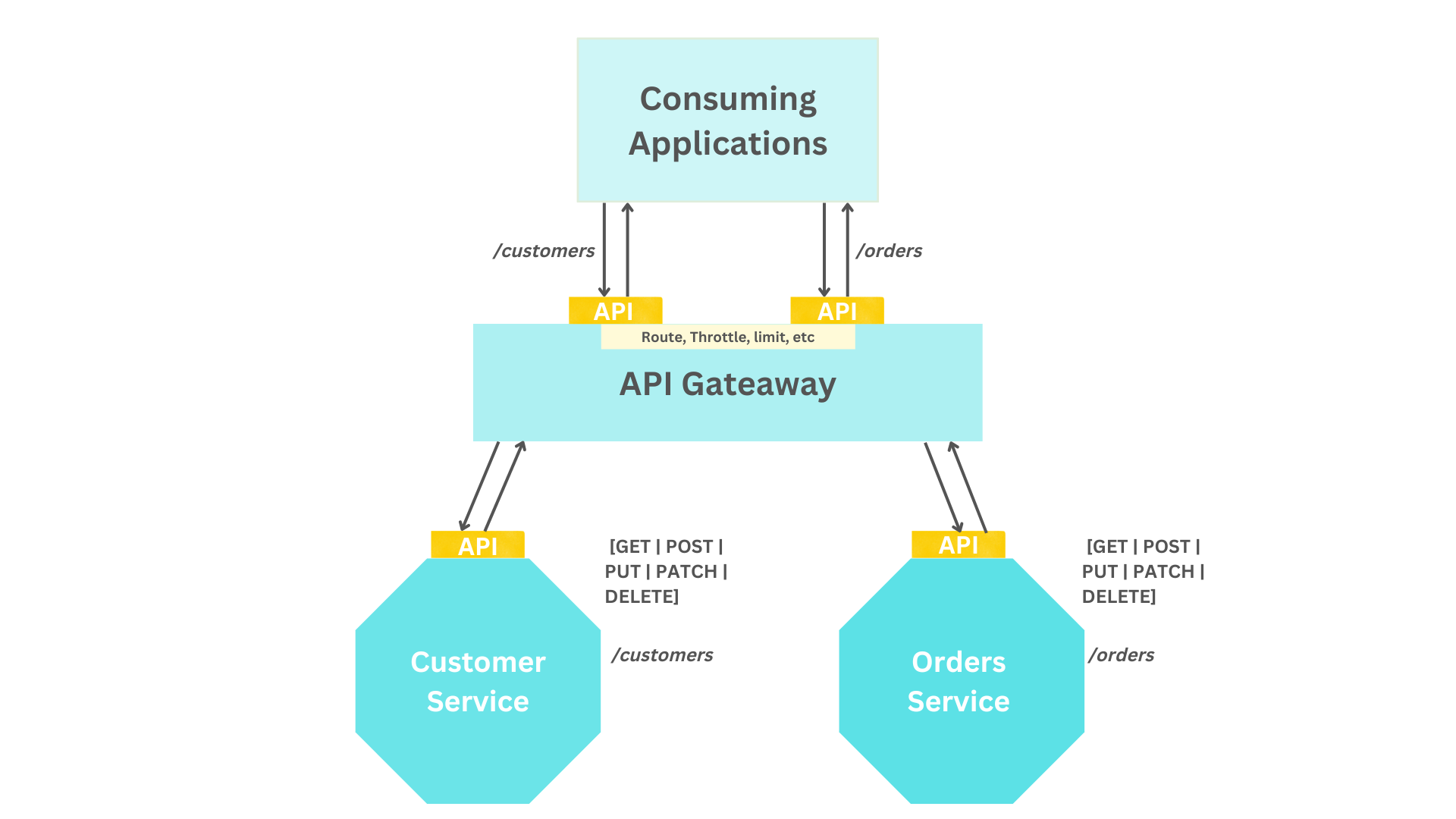
+The first in the list is the **API resource routing** method which uses an API Gateway to route incoming calls based on unique resource identifiers (URIs). Implementing an API gateway as the single entry point to all services means that API consumers only have to be aware of one URL domain. In this way, it becomes the API gateway's responsibility to route the traffic to the corresponding service endpoints and also enforce any applied policies as it is depicted in the below diagram.
+
+
+
+It reduces complexity on the API consumer side because they do not need to track and consume functionality from multiple HTTP endpoints in case there are many services in the system. Also, no need to implement all cross-cutting concerns, such as authentication/authorization, throttling, and rate limiting separately for each service. Most API Gateways like [Apache APISIX](https://apisix.apache.org/docs/apisix/terminology/api-gateway/) has already these core features.
Review Comment:
>they do not need to track and consume functionality from multiple HTTP endpoints in case there are many services in the system
I don't know what it means
>Also, no need to implement all cross-cutting concerns, such as authentication/authorization, throttling, and rate limiting separately for each service
YES!!!!!!!! This should be in bold, blinking, red characters. That's THE selling point.
##########
blog/en/blog/2022/10/27/ten-use-cases-api-gateway.md:
##########
@@ -0,0 +1,180 @@
+---
+title: "10 most use cases of an API Gateway in API-Led architecture"
+authors:
+ - name: Bobur Umurzokov
+ title: Author
+ url: https://github.com/Boburmirzo
+ image_url: https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/u/14247607
+keywords:
+- API Gateway
+- Apache APISIX
+- API
+- Architecture
+- Use-cases
+- Microservices
+description: This post elaborates on the 10 most common usages of an API Gateway such as Apache APISIX in architecting API-Led Connectivity.
+tags: [Case Studies]
+image: https://static.apiseven.com/2022/10/27/635a40e58b27a.png
+---
+
+> This post elaborates on the **10 most common usages** of an _API Gateway_ such as [Apache APISIX](https://apisix.apache.org/) in architecting [API-Led Connectivity](https://blogs.mulesoft.com/learn-apis/api-led-connectivity/what-is-api-led-connectivity/). We understand different solutions where you can make use of the API Gateway capabilities to design reliable, high-performance, and simple APIs for other developers.
+
+<!--truncate-->
+
+Here is the summary of 10 patterns that uses the API Gateway (but not all):
+
+1. API Resource routing.
+2. API Content-based routing.
+3. API Geo-routing.
+4. API Aggregator.
+5. API Centralized Authentication.
+6. API Format Conversion.
+7. API Observability.
+8. API Caching.
+9. API Fault handling.
+10. Sidecar API Gateway.
+
+## API-Led Architecture
+
+First of all, let’s revise once again these 3 terms like: **API Gateway**, **API-Led architecture**, and **API-Led Connectivity**.
+
+[API Gateway](https://wikitech.wikimedia.org/wiki/API_Gateway) is a _pattern_ formed by adding a layer between the client and the server that acts as a reverse proxy forwarding request from the client to the server. It allows all clients to access the services they want to access with a single API Gateway layer.
Review Comment:
I'd avoid talking about a reverse-proxy since it means something for most people. Then, they might wonder what's the difference. I'd use the term _facade_.
##########
blog/en/blog/2022/10/27/ten-use-cases-api-gateway.md:
##########
@@ -0,0 +1,180 @@
+---
+title: "10 most use cases of an API Gateway in API-Led architecture"
+authors:
+ - name: Bobur Umurzokov
+ title: Author
+ url: https://github.com/Boburmirzo
+ image_url: https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/u/14247607
+keywords:
+- API Gateway
+- Apache APISIX
+- API
+- Architecture
+- Use-cases
+- Microservices
+description: This post elaborates on the 10 most common usages of an API Gateway such as Apache APISIX in architecting API-Led Connectivity.
+tags: [Case Studies]
+image: https://static.apiseven.com/2022/10/27/635a40e58b27a.png
+---
+
+> This post elaborates on the **10 most common usages** of an _API Gateway_ such as [Apache APISIX](https://apisix.apache.org/) in architecting [API-Led Connectivity](https://blogs.mulesoft.com/learn-apis/api-led-connectivity/what-is-api-led-connectivity/). We understand different solutions where you can make use of the API Gateway capabilities to design reliable, high-performance, and simple APIs for other developers.
+
+<!--truncate-->
+
+Here is the summary of 10 patterns that uses the API Gateway (but not all):
+
+1. API Resource routing.
+2. API Content-based routing.
+3. API Geo-routing.
+4. API Aggregator.
+5. API Centralized Authentication.
+6. API Format Conversion.
+7. API Observability.
+8. API Caching.
+9. API Fault handling.
+10. Sidecar API Gateway.
+
+## API-Led Architecture
+
+First of all, let’s revise once again these 3 terms like: **API Gateway**, **API-Led architecture**, and **API-Led Connectivity**.
+
+[API Gateway](https://wikitech.wikimedia.org/wiki/API_Gateway) is a _pattern_ formed by adding a layer between the client and the server that acts as a reverse proxy forwarding request from the client to the server. It allows all clients to access the services they want to access with a single API Gateway layer.
+
+[API-led](https://dzone.com/articles/mulesoft-api-led-connectivity-architectural-and-de) is an _architectural approach_ that puts APIs at the heart of communications between applications and the business capabilities they need to access, in order to consistently deliver seamless functionality across all digital channels.
+
+
+
+**API-led connectivity** refers to _the technique_ of using reusable and well-designed APIs to link data and applications which in turn it is based on **API-Led architecture**. It’s _a modern approach_ that looks at the best ways of reusing APIs to boost your innovation and move quickly in the market. At the most basic level, API-led architecture should address things like:
+
+- Securing APIs from unauthorized access and significant security threats.
+- Ensuring that consuming applications can always find the right API endpoint.
+- Throttling and/or limiting the number of calls made to an API to ensure continuous availability.
+- Supporting capabilities such as API design, testing, continuous integration, life cycle management, monitoring, and operations, to name a few.
+- Error handling and preventing error propagation across the stack.
+- Real-time monitoring of APIs with rich analytics and insight.
+- An approach for implementing scalable and flexible business capabilities, for example, in support of microservices architectures.
+
+Let’s describe in subsequent sections each usage of an API Gateway to address common requirements/challenges that arise when adopting API-led architectures.
+
+---
+
+## API resource routing
+
+The first in the list is the **API resource routing** method which uses an API Gateway to route incoming calls based on unique resource identifiers (URIs). Implementing an API gateway as the single entry point to all services means that API consumers only have to be aware of one URL domain. In this way, it becomes the API gateway's responsibility to route the traffic to the corresponding service endpoints and also enforce any applied policies as it is depicted in the below diagram.
+
+
+
+It reduces complexity on the API consumer side because they do not need to track and consume functionality from multiple HTTP endpoints in case there are many services in the system. Also, no need to implement all cross-cutting concerns, such as authentication/authorization, throttling, and rate limiting separately for each service. Most API Gateways like [Apache APISIX](https://apisix.apache.org/docs/apisix/terminology/api-gateway/) has already these core features.
+
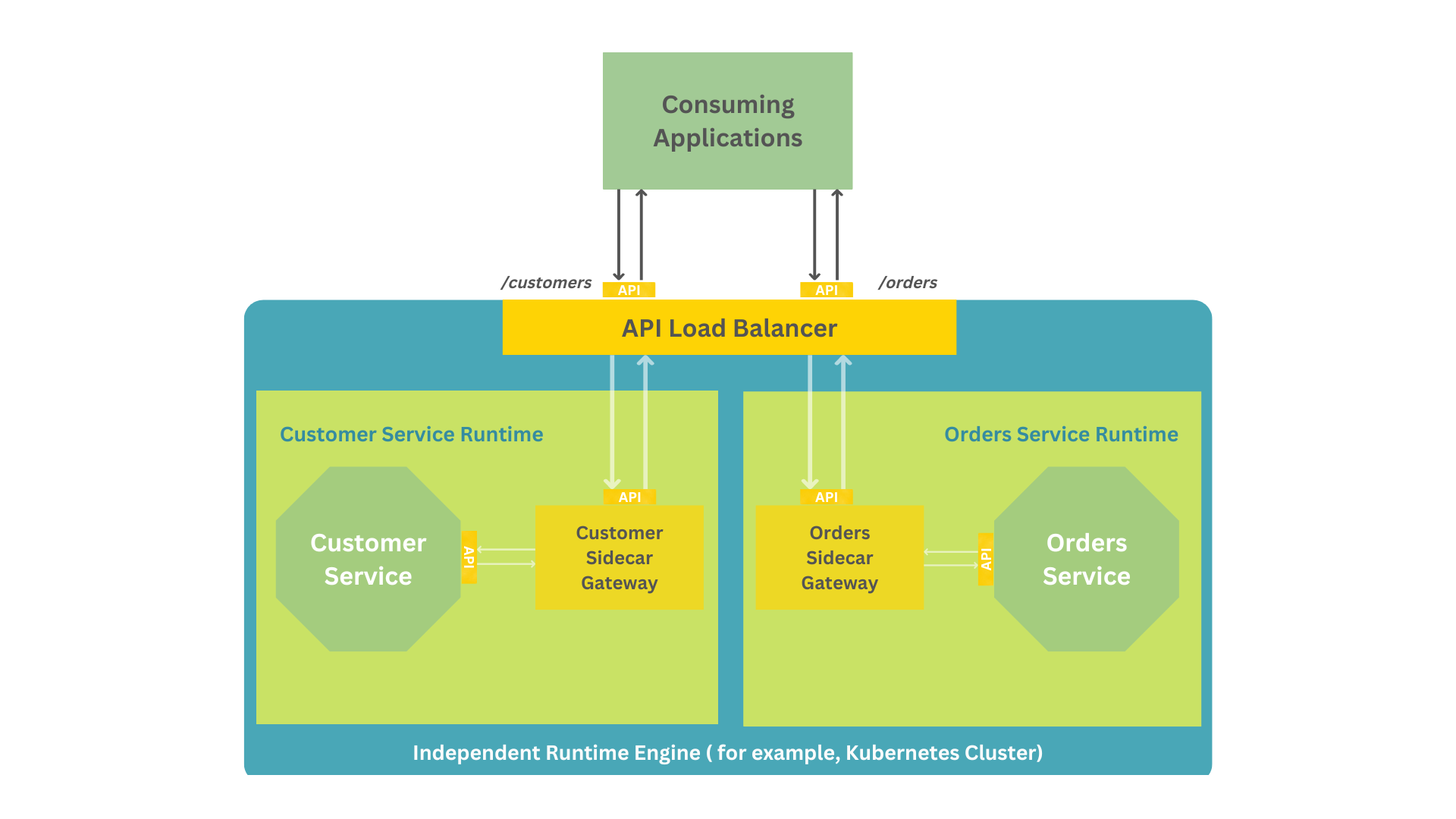
+## API content-based routing
+
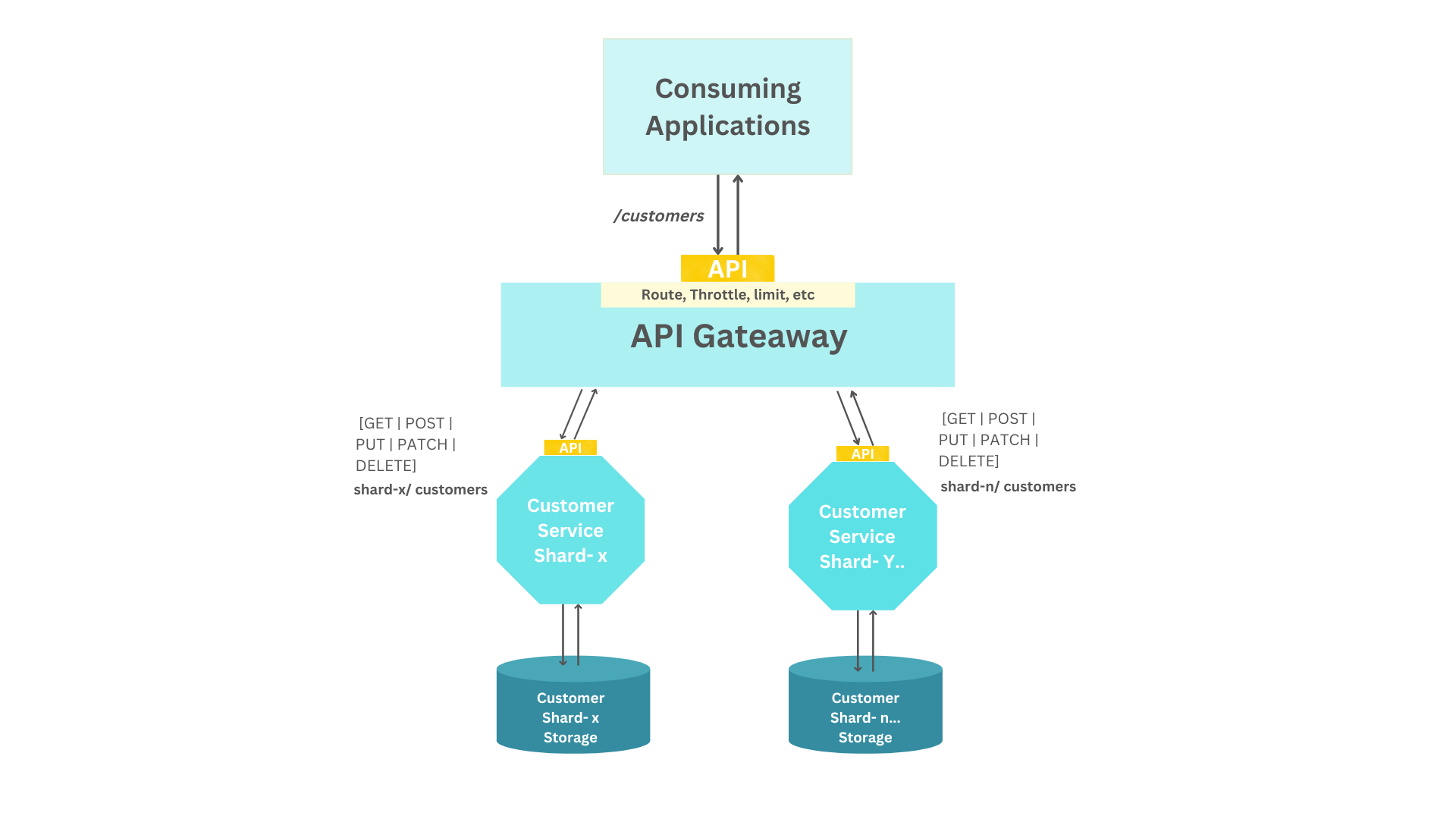
+Similarly, **API content-based** routing mechanism also uses an API gateway to route calls based on the content of a request (for example, based on the HTTP header or message body) instead of just the URI.
+
+Take a scenario when database sharding is applied in order to distribute the load across multiple database instances. This technique is typically applied when the overall number of records stored is huge and a single instance struggles to manage the load. Instead, records are spread across multiple database instances. Then, you implement multiple services, one per unique datastore, and adopt an API gateway as the only entry point to all services. You could then configure the API gateway to route calls to the corresponding service based on a key obtained either from the HTTP header or the payload.
+
+
+
+In the above diagram, an API gateway is exposing a single `/customers` resource for multiple customer services, each with a different data store.
+
+## API geo-routing
+
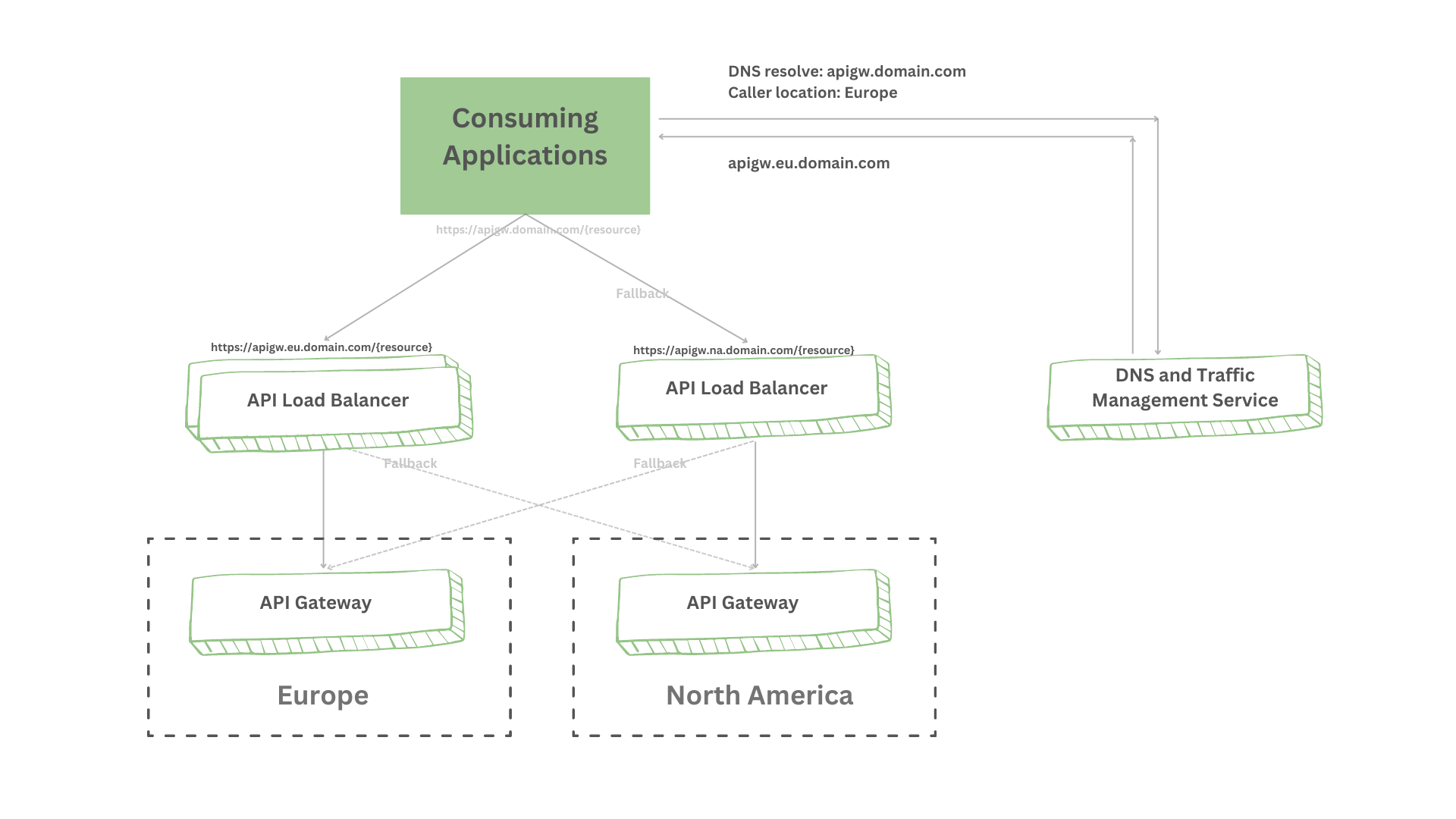
+**API geo-routing** solution routes API calls to the nearest API gateway based on where they originate. In order to prevent latency issues and other unforeseen issues that may occur due to distance (for example, a consuming application from Asia calling an API located in North America), API gateways and other service infrastructure have been deployed in multiple regions across the world as needed. For example, using different sub-domains for each API gateway in each region and letting the consuming application determine the nearest gateway based on application logic. Then, an API gateway provides internal load balancing to make sure that incoming requests are distributed across the available instances of a service.
+
+
+
+As you can see in the preceding diagram, it uses a DNS, traffic management service, and an API Gateway to resolve each subdomain against the region’s load balancer and passes the client request further down to the closest API Gateway.
+
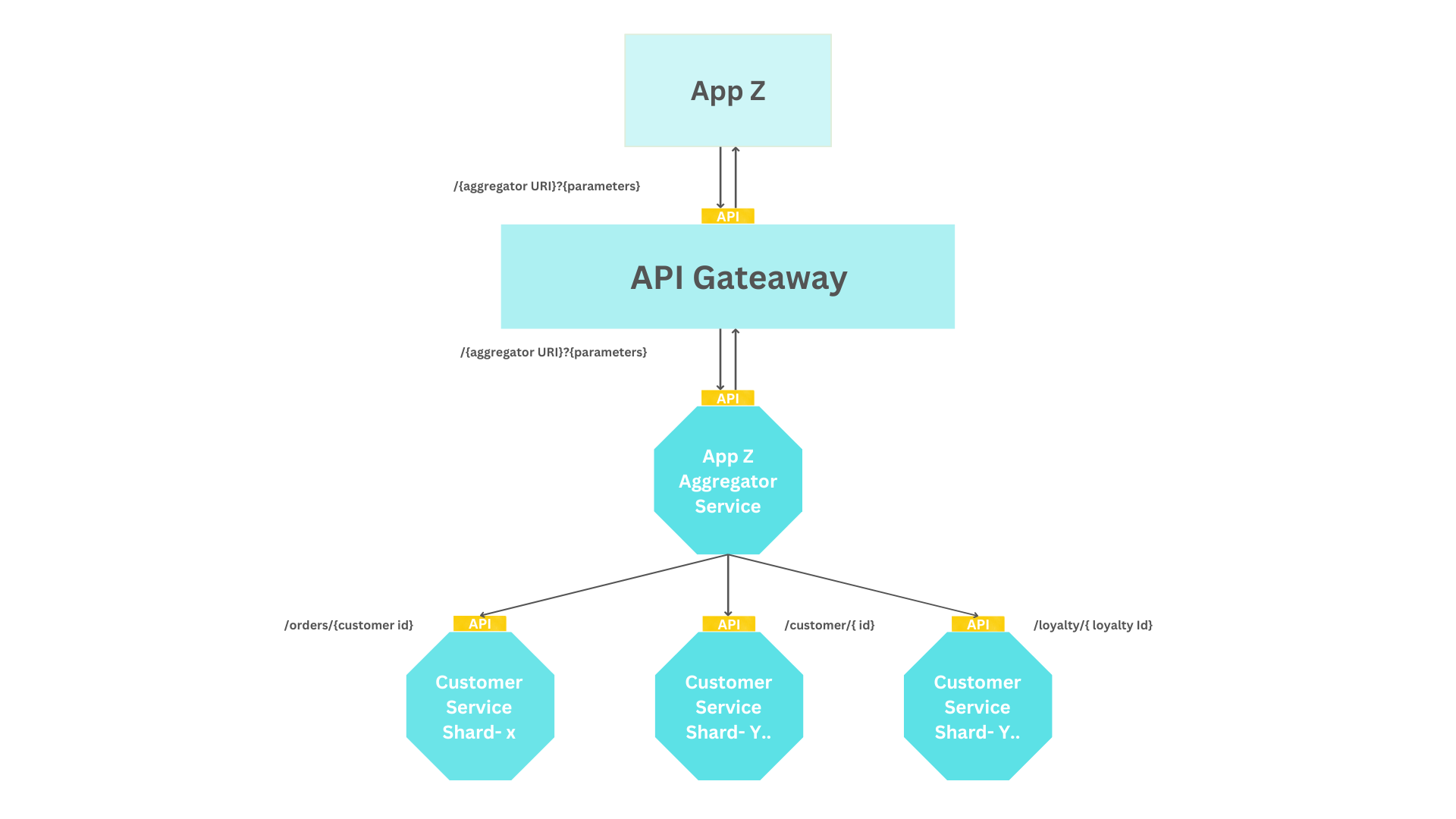
+## API aggregator
+
+This technique performs operations (for example, queries) against multiple services and returns the result to the client service with a single `HTTP request/response` call. Instead of having a client application make several calls to multiple APIs, an API aggregator uses an API Gateway to do this on behalf of the consumer on the server side.
+
+For example, consider a mobile app that makes multiple calls to different APIs to show the data for a single screen. In this case, it increases complexity in the client-side code, over-utilization of network resources, and even poor user experience as the application is more exposed to latency issues. API Gateway can accept as input all information required, does request authentication and validation, understands all data structures from all APIs that it interacts with, and is capable of transforming the response payloads so they can be sent back to the mobile app as a uniform payload needed for the consumer.
+
+
+
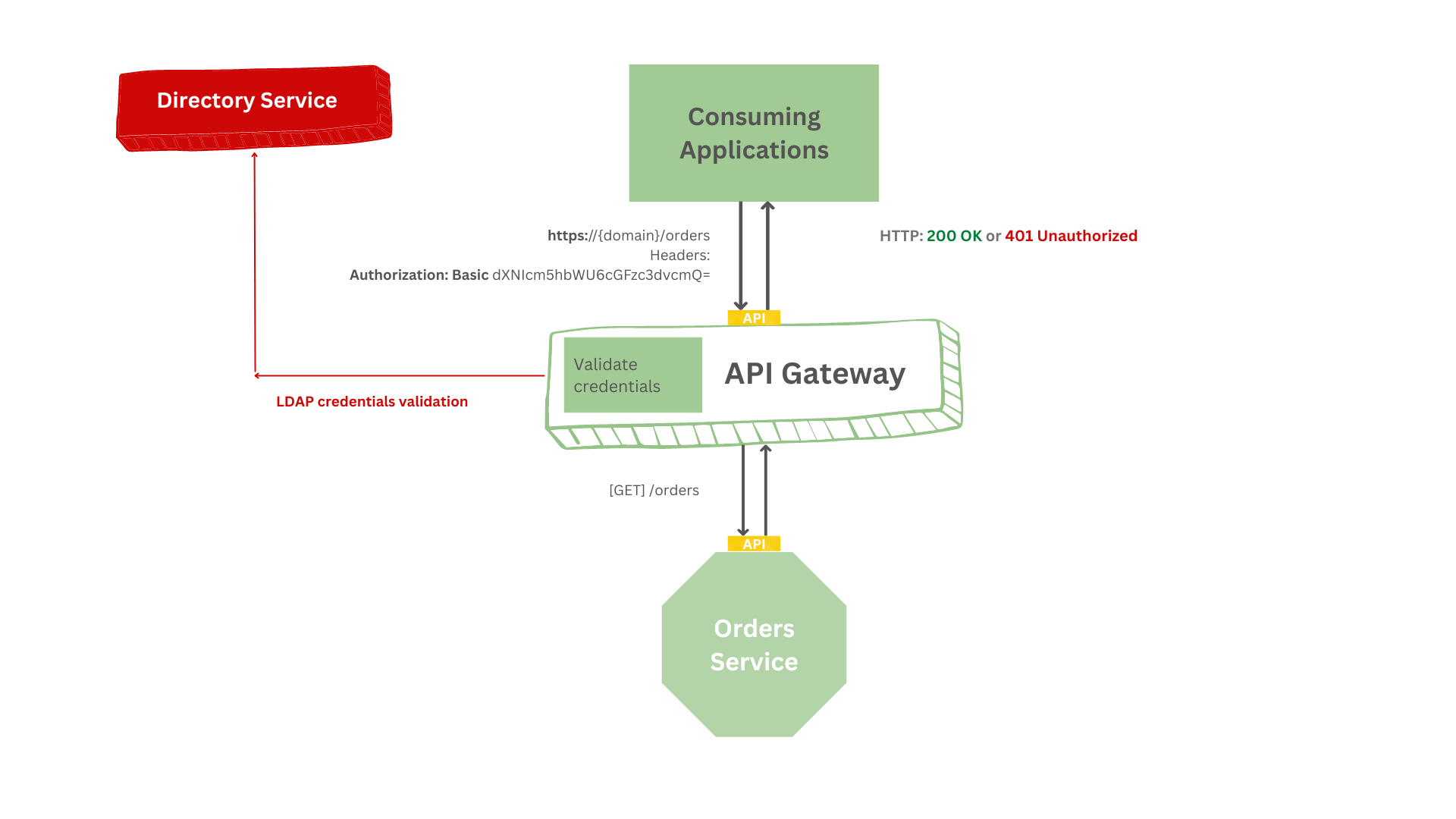
+## API Centralized Authentication
+
+In this design, an API Gateway acts as a **centralized authentication gateway**. As an authenticator, API Gateway looks for access credentials in the `HTTP header` - for example, a bearer token, and implements business logic that validates those credentials with an IDP, identity provider such as [Okta](https://www.okta.com/), [Cognito](https://aws.amazon.com/cognito/), [Azure Active Directory](https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/services/active-directory/) or [Ory Hydra](https://www.ory.sh/hydra/)) typically using the [OpenID Connect](https://openid.net/connect/) (OIDC) is an authentication protocol based on the [OAuth 2.0](https://oauth.net/2/) and checking whether they have access or not.
+
+
+
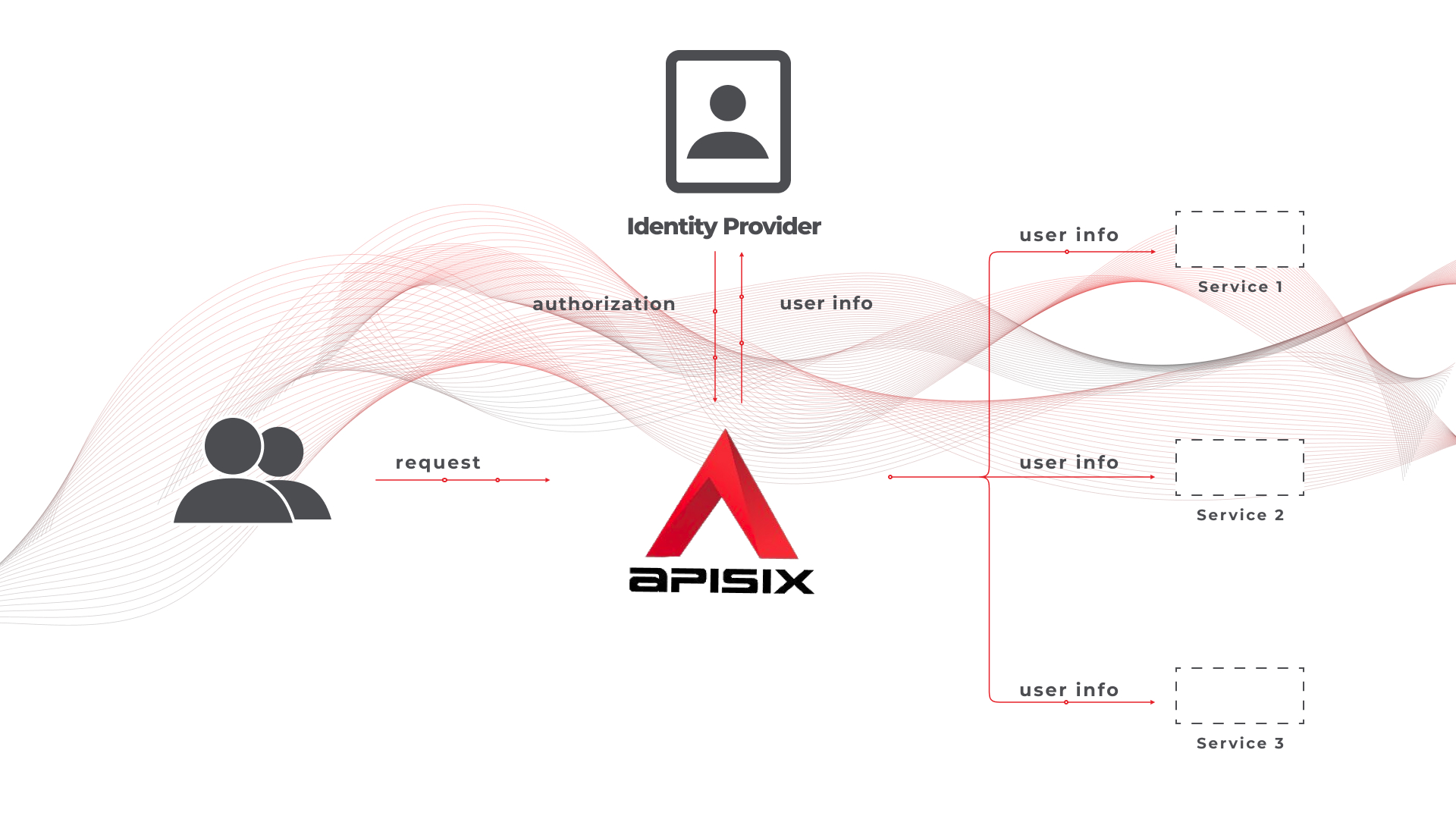
+Centralized authentication with the API Gateway can solve many problems and have some benefits as it completely offloads user management from an application and it improves performance by responding quickly to authentication requests received from client applications.
+
+
+
+For example, [Apache APISIX](https://apisix.apache.org/) offers a variety of [plugins](https://apisix.apache.org/docs/apisix/plugins/openid-connect/) to enable different methods of API gateway authentication. We looked at some of the most commonly used in this blog post [Centralized Authentication with Apache APISIX Plugins](https://dev.to/apisix/centralized-authentication-with-apache-apisix-plugins-30fo). You can even enable multiple methods for authentication for the given API.
+
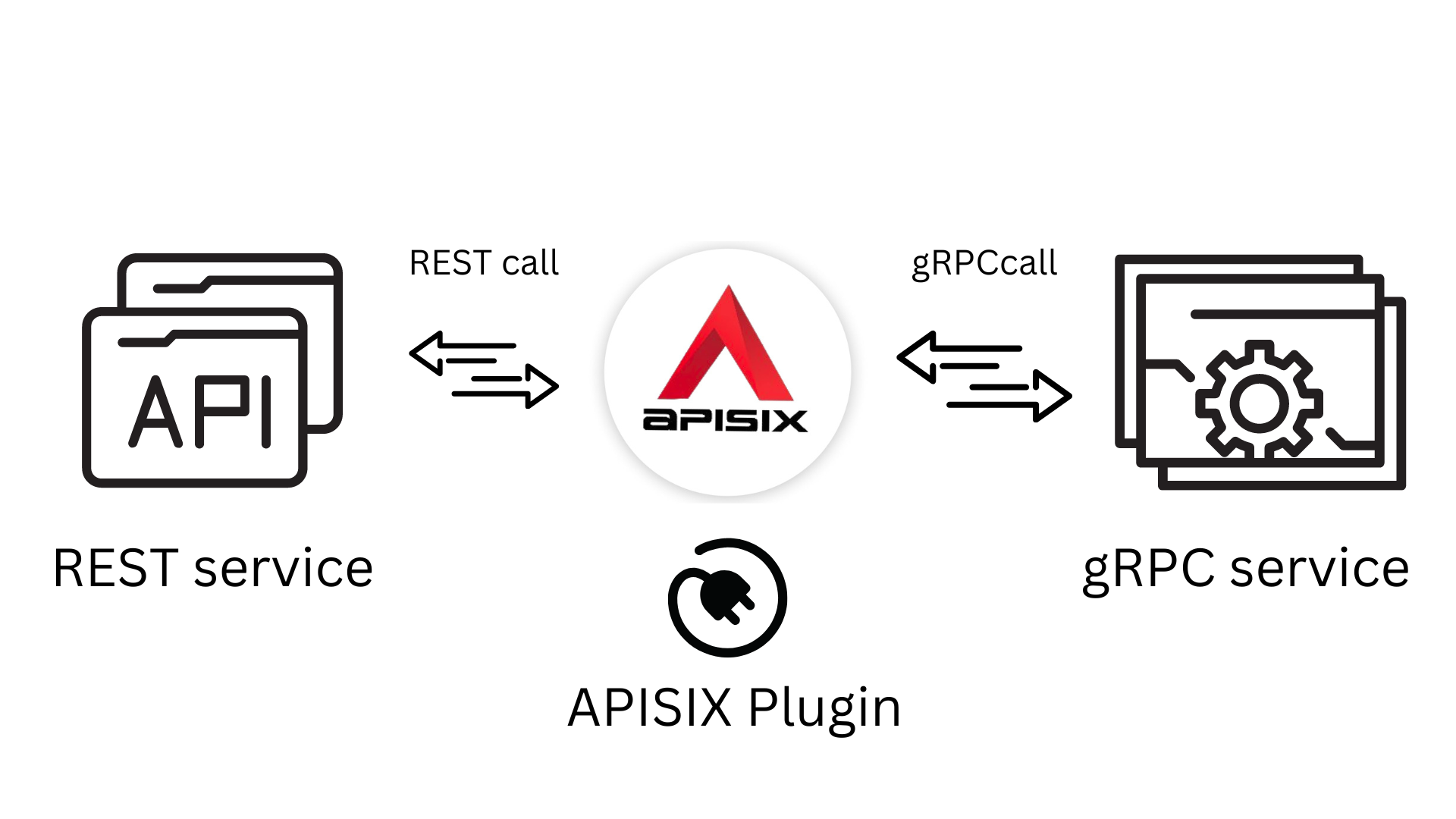
+## API Format Conversion
+
+This refers to having the ability to convert payloads from one format to another over the same transport. For example, from XML/SOAP over HTTPS to JSON over HTTPS and vice versa. API Gateways, by default offer capabilities in support of REST API and some specialized API gateways support, in addition to payload conversions, transport conversions such as converting from Message Queuing Telemetry Transport (MQTT) over TCP (a very popular transport in IoT) to JSON over HTTPS.
+
+
+
+For example, Apache APISIX is able to receive an HTTP request, then transcode it and forwards it to a gRPC service, gets the response, and return it back to the client in HTTP format by means of its [gRPC Transcode](https://apisix.apache.org/docs/apisix/plugins/grpc-transcode/) plug-in.
+
+## API Observability
+
+By now, we know that an API gateway offers a central control point for incoming traffic to a variety of destinations but it can also be a central point for observation as well since it is uniquely qualified to know about all the traffic moving between clients and our service networks. There is always the possibility to instrument the API gateways so observability data (structured logs, metrics, and traces) can be collected in order to use specialized monitoring tools.
+
+
+
+For example, Apache APISIX provides [pre-built connectors](https://apisix.apache.org/docs/apisix/plugins/prometheus/) (plug-ins) that you can easily integrate with external monitoring tools. You can leverage these connectors to ingest log data from your API gateways to further derive useful metrics and gain complete visibility into the usage, you can manage performance, and security of your APIs in your environment. There is also a dedicated post on [how to use these observability plugins](https://medium.com/@ApacheAPISIX/api-observability-with-apache-apisix-plugins-34584dc1ce3a).
+
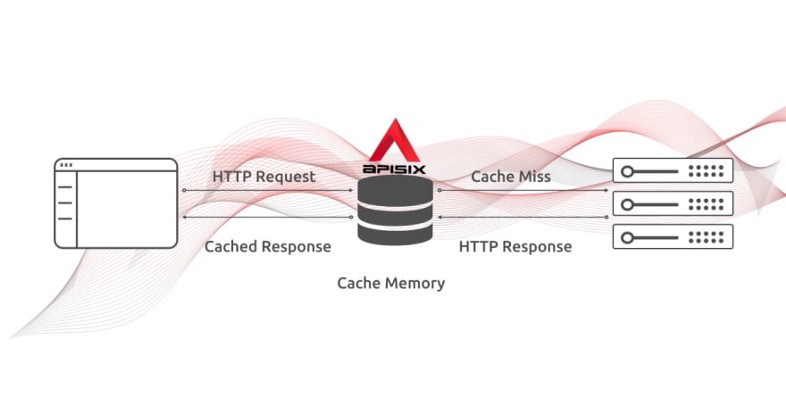
+## API Caching
+
+**API Caching** is yet another level of caching that is usually implemented inside API Gateway. It can reduce the number of calls made to your endpoint and also improve the latency of requests to your API by caching a response from the upstream. If the API Gateway cache has a fresh copy of the requested resource, it uses that copy to satisfy the request directly instead of making a request to the endpoint. If the cached data is not found, the request travels to the intended upstream services (backend services).
+
+
+
+You can read more about [API Gateway Caching with Apache APISIX](https://medium.com/@ApacheAPISIX/api-gateway-caching-for-asp-net-core-web-api-cf24d0e598fc) in the dedicated blog post.
+
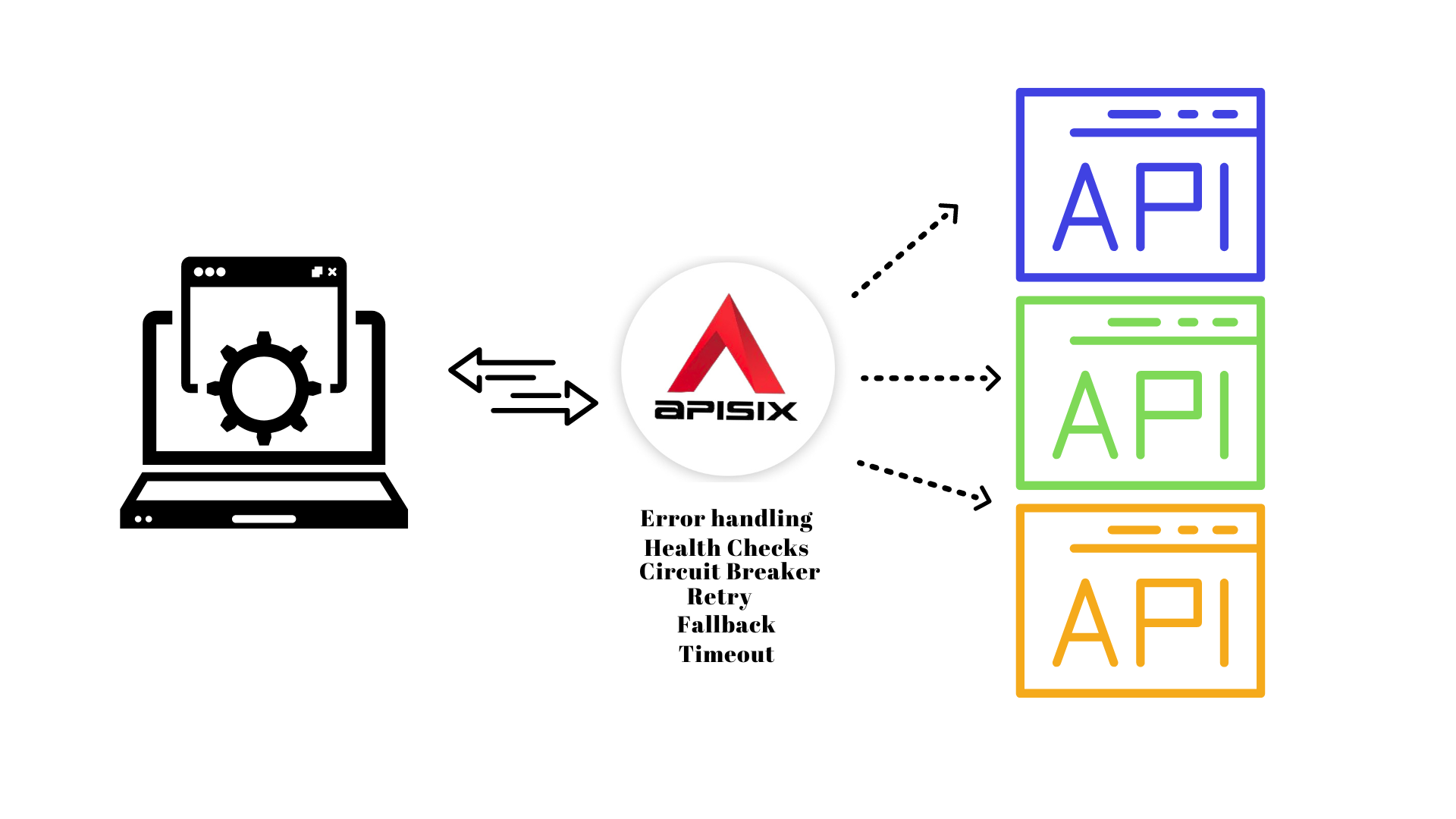
+## API Fault handling
+
+It is critical to handle failures in service-to-service calls gracefully. Also, we want to be sure that any resilience mechanisms we have in place such as error handling code, [circuit breaker](https://dev.to/apisix/implementing-resilient-applications-with-api-gateway-circuit-breaker-ggk), [health checks](https://dev.to/apisix/implementing-resilient-applications-with-api-gateway-health-check-338c), [retry](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/architecture/patterns/retry), fallback, redundant instances, and so on. Modern API Gateways support all the above error-handling features including automatic retries and timeouts.
+
+
+
+For example, APISIX acts as an orchestrator that can use this status report to decide how to manage the traffic, load balance to a healthy node, fail-fast due to some cascading failures or simply alerts you when it notices something goes wrong. API Gateway also ensures that routing and other network-level components work together successfully to deliver a request to the API process. It helps you to detect in the early stage and fix issues for your running application much more easily.
+
+## Sidecar API gateway
+
+**Sidecar** implements an API gateway as a container attached to a service in an independent runtime, such as [Kubernetes](https://kubernetes.io/). Sidecar is a pattern that corresponds to a [sidecar](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sidecar) attached to a motorcycle, similarly, it is attached to a parent application and provides supporting features for the application. The sidecar also shares the same lifecycle as the parent application, is created and retired alongside the parent, and introduces additional features such as monitoring, logging, configuration, and networking services. The benefits of adopting this pattern are that each service runtime can configure its own API gateway in the best way. Because the requirement to enable the API gateway functionalities and setups can vary from service to service. At the same time, it separates concerns if an issue occurs in the shared API gateway infrastructure then all services will not be impacted.
Review Comment:
It's too far-fetched IMHO. I wouldn't use it.
##########
blog/en/blog/2022/10/27/ten-use-cases-api-gateway.md:
##########
@@ -0,0 +1,180 @@
+---
+title: "10 most use cases of an API Gateway in API-Led architecture"
+authors:
+ - name: Bobur Umurzokov
+ title: Author
+ url: https://github.com/Boburmirzo
+ image_url: https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/u/14247607
+keywords:
+- API Gateway
+- Apache APISIX
+- API
+- Architecture
+- Use-cases
+- Microservices
+description: This post elaborates on the 10 most common usages of an API Gateway such as Apache APISIX in architecting API-Led Connectivity.
+tags: [Case Studies]
+image: https://static.apiseven.com/2022/10/27/635a40e58b27a.png
+---
+
+> This post elaborates on the **10 most common usages** of an _API Gateway_ such as [Apache APISIX](https://apisix.apache.org/) in architecting [API-Led Connectivity](https://blogs.mulesoft.com/learn-apis/api-led-connectivity/what-is-api-led-connectivity/). We understand different solutions where you can make use of the API Gateway capabilities to design reliable, high-performance, and simple APIs for other developers.
+
+<!--truncate-->
+
+Here is the summary of 10 patterns that uses the API Gateway (but not all):
+
+1. API Resource routing.
+2. API Content-based routing.
+3. API Geo-routing.
+4. API Aggregator.
+5. API Centralized Authentication.
+6. API Format Conversion.
+7. API Observability.
+8. API Caching.
+9. API Fault handling.
+10. Sidecar API Gateway.
+
+## API-Led Architecture
+
+First of all, let’s revise once again these 3 terms like: **API Gateway**, **API-Led architecture**, and **API-Led Connectivity**.
+
+[API Gateway](https://wikitech.wikimedia.org/wiki/API_Gateway) is a _pattern_ formed by adding a layer between the client and the server that acts as a reverse proxy forwarding request from the client to the server. It allows all clients to access the services they want to access with a single API Gateway layer.
+
+[API-led](https://dzone.com/articles/mulesoft-api-led-connectivity-architectural-and-de) is an _architectural approach_ that puts APIs at the heart of communications between applications and the business capabilities they need to access, in order to consistently deliver seamless functionality across all digital channels.
+
+
+
+**API-led connectivity** refers to _the technique_ of using reusable and well-designed APIs to link data and applications which in turn it is based on **API-Led architecture**. It’s _a modern approach_ that looks at the best ways of reusing APIs to boost your innovation and move quickly in the market. At the most basic level, API-led architecture should address things like:
+
+- Securing APIs from unauthorized access and significant security threats.
+- Ensuring that consuming applications can always find the right API endpoint.
+- Throttling and/or limiting the number of calls made to an API to ensure continuous availability.
+- Supporting capabilities such as API design, testing, continuous integration, life cycle management, monitoring, and operations, to name a few.
+- Error handling and preventing error propagation across the stack.
+- Real-time monitoring of APIs with rich analytics and insight.
+- An approach for implementing scalable and flexible business capabilities, for example, in support of microservices architectures.
+
+Let’s describe in subsequent sections each usage of an API Gateway to address common requirements/challenges that arise when adopting API-led architectures.
+
+---
+
+## API resource routing
+
+The first in the list is the **API resource routing** method which uses an API Gateway to route incoming calls based on unique resource identifiers (URIs). Implementing an API gateway as the single entry point to all services means that API consumers only have to be aware of one URL domain. In this way, it becomes the API gateway's responsibility to route the traffic to the corresponding service endpoints and also enforce any applied policies as it is depicted in the below diagram.
+
+
+
+It reduces complexity on the API consumer side because they do not need to track and consume functionality from multiple HTTP endpoints in case there are many services in the system. Also, no need to implement all cross-cutting concerns, such as authentication/authorization, throttling, and rate limiting separately for each service. Most API Gateways like [Apache APISIX](https://apisix.apache.org/docs/apisix/terminology/api-gateway/) has already these core features.
+
+## API content-based routing
+
+Similarly, **API content-based** routing mechanism also uses an API gateway to route calls based on the content of a request (for example, based on the HTTP header or message body) instead of just the URI.
+
+Take a scenario when database sharding is applied in order to distribute the load across multiple database instances. This technique is typically applied when the overall number of records stored is huge and a single instance struggles to manage the load. Instead, records are spread across multiple database instances. Then, you implement multiple services, one per unique datastore, and adopt an API gateway as the only entry point to all services. You could then configure the API gateway to route calls to the corresponding service based on a key obtained either from the HTTP header or the payload.
+
+
+
+In the above diagram, an API gateway is exposing a single `/customers` resource for multiple customer services, each with a different data store.
+
+## API geo-routing
+
+**API geo-routing** solution routes API calls to the nearest API gateway based on where they originate. In order to prevent latency issues and other unforeseen issues that may occur due to distance (for example, a consuming application from Asia calling an API located in North America), API gateways and other service infrastructure have been deployed in multiple regions across the world as needed. For example, using different sub-domains for each API gateway in each region and letting the consuming application determine the nearest gateway based on application logic. Then, an API gateway provides internal load balancing to make sure that incoming requests are distributed across the available instances of a service.
+
+
+
+As you can see in the preceding diagram, it uses a DNS, traffic management service, and an API Gateway to resolve each subdomain against the region’s load balancer and passes the client request further down to the closest API Gateway.
+
+## API aggregator
+
+This technique performs operations (for example, queries) against multiple services and returns the result to the client service with a single `HTTP request/response` call. Instead of having a client application make several calls to multiple APIs, an API aggregator uses an API Gateway to do this on behalf of the consumer on the server side.
+
+For example, consider a mobile app that makes multiple calls to different APIs to show the data for a single screen. In this case, it increases complexity in the client-side code, over-utilization of network resources, and even poor user experience as the application is more exposed to latency issues. API Gateway can accept as input all information required, does request authentication and validation, understands all data structures from all APIs that it interacts with, and is capable of transforming the response payloads so they can be sent back to the mobile app as a uniform payload needed for the consumer.
+
+
+
+## API Centralized Authentication
+
+In this design, an API Gateway acts as a **centralized authentication gateway**. As an authenticator, API Gateway looks for access credentials in the `HTTP header` - for example, a bearer token, and implements business logic that validates those credentials with an IDP, identity provider such as [Okta](https://www.okta.com/), [Cognito](https://aws.amazon.com/cognito/), [Azure Active Directory](https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/services/active-directory/) or [Ory Hydra](https://www.ory.sh/hydra/)) typically using the [OpenID Connect](https://openid.net/connect/) (OIDC) is an authentication protocol based on the [OAuth 2.0](https://oauth.net/2/) and checking whether they have access or not.
+
+
+
+Centralized authentication with the API Gateway can solve many problems and have some benefits as it completely offloads user management from an application and it improves performance by responding quickly to authentication requests received from client applications.
+
+
+
+For example, [Apache APISIX](https://apisix.apache.org/) offers a variety of [plugins](https://apisix.apache.org/docs/apisix/plugins/openid-connect/) to enable different methods of API gateway authentication. We looked at some of the most commonly used in this blog post [Centralized Authentication with Apache APISIX Plugins](https://dev.to/apisix/centralized-authentication-with-apache-apisix-plugins-30fo). You can even enable multiple methods for authentication for the given API.
+
+## API Format Conversion
+
+This refers to having the ability to convert payloads from one format to another over the same transport. For example, from XML/SOAP over HTTPS to JSON over HTTPS and vice versa. API Gateways, by default offer capabilities in support of REST API and some specialized API gateways support, in addition to payload conversions, transport conversions such as converting from Message Queuing Telemetry Transport (MQTT) over TCP (a very popular transport in IoT) to JSON over HTTPS.
+
+
+
+For example, Apache APISIX is able to receive an HTTP request, then transcode it and forwards it to a gRPC service, gets the response, and return it back to the client in HTTP format by means of its [gRPC Transcode](https://apisix.apache.org/docs/apisix/plugins/grpc-transcode/) plug-in.
+
+## API Observability
+
+By now, we know that an API gateway offers a central control point for incoming traffic to a variety of destinations but it can also be a central point for observation as well since it is uniquely qualified to know about all the traffic moving between clients and our service networks. There is always the possibility to instrument the API gateways so observability data (structured logs, metrics, and traces) can be collected in order to use specialized monitoring tools.
+
+
+
+For example, Apache APISIX provides [pre-built connectors](https://apisix.apache.org/docs/apisix/plugins/prometheus/) (plug-ins) that you can easily integrate with external monitoring tools. You can leverage these connectors to ingest log data from your API gateways to further derive useful metrics and gain complete visibility into the usage, you can manage performance, and security of your APIs in your environment. There is also a dedicated post on [how to use these observability plugins](https://medium.com/@ApacheAPISIX/api-observability-with-apache-apisix-plugins-34584dc1ce3a).
+
+## API Caching
+
+**API Caching** is yet another level of caching that is usually implemented inside API Gateway. It can reduce the number of calls made to your endpoint and also improve the latency of requests to your API by caching a response from the upstream. If the API Gateway cache has a fresh copy of the requested resource, it uses that copy to satisfy the request directly instead of making a request to the endpoint. If the cached data is not found, the request travels to the intended upstream services (backend services).
+
+
+
+You can read more about [API Gateway Caching with Apache APISIX](https://medium.com/@ApacheAPISIX/api-gateway-caching-for-asp-net-core-web-api-cf24d0e598fc) in the dedicated blog post.
+
+## API Fault handling
+
+It is critical to handle failures in service-to-service calls gracefully. Also, we want to be sure that any resilience mechanisms we have in place such as error handling code, [circuit breaker](https://dev.to/apisix/implementing-resilient-applications-with-api-gateway-circuit-breaker-ggk), [health checks](https://dev.to/apisix/implementing-resilient-applications-with-api-gateway-health-check-338c), [retry](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/architecture/patterns/retry), fallback, redundant instances, and so on. Modern API Gateways support all the above error-handling features including automatic retries and timeouts.
Review Comment:
It only works if inter-service communication also goes through the gateway. I honestly don't know if it's widespread. You should at least mention this requirement.
##########
blog/en/blog/2022/10/27/ten-use-cases-api-gateway.md:
##########
@@ -0,0 +1,180 @@
+---
Review Comment:
Nitpicking: diagrams all have different styles. Can you choose a style and keep it consistent across all diagrams?
##########
blog/en/blog/2022/10/27/ten-use-cases-api-gateway.md:
##########
@@ -0,0 +1,180 @@
+---
+title: "10 most use cases of an API Gateway in API-Led architecture"
+authors:
+ - name: Bobur Umurzokov
+ title: Author
+ url: https://github.com/Boburmirzo
+ image_url: https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/u/14247607
+keywords:
+- API Gateway
+- Apache APISIX
+- API
+- Architecture
+- Use-cases
+- Microservices
+description: This post elaborates on the 10 most common usages of an API Gateway such as Apache APISIX in architecting API-Led Connectivity.
+tags: [Case Studies]
+image: https://static.apiseven.com/2022/10/27/635a40e58b27a.png
+---
+
+> This post elaborates on the **10 most common usages** of an _API Gateway_ such as [Apache APISIX](https://apisix.apache.org/) in architecting [API-Led Connectivity](https://blogs.mulesoft.com/learn-apis/api-led-connectivity/what-is-api-led-connectivity/). We understand different solutions where you can make use of the API Gateway capabilities to design reliable, high-performance, and simple APIs for other developers.
+
+<!--truncate-->
+
+Here is the summary of 10 patterns that uses the API Gateway (but not all):
+
+1. API Resource routing.
+2. API Content-based routing.
+3. API Geo-routing.
+4. API Aggregator.
+5. API Centralized Authentication.
+6. API Format Conversion.
+7. API Observability.
+8. API Caching.
+9. API Fault handling.
+10. Sidecar API Gateway.
+
+## API-Led Architecture
+
+First of all, let’s revise once again these 3 terms like: **API Gateway**, **API-Led architecture**, and **API-Led Connectivity**.
+
+[API Gateway](https://wikitech.wikimedia.org/wiki/API_Gateway) is a _pattern_ formed by adding a layer between the client and the server that acts as a reverse proxy forwarding request from the client to the server. It allows all clients to access the services they want to access with a single API Gateway layer.
+
+[API-led](https://dzone.com/articles/mulesoft-api-led-connectivity-architectural-and-de) is an _architectural approach_ that puts APIs at the heart of communications between applications and the business capabilities they need to access, in order to consistently deliver seamless functionality across all digital channels.
+
+
+
+**API-led connectivity** refers to _the technique_ of using reusable and well-designed APIs to link data and applications which in turn it is based on **API-Led architecture**. It’s _a modern approach_ that looks at the best ways of reusing APIs to boost your innovation and move quickly in the market. At the most basic level, API-led architecture should address things like:
Review Comment:
Remove the term "modern", it's loaded and doesn't add anything.
##########
blog/en/blog/2022/10/27/ten-use-cases-api-gateway.md:
##########
@@ -0,0 +1,180 @@
+---
+title: "10 most use cases of an API Gateway in API-Led architecture"
+authors:
+ - name: Bobur Umurzokov
+ title: Author
+ url: https://github.com/Boburmirzo
+ image_url: https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/u/14247607
+keywords:
+- API Gateway
+- Apache APISIX
+- API
+- Architecture
+- Use-cases
+- Microservices
+description: This post elaborates on the 10 most common usages of an API Gateway such as Apache APISIX in architecting API-Led Connectivity.
+tags: [Case Studies]
+image: https://static.apiseven.com/2022/10/27/635a40e58b27a.png
+---
+
+> This post elaborates on the **10 most common usages** of an _API Gateway_ such as [Apache APISIX](https://apisix.apache.org/) in architecting [API-Led Connectivity](https://blogs.mulesoft.com/learn-apis/api-led-connectivity/what-is-api-led-connectivity/). We understand different solutions where you can make use of the API Gateway capabilities to design reliable, high-performance, and simple APIs for other developers.
+
+<!--truncate-->
+
+Here is the summary of 10 patterns that uses the API Gateway (but not all):
+
+1. API Resource routing.
+2. API Content-based routing.
+3. API Geo-routing.
+4. API Aggregator.
+5. API Centralized Authentication.
+6. API Format Conversion.
+7. API Observability.
+8. API Caching.
+9. API Fault handling.
+10. Sidecar API Gateway.
+
+## API-Led Architecture
+
+First of all, let’s revise once again these 3 terms like: **API Gateway**, **API-Led architecture**, and **API-Led Connectivity**.
+
+[API Gateway](https://wikitech.wikimedia.org/wiki/API_Gateway) is a _pattern_ formed by adding a layer between the client and the server that acts as a reverse proxy forwarding request from the client to the server. It allows all clients to access the services they want to access with a single API Gateway layer.
+
+[API-led](https://dzone.com/articles/mulesoft-api-led-connectivity-architectural-and-de) is an _architectural approach_ that puts APIs at the heart of communications between applications and the business capabilities they need to access, in order to consistently deliver seamless functionality across all digital channels.
+
+
+
+**API-led connectivity** refers to _the technique_ of using reusable and well-designed APIs to link data and applications which in turn it is based on **API-Led architecture**. It’s _a modern approach_ that looks at the best ways of reusing APIs to boost your innovation and move quickly in the market. At the most basic level, API-led architecture should address things like:
+
+- Securing APIs from unauthorized access and significant security threats.
+- Ensuring that consuming applications can always find the right API endpoint.
+- Throttling and/or limiting the number of calls made to an API to ensure continuous availability.
+- Supporting capabilities such as API design, testing, continuous integration, life cycle management, monitoring, and operations, to name a few.
+- Error handling and preventing error propagation across the stack.
+- Real-time monitoring of APIs with rich analytics and insight.
+- An approach for implementing scalable and flexible business capabilities, for example, in support of microservices architectures.
+
+Let’s describe in subsequent sections each usage of an API Gateway to address common requirements/challenges that arise when adopting API-led architectures.
+
+---
+
+## API resource routing
+
+The first in the list is the **API resource routing** method which uses an API Gateway to route incoming calls based on unique resource identifiers (URIs). Implementing an API gateway as the single entry point to all services means that API consumers only have to be aware of one URL domain. In this way, it becomes the API gateway's responsibility to route the traffic to the corresponding service endpoints and also enforce any applied policies as it is depicted in the below diagram.
+
+
+
+It reduces complexity on the API consumer side because they do not need to track and consume functionality from multiple HTTP endpoints in case there are many services in the system. Also, no need to implement all cross-cutting concerns, such as authentication/authorization, throttling, and rate limiting separately for each service. Most API Gateways like [Apache APISIX](https://apisix.apache.org/docs/apisix/terminology/api-gateway/) has already these core features.
+
+## API content-based routing
+
+Similarly, **API content-based** routing mechanism also uses an API gateway to route calls based on the content of a request (for example, based on the HTTP header or message body) instead of just the URI.
+
+Take a scenario when database sharding is applied in order to distribute the load across multiple database instances. This technique is typically applied when the overall number of records stored is huge and a single instance struggles to manage the load. Instead, records are spread across multiple database instances. Then, you implement multiple services, one per unique datastore, and adopt an API gateway as the only entry point to all services. You could then configure the API gateway to route calls to the corresponding service based on a key obtained either from the HTTP header or the payload.
+
+
+
+In the above diagram, an API gateway is exposing a single `/customers` resource for multiple customer services, each with a different data store.
+
+## API geo-routing
+
+**API geo-routing** solution routes API calls to the nearest API gateway based on where they originate. In order to prevent latency issues and other unforeseen issues that may occur due to distance (for example, a consuming application from Asia calling an API located in North America), API gateways and other service infrastructure have been deployed in multiple regions across the world as needed. For example, using different sub-domains for each API gateway in each region and letting the consuming application determine the nearest gateway based on application logic. Then, an API gateway provides internal load balancing to make sure that incoming requests are distributed across the available instances of a service.
+
+
+
+As you can see in the preceding diagram, it uses a DNS, traffic management service, and an API Gateway to resolve each subdomain against the region’s load balancer and passes the client request further down to the closest API Gateway.
+
+## API aggregator
+
+This technique performs operations (for example, queries) against multiple services and returns the result to the client service with a single `HTTP request/response` call. Instead of having a client application make several calls to multiple APIs, an API aggregator uses an API Gateway to do this on behalf of the consumer on the server side.
+
+For example, consider a mobile app that makes multiple calls to different APIs to show the data for a single screen. In this case, it increases complexity in the client-side code, over-utilization of network resources, and even poor user experience as the application is more exposed to latency issues. API Gateway can accept as input all information required, does request authentication and validation, understands all data structures from all APIs that it interacts with, and is capable of transforming the response payloads so they can be sent back to the mobile app as a uniform payload needed for the consumer.
+
+
+
+## API Centralized Authentication
+
+In this design, an API Gateway acts as a **centralized authentication gateway**. As an authenticator, API Gateway looks for access credentials in the `HTTP header` - for example, a bearer token, and implements business logic that validates those credentials with an IDP, identity provider such as [Okta](https://www.okta.com/), [Cognito](https://aws.amazon.com/cognito/), [Azure Active Directory](https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/services/active-directory/) or [Ory Hydra](https://www.ory.sh/hydra/)) typically using the [OpenID Connect](https://openid.net/connect/) (OIDC) is an authentication protocol based on the [OAuth 2.0](https://oauth.net/2/) and checking whether they have access or not.
+
+
+
+Centralized authentication with the API Gateway can solve many problems and have some benefits as it completely offloads user management from an application and it improves performance by responding quickly to authentication requests received from client applications.
+
+
Review Comment:
Nitpick: why do you use a sketchy diagram representation while the rest isn't?
--
This is an automated message from the Apache Git Service.
To respond to the message, please log on to GitHub and use the
URL above to go to the specific comment.
To unsubscribe, e-mail: notifications-unsubscribe@apisix.apache.org
For queries about this service, please contact Infrastructure at:
users@infra.apache.org
[GitHub] [apisix-website] SylviaBABY commented on a diff in pull request #1380: docs: Add new blog post 10 usecases of an API Gateway
Posted by GitBox <gi...@apache.org>.
SylviaBABY commented on code in PR #1380:
URL: https://github.com/apache/apisix-website/pull/1380#discussion_r1006608742
##########
blog/en/blog/2022/10/27/ten-use-cases-api-gateway.md:
##########
@@ -0,0 +1,180 @@
+---
+title: "10 most use cases of an API Gateway in API-Led architecture"
+authors:
+ - name: Bobur Umurzokov
+ title: Author
+ url: https://github.com/Boburmirzo
+ image_url: https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/u/14247607
+keywords:
+- API Gateway
+- Apache APISIX
+- API
+- Architecture
+- Use-cases
+- Microservices
+description: This post elaborates on the 10 most common usages of an API Gateway such as Apache APISIX in architecting API-Led Connectivity.
+tags: [Case Studies]
+image: https://static.apiseven.com/2022/10/27/635a40e58b27a.png
+---
+
+> This post elaborates on the **10 most common usages** of an _API Gateway_ such as [Apache APISIX](https://apisix.apache.org/) in architecting [API-Led Connectivity](https://blogs.mulesoft.com/learn-apis/api-led-connectivity/what-is-api-led-connectivity/). We understand different solutions where you can make use of the API Gateway capabilities to design reliable, high-performance, and simple APIs for other developers.
+
+<!--truncate-->
+
+Here is the summary of 10 patterns that uses the API Gateway (but not all):
+
+1. API Resource routing.
+2. API Content-based routing.
+3. API Geo-routing.
+4. API Aggregator.
+5. API Centralized Authentication.
+6. API Format Conversion.
+7. API Observability.
+8. API Caching.
+9. API Fault handling.
+10. Sidecar API Gateway.
+
+## API-Led Architecture
+
+First of all, let’s revise once again these 3 terms like: **API Gateway**, **API-Led architecture**, and **API-Led Connectivity**.
+
+[API Gateway](https://wikitech.wikimedia.org/wiki/API_Gateway) is a _pattern_ formed by adding a layer between the client and the server that acts as a reverse proxy forwarding request from the client to the server. It allows all clients to access the services they want to access with a single API Gateway layer.
+
+[API-led](https://dzone.com/articles/mulesoft-api-led-connectivity-architectural-and-de) is an _architectural approach_ that puts APIs at the heart of communications between applications and the business capabilities they need to access, in order to consistently deliver seamless functionality across all digital channels.
+
+
+
+**API-led connectivity** refers to _the technique_ of using reusable and well-designed APIs to link data and applications which in turn it is based on **API-Led architecture**. It’s _a modern approach_ that looks at the best ways of reusing APIs to boost your innovation and move quickly in the market. At the most basic level, API-led architecture should address things like:
+
+- Securing APIs from unauthorized access and significant security threats.
+- Ensuring that consuming applications can always find the right API endpoint.
+- Throttling and/or limiting the number of calls made to an API to ensure continuous availability.
+- Supporting capabilities such as API design, testing, continuous integration, life cycle management, monitoring, and operations, to name a few.
+- Error handling and preventing error propagation across the stack.
+- Real-time monitoring of APIs with rich analytics and insight.
+- An approach for implementing scalable and flexible business capabilities, for example, in support of microservices architectures.
+
+Let’s describe in subsequent sections each usage of an API Gateway to address common requirements/challenges that arise when adopting API-led architectures.
+
+---
+
+## API resource routing
+
+The first in the list is the **API resource routing** method which uses an API Gateway to route incoming calls based on unique resource identifiers (URIs). Implementing an API gateway as the single entry point to all services means that API consumers only have to be aware of one URL domain. In this way, it becomes the API gateway's responsibility to route the traffic to the corresponding service endpoints and also enforce any applied policies as it is depicted in the below diagram.
+
+
+
+It reduces complexity on the API consumer side because they do not need to track and consume functionality from multiple HTTP endpoints in case there are many services in the system. Also, no need to implement all cross-cutting concerns, such as authentication/authorization, throttling, and rate limiting separately for each service. Most API Gateways like [Apache APISIX](https://apisix.apache.org/docs/apisix/terminology/api-gateway/) has already these core features.
+
+## API content-based routing
+
+Similarly, **API content-based** routing mechanism also uses an API gateway to route calls based on the content of a request (for example, based on the HTTP header or message body) instead of just the URI.
+
+Take a scenario when database sharding is applied in order to distribute the load across multiple database instances. This technique is typically applied when the overall number of records stored is huge and a single instance struggles to manage the load. Instead, records are spread across multiple database instances. Then, you implement multiple services, one per unique datastore, and adopt an API gateway as the only entry point to all services. You could then configure the API gateway to route calls to the corresponding service based on a key obtained either from the HTTP header or the payload.
+
+
+
+In the above diagram, an API gateway is exposing a single `/customers` resource for multiple customer services, each with a different data store.
+
+## API geo-routing
+
+**API geo-routing** solution routes API calls to the nearest API gateway based on where they originate. In order to prevent latency issues and other unforeseen issues that may occur due to distance (for example, a consuming application from Asia calling an API located in North America), API gateways and other service infrastructure have been deployed in multiple regions across the world as needed. For example, using different sub-domains for each API gateway in each region and letting the consuming application determine the nearest gateway based on application logic. Then, an API gateway provides internal load balancing to make sure that incoming requests are distributed across the available instances of a service.
+
+
+
+As you can see in the preceding diagram, it uses a DNS, traffic management service, and an API Gateway to resolve each subdomain against the region’s load balancer and passes the client request further down to the closest API Gateway.
+
+## API aggregator
+
+This technique performs operations (for example, queries) against multiple services and returns the result to the client service with a single `HTTP request/response` call. Instead of having a client application make several calls to multiple APIs, an API aggregator uses an API Gateway to do this on behalf of the consumer on the server side.
+
+For example, consider a mobile app that makes multiple calls to different APIs to show the data for a single screen. In this case, it increases complexity in the client-side code, over-utilization of network resources, and even poor user experience as the application is more exposed to latency issues. API Gateway can accept as input all information required, does request authentication and validation, understands all data structures from all APIs that it interacts with, and is capable of transforming the response payloads so they can be sent back to the mobile app as a uniform payload needed for the consumer.
+
+
+
+## API Centralized Authentication
+
+In this design, an API Gateway acts as a **centralized authentication gateway**. As an authenticator, API Gateway looks for access credentials in the `HTTP header` - for example, a bearer token, and implements business logic that validates those credentials with an IDP, identity provider such as [Okta](https://www.okta.com/), [Cognito](https://aws.amazon.com/cognito/), [Azure Active Directory](https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/services/active-directory/) or [Ory Hydra](https://www.ory.sh/hydra/)) typically using the [OpenID Connect](https://openid.net/connect/) (OIDC) is an authentication protocol based on the [OAuth 2.0](https://oauth.net/2/) and checking whether they have access or not.
+
+
+
+Centralized authentication with the API Gateway can solve many problems and have some benefits as it completely offloads user management from an application and it improves performance by responding quickly to authentication requests received from client applications.
+
+
+
+For example, [Apache APISIX](https://apisix.apache.org/) offers a variety of [plugins](https://apisix.apache.org/docs/apisix/plugins/openid-connect/) to enable different methods of API gateway authentication. We looked at some of the most commonly used in this blog post [Centralized Authentication with Apache APISIX Plugins](https://dev.to/apisix/centralized-authentication-with-apache-apisix-plugins-30fo). You can even enable multiple methods for authentication for the given API.
+
+## API Format Conversion
+
+This refers to having the ability to convert payloads from one format to another over the same transport. For example, from XML/SOAP over HTTPS to JSON over HTTPS and vice versa. API Gateways, by default offer capabilities in support of REST API and some specialized API gateways support, in addition to payload conversions, transport conversions such as converting from Message Queuing Telemetry Transport (MQTT) over TCP (a very popular transport in IoT) to JSON over HTTPS.
+
+
+
+For example, Apache APISIX is able to receive an HTTP request, then transcode it and forwards it to a gRPC service, gets the response, and return it back to the client in HTTP format by means of its [gRPC Transcode](https://apisix.apache.org/docs/apisix/plugins/grpc-transcode/) plug-in.
+
+## API Observability
+
+By now, we know that an API gateway offers a central control point for incoming traffic to a variety of destinations but it can also be a central point for observation as well since it is uniquely qualified to know about all the traffic moving between clients and our service networks. There is always the possibility to instrument the API gateways so observability data (structured logs, metrics, and traces) can be collected in order to use specialized monitoring tools.
+
+
+
+For example, Apache APISIX provides [pre-built connectors](https://apisix.apache.org/docs/apisix/plugins/prometheus/) (plug-ins) that you can easily integrate with external monitoring tools. You can leverage these connectors to ingest log data from your API gateways to further derive useful metrics and gain complete visibility into the usage, you can manage performance, and security of your APIs in your environment. There is also a dedicated post on [how to use these observability plugins](https://medium.com/@ApacheAPISIX/api-observability-with-apache-apisix-plugins-34584dc1ce3a).
+
+## API Caching
+
+**API Caching** is yet another level of caching that is usually implemented inside API Gateway. It can reduce the number of calls made to your endpoint and also improve the latency of requests to your API by caching a response from the upstream. If the API Gateway cache has a fresh copy of the requested resource, it uses that copy to satisfy the request directly instead of making a request to the endpoint. If the cached data is not found, the request travels to the intended upstream services (backend services).
+
+
+
+You can read more about [API Gateway Caching with Apache APISIX](https://medium.com/@ApacheAPISIX/api-gateway-caching-for-asp-net-core-web-api-cf24d0e598fc) in the dedicated blog post.
+
+## API Fault handling
+
+It is critical to handle failures in service-to-service calls gracefully. Also, we want to be sure that any resilience mechanisms we have in place such as error handling code, [circuit breaker](https://dev.to/apisix/implementing-resilient-applications-with-api-gateway-circuit-breaker-ggk), [health checks](https://dev.to/apisix/implementing-resilient-applications-with-api-gateway-health-check-338c), [retry](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/architecture/patterns/retry), fallback, redundant instances, and so on. Modern API Gateways support all the above error-handling features including automatic retries and timeouts.
+
+
+
+For example, APISIX acts as an orchestrator that can use this status report to decide how to manage the traffic, load balance to a healthy node, fail-fast due to some cascading failures or simply alerts you when it notices something goes wrong. API Gateway also ensures that routing and other network-level components work together successfully to deliver a request to the API process. It helps you to detect in the early stage and fix issues for your running application much more easily.
+
+## Sidecar API gateway
+
+**Sidecar** implements an API gateway as a container attached to a service in an independent runtime, such as [Kubernetes](https://kubernetes.io/). Sidecar is a pattern that corresponds to a [sidecar](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sidecar) attached to a motorcycle, similarly, it is attached to a parent application and provides supporting features for the application. The sidecar also shares the same lifecycle as the parent application, is created and retired alongside the parent, and introduces additional features such as monitoring, logging, configuration, and networking services. The benefits of adopting this pattern are that each service runtime can configure its own API gateway in the best way. Because the requirement to enable the API gateway functionalities and setups can vary from service to service. At the same time, it separates concerns if an issue occurs in the shared API gateway infrastructure then all services will not be impacted.
+
+
+
+The preceding diagram illustrates an ingress acting as an API load balancer and resource router into each service endpoint. The entry point for the service is not the service endpoint itself but rather a sidecar API gateway. The sidecar can then perform any of the capabilities offered by the API gateway in addition to routing traffic to the service endpoint.
+
+## Summary
+
+Throughout the post, we described some of the use cases of API Gateway in designing API-Led architecture like how an API handles authentication, transformation, aggregation, caching, observability, how an API gateway can be applied in order to route access to multiple backend endpoints and so on. However, there are many other use cases one might think of.
+
+For example, I explained in another blog post how to [develop API services using CQRS, API Gateway and Serverless](https://apisix.apache.org/blog/2022/09/23/build-event-driven-api/) where the API Gateway used for resource routing to route all read calls to the product's query service and upsert calls to the product's command service based on HTTP request type.
+
+### Related resources
+
+➔ [API Gateway](https://apisix.apache.org/docs/apisix/terminology/api-gateway/).
+
+➔ [Read book: Enterprise API Management: Design and deliver valuable business APIs](https://www.amazon.com/Enterprise-Management-Luis-Augusto-Weir/dp/1787284433).
+
+### Recommended content 💁
+
+➔ Watch Video Tutorial:
+
+- [Getting Started with Apache APISIX](https://youtu.be/dUOjJkb61so).
+
+- [APIs security with Apache APISIX](https://youtu.be/hMFjhwLMtQ8).
+
+- [Implementing resilient applications with API Gateway (Circuit breaker)](https://youtu.be/aWzo0ysH__c).
+
+➔ Read the blog posts:
+
+- [Implementing resilient applications with API Gateway (Health Check)](https://dev.to/apisix/implementing-resilient-applications-with-api-gateway-health-check-338c).
+
+- [Overview of Apache APISIX API Gateway Plugins](https://dev.to/apisix/overview-of-apache-apisix-api-gateway-plugins-2m8o).
+
+### Community⤵️
Review Comment:
Need to add a space line for each piece of content
<img width="894" alt="image" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/39793568/198243373-656cca7c-f6e2-4b31-992e-f2401f271d72.png">
--
This is an automated message from the Apache Git Service.
To respond to the message, please log on to GitHub and use the
URL above to go to the specific comment.
To unsubscribe, e-mail: notifications-unsubscribe@apisix.apache.org
For queries about this service, please contact Infrastructure at:
users@infra.apache.org
[GitHub] [apisix-website] Boburmirzo commented on a diff in pull request #1380: docs: Add new blog post 10 usecases of an API Gateway
Posted by GitBox <gi...@apache.org>.
Boburmirzo commented on code in PR #1380:
URL: https://github.com/apache/apisix-website/pull/1380#discussion_r1006704511
##########
blog/en/blog/2022/10/27/ten-use-cases-api-gateway.md:
##########
@@ -0,0 +1,180 @@
+---
+title: "10 most use cases of an API Gateway in API-Led architecture"
+authors:
+ - name: Bobur Umurzokov
+ title: Author
+ url: https://github.com/Boburmirzo
+ image_url: https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/u/14247607
+keywords:
+- API Gateway
+- Apache APISIX
+- API
+- Architecture
+- Use-cases
+- Microservices
+description: This post elaborates on the 10 most common usages of an API Gateway such as Apache APISIX in architecting API-Led Connectivity.
+tags: [Case Studies]
+image: https://static.apiseven.com/2022/10/27/635a40e58b27a.png
+---
+
+> This post elaborates on the **10 most common usages** of an _API Gateway_ such as [Apache APISIX](https://apisix.apache.org/) in architecting [API-Led Connectivity](https://blogs.mulesoft.com/learn-apis/api-led-connectivity/what-is-api-led-connectivity/). We understand different solutions where you can make use of the API Gateway capabilities to design reliable, high-performance, and simple APIs for other developers.
+
+<!--truncate-->
+
+Here is the summary of 10 patterns that uses the API Gateway (but not all):
+
+1. API Resource routing.
+2. API Content-based routing.
+3. API Geo-routing.
+4. API Aggregator.
+5. API Centralized Authentication.
+6. API Format Conversion.
+7. API Observability.
+8. API Caching.
+9. API Fault handling.
+10. Sidecar API Gateway.
+
+## API-Led Architecture
+
+First of all, let’s revise once again these 3 terms like: **API Gateway**, **API-Led architecture**, and **API-Led Connectivity**.
+
+[API Gateway](https://wikitech.wikimedia.org/wiki/API_Gateway) is a _pattern_ formed by adding a layer between the client and the server that acts as a reverse proxy forwarding request from the client to the server. It allows all clients to access the services they want to access with a single API Gateway layer.
+
+[API-led](https://dzone.com/articles/mulesoft-api-led-connectivity-architectural-and-de) is an _architectural approach_ that puts APIs at the heart of communications between applications and the business capabilities they need to access, in order to consistently deliver seamless functionality across all digital channels.
+
+
+
+**API-led connectivity** refers to _the technique_ of using reusable and well-designed APIs to link data and applications which in turn it is based on **API-Led architecture**. It’s _a modern approach_ that looks at the best ways of reusing APIs to boost your innovation and move quickly in the market. At the most basic level, API-led architecture should address things like:
+
+- Securing APIs from unauthorized access and significant security threats.
+- Ensuring that consuming applications can always find the right API endpoint.
+- Throttling and/or limiting the number of calls made to an API to ensure continuous availability.
+- Supporting capabilities such as API design, testing, continuous integration, life cycle management, monitoring, and operations, to name a few.
+- Error handling and preventing error propagation across the stack.
+- Real-time monitoring of APIs with rich analytics and insight.
+- An approach for implementing scalable and flexible business capabilities, for example, in support of microservices architectures.
+
+Let’s describe in subsequent sections each usage of an API Gateway to address common requirements/challenges that arise when adopting API-led architectures.
+
+---
+
+## API resource routing
+
+The first in the list is the **API resource routing** method which uses an API Gateway to route incoming calls based on unique resource identifiers (URIs). Implementing an API gateway as the single entry point to all services means that API consumers only have to be aware of one URL domain. In this way, it becomes the API gateway's responsibility to route the traffic to the corresponding service endpoints and also enforce any applied policies as it is depicted in the below diagram.
+
+
+
+It reduces complexity on the API consumer side because they do not need to track and consume functionality from multiple HTTP endpoints in case there are many services in the system. Also, no need to implement all cross-cutting concerns, such as authentication/authorization, throttling, and rate limiting separately for each service. Most API Gateways like [Apache APISIX](https://apisix.apache.org/docs/apisix/terminology/api-gateway/) has already these core features.
Review Comment:
> I don't know what it means
It means "the client applications do not need to consume functionality from multiple HTTP endpoints" I will rephrase it.
--
This is an automated message from the Apache Git Service.
To respond to the message, please log on to GitHub and use the
URL above to go to the specific comment.
To unsubscribe, e-mail: notifications-unsubscribe@apisix.apache.org
For queries about this service, please contact Infrastructure at:
users@infra.apache.org
[GitHub] [apisix-website] Boburmirzo commented on a diff in pull request #1380: docs: Add new blog post 10 usecases of an API Gateway
Posted by GitBox <gi...@apache.org>.
Boburmirzo commented on code in PR #1380:
URL: https://github.com/apache/apisix-website/pull/1380#discussion_r1006702678
##########
blog/en/blog/2022/10/27/ten-use-cases-api-gateway.md:
##########
@@ -0,0 +1,180 @@
+---
+title: "10 most use cases of an API Gateway in API-Led architecture"
+authors:
+ - name: Bobur Umurzokov
+ title: Author
+ url: https://github.com/Boburmirzo
+ image_url: https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/u/14247607
+keywords:
+- API Gateway
+- Apache APISIX
+- API
+- Architecture
+- Use-cases
+- Microservices
+description: This post elaborates on the 10 most common usages of an API Gateway such as Apache APISIX in architecting API-Led Connectivity.
+tags: [Case Studies]
+image: https://static.apiseven.com/2022/10/27/635a40e58b27a.png
+---
+
+> This post elaborates on the **10 most common usages** of an _API Gateway_ such as [Apache APISIX](https://apisix.apache.org/) in architecting [API-Led Connectivity](https://blogs.mulesoft.com/learn-apis/api-led-connectivity/what-is-api-led-connectivity/). We understand different solutions where you can make use of the API Gateway capabilities to design reliable, high-performance, and simple APIs for other developers.
+
+<!--truncate-->
+
+Here is the summary of 10 patterns that uses the API Gateway (but not all):
+
+1. API Resource routing.
+2. API Content-based routing.
+3. API Geo-routing.
+4. API Aggregator.
+5. API Centralized Authentication.
+6. API Format Conversion.
+7. API Observability.
+8. API Caching.
+9. API Fault handling.
+10. Sidecar API Gateway.
+
+## API-Led Architecture
+
+First of all, let’s revise once again these 3 terms like: **API Gateway**, **API-Led architecture**, and **API-Led Connectivity**.
+
+[API Gateway](https://wikitech.wikimedia.org/wiki/API_Gateway) is a _pattern_ formed by adding a layer between the client and the server that acts as a reverse proxy forwarding request from the client to the server. It allows all clients to access the services they want to access with a single API Gateway layer.
Review Comment:
Right, replaced it with a single entry point
--
This is an automated message from the Apache Git Service.
To respond to the message, please log on to GitHub and use the
URL above to go to the specific comment.
To unsubscribe, e-mail: notifications-unsubscribe@apisix.apache.org
For queries about this service, please contact Infrastructure at:
users@infra.apache.org
[GitHub] [apisix-website] Boburmirzo commented on a diff in pull request #1380: docs: Add new blog post 10 usecases of an API Gateway
Posted by GitBox <gi...@apache.org>.
Boburmirzo commented on code in PR #1380:
URL: https://github.com/apache/apisix-website/pull/1380#discussion_r1006614794
##########
blog/en/blog/2022/10/27/ten-use-cases-api-gateway.md:
##########
@@ -0,0 +1,180 @@
+---
+title: "10 most use cases of an API Gateway in API-Led architecture"
+authors:
+ - name: Bobur Umurzokov
+ title: Author
+ url: https://github.com/Boburmirzo
+ image_url: https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/u/14247607
+keywords:
+- API Gateway
+- Apache APISIX
+- API
+- Architecture
+- Use-cases
+- Microservices
+description: This post elaborates on the 10 most common usages of an API Gateway such as Apache APISIX in architecting API-Led Connectivity.
+tags: [Case Studies]
+image: https://static.apiseven.com/2022/10/27/635a40e58b27a.png
+---
+
+> This post elaborates on the **10 most common usages** of an _API Gateway_ such as [Apache APISIX](https://apisix.apache.org/) in architecting [API-Led Connectivity](https://blogs.mulesoft.com/learn-apis/api-led-connectivity/what-is-api-led-connectivity/). We understand different solutions where you can make use of the API Gateway capabilities to design reliable, high-performance, and simple APIs for other developers.
+
+<!--truncate-->
+
+Here is the summary of 10 patterns that uses the API Gateway (but not all):
+
+1. API Resource routing.
+2. API Content-based routing.
+3. API Geo-routing.
+4. API Aggregator.
+5. API Centralized Authentication.
+6. API Format Conversion.
+7. API Observability.
+8. API Caching.
+9. API Fault handling.
+10. Sidecar API Gateway.
+
+## API-Led Architecture
+
+First of all, let’s revise once again these 3 terms like: **API Gateway**, **API-Led architecture**, and **API-Led Connectivity**.
+
+[API Gateway](https://wikitech.wikimedia.org/wiki/API_Gateway) is a _pattern_ formed by adding a layer between the client and the server that acts as a reverse proxy forwarding request from the client to the server. It allows all clients to access the services they want to access with a single API Gateway layer.
+
+[API-led](https://dzone.com/articles/mulesoft-api-led-connectivity-architectural-and-de) is an _architectural approach_ that puts APIs at the heart of communications between applications and the business capabilities they need to access, in order to consistently deliver seamless functionality across all digital channels.
+
+
+
+**API-led connectivity** refers to _the technique_ of using reusable and well-designed APIs to link data and applications which in turn it is based on **API-Led architecture**. It’s _a modern approach_ that looks at the best ways of reusing APIs to boost your innovation and move quickly in the market. At the most basic level, API-led architecture should address things like:
+
+- Securing APIs from unauthorized access and significant security threats.
+- Ensuring that consuming applications can always find the right API endpoint.
+- Throttling and/or limiting the number of calls made to an API to ensure continuous availability.
+- Supporting capabilities such as API design, testing, continuous integration, life cycle management, monitoring, and operations, to name a few.
+- Error handling and preventing error propagation across the stack.
+- Real-time monitoring of APIs with rich analytics and insight.
+- An approach for implementing scalable and flexible business capabilities, for example, in support of microservices architectures.
+
+Let’s describe in subsequent sections each usage of an API Gateway to address common requirements/challenges that arise when adopting API-led architectures.
+
+---
+
+## API resource routing
+
+The first in the list is the **API resource routing** method which uses an API Gateway to route incoming calls based on unique resource identifiers (URIs). Implementing an API gateway as the single entry point to all services means that API consumers only have to be aware of one URL domain. In this way, it becomes the API gateway's responsibility to route the traffic to the corresponding service endpoints and also enforce any applied policies as it is depicted in the below diagram.
+
+
+
+It reduces complexity on the API consumer side because they do not need to track and consume functionality from multiple HTTP endpoints in case there are many services in the system. Also, no need to implement all cross-cutting concerns, such as authentication/authorization, throttling, and rate limiting separately for each service. Most API Gateways like [Apache APISIX](https://apisix.apache.org/docs/apisix/terminology/api-gateway/) has already these core features.
+
+## API content-based routing
+
+Similarly, **API content-based** routing mechanism also uses an API gateway to route calls based on the content of a request (for example, based on the HTTP header or message body) instead of just the URI.
+
+Take a scenario when database sharding is applied in order to distribute the load across multiple database instances. This technique is typically applied when the overall number of records stored is huge and a single instance struggles to manage the load. Instead, records are spread across multiple database instances. Then, you implement multiple services, one per unique datastore, and adopt an API gateway as the only entry point to all services. You could then configure the API gateway to route calls to the corresponding service based on a key obtained either from the HTTP header or the payload.
+
+
+
+In the above diagram, an API gateway is exposing a single `/customers` resource for multiple customer services, each with a different data store.
+
+## API geo-routing
+
+**API geo-routing** solution routes API calls to the nearest API gateway based on where they originate. In order to prevent latency issues and other unforeseen issues that may occur due to distance (for example, a consuming application from Asia calling an API located in North America), API gateways and other service infrastructure have been deployed in multiple regions across the world as needed. For example, using different sub-domains for each API gateway in each region and letting the consuming application determine the nearest gateway based on application logic. Then, an API gateway provides internal load balancing to make sure that incoming requests are distributed across the available instances of a service.
+
+
+
+As you can see in the preceding diagram, it uses a DNS, traffic management service, and an API Gateway to resolve each subdomain against the region’s load balancer and passes the client request further down to the closest API Gateway.
+
+## API aggregator
+
+This technique performs operations (for example, queries) against multiple services and returns the result to the client service with a single `HTTP request/response` call. Instead of having a client application make several calls to multiple APIs, an API aggregator uses an API Gateway to do this on behalf of the consumer on the server side.
+
+For example, consider a mobile app that makes multiple calls to different APIs to show the data for a single screen. In this case, it increases complexity in the client-side code, over-utilization of network resources, and even poor user experience as the application is more exposed to latency issues. API Gateway can accept as input all information required, does request authentication and validation, understands all data structures from all APIs that it interacts with, and is capable of transforming the response payloads so they can be sent back to the mobile app as a uniform payload needed for the consumer.
+
+
+
+## API Centralized Authentication
+
+In this design, an API Gateway acts as a **centralized authentication gateway**. As an authenticator, API Gateway looks for access credentials in the `HTTP header` - for example, a bearer token, and implements business logic that validates those credentials with an IDP, identity provider such as [Okta](https://www.okta.com/), [Cognito](https://aws.amazon.com/cognito/), [Azure Active Directory](https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/services/active-directory/) or [Ory Hydra](https://www.ory.sh/hydra/)) typically using the [OpenID Connect](https://openid.net/connect/) (OIDC) is an authentication protocol based on the [OAuth 2.0](https://oauth.net/2/) and checking whether they have access or not.
+
+
+
+Centralized authentication with the API Gateway can solve many problems and have some benefits as it completely offloads user management from an application and it improves performance by responding quickly to authentication requests received from client applications.
+
+
+
+For example, [Apache APISIX](https://apisix.apache.org/) offers a variety of [plugins](https://apisix.apache.org/docs/apisix/plugins/openid-connect/) to enable different methods of API gateway authentication. We looked at some of the most commonly used in this blog post [Centralized Authentication with Apache APISIX Plugins](https://dev.to/apisix/centralized-authentication-with-apache-apisix-plugins-30fo). You can even enable multiple methods for authentication for the given API.
+
+## API Format Conversion
+
+This refers to having the ability to convert payloads from one format to another over the same transport. For example, from XML/SOAP over HTTPS to JSON over HTTPS and vice versa. API Gateways, by default offer capabilities in support of REST API and some specialized API gateways support, in addition to payload conversions, transport conversions such as converting from Message Queuing Telemetry Transport (MQTT) over TCP (a very popular transport in IoT) to JSON over HTTPS.
+
+
+
+For example, Apache APISIX is able to receive an HTTP request, then transcode it and forwards it to a gRPC service, gets the response, and return it back to the client in HTTP format by means of its [gRPC Transcode](https://apisix.apache.org/docs/apisix/plugins/grpc-transcode/) plug-in.
+
+## API Observability
+
+By now, we know that an API gateway offers a central control point for incoming traffic to a variety of destinations but it can also be a central point for observation as well since it is uniquely qualified to know about all the traffic moving between clients and our service networks. There is always the possibility to instrument the API gateways so observability data (structured logs, metrics, and traces) can be collected in order to use specialized monitoring tools.
+
+
+
+For example, Apache APISIX provides [pre-built connectors](https://apisix.apache.org/docs/apisix/plugins/prometheus/) (plug-ins) that you can easily integrate with external monitoring tools. You can leverage these connectors to ingest log data from your API gateways to further derive useful metrics and gain complete visibility into the usage, you can manage performance, and security of your APIs in your environment. There is also a dedicated post on [how to use these observability plugins](https://medium.com/@ApacheAPISIX/api-observability-with-apache-apisix-plugins-34584dc1ce3a).
+
+## API Caching
+
+**API Caching** is yet another level of caching that is usually implemented inside API Gateway. It can reduce the number of calls made to your endpoint and also improve the latency of requests to your API by caching a response from the upstream. If the API Gateway cache has a fresh copy of the requested resource, it uses that copy to satisfy the request directly instead of making a request to the endpoint. If the cached data is not found, the request travels to the intended upstream services (backend services).
+
+
+
+You can read more about [API Gateway Caching with Apache APISIX](https://medium.com/@ApacheAPISIX/api-gateway-caching-for-asp-net-core-web-api-cf24d0e598fc) in the dedicated blog post.
+
+## API Fault handling
+
+It is critical to handle failures in service-to-service calls gracefully. Also, we want to be sure that any resilience mechanisms we have in place such as error handling code, [circuit breaker](https://dev.to/apisix/implementing-resilient-applications-with-api-gateway-circuit-breaker-ggk), [health checks](https://dev.to/apisix/implementing-resilient-applications-with-api-gateway-health-check-338c), [retry](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/architecture/patterns/retry), fallback, redundant instances, and so on. Modern API Gateways support all the above error-handling features including automatic retries and timeouts.
+
+
+
+For example, APISIX acts as an orchestrator that can use this status report to decide how to manage the traffic, load balance to a healthy node, fail-fast due to some cascading failures or simply alerts you when it notices something goes wrong. API Gateway also ensures that routing and other network-level components work together successfully to deliver a request to the API process. It helps you to detect in the early stage and fix issues for your running application much more easily.
+
+## Sidecar API gateway
+
+**Sidecar** implements an API gateway as a container attached to a service in an independent runtime, such as [Kubernetes](https://kubernetes.io/). Sidecar is a pattern that corresponds to a [sidecar](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sidecar) attached to a motorcycle, similarly, it is attached to a parent application and provides supporting features for the application. The sidecar also shares the same lifecycle as the parent application, is created and retired alongside the parent, and introduces additional features such as monitoring, logging, configuration, and networking services. The benefits of adopting this pattern are that each service runtime can configure its own API gateway in the best way. Because the requirement to enable the API gateway functionalities and setups can vary from service to service. At the same time, it separates concerns if an issue occurs in the shared API gateway infrastructure then all services will not be impacted.
+
+
+
+The preceding diagram illustrates an ingress acting as an API load balancer and resource router into each service endpoint. The entry point for the service is not the service endpoint itself but rather a sidecar API gateway. The sidecar can then perform any of the capabilities offered by the API gateway in addition to routing traffic to the service endpoint.
+
+## Summary
+
+Throughout the post, we described some of the use cases of API Gateway in designing API-Led architecture like how an API handles authentication, transformation, aggregation, caching, observability, how an API gateway can be applied in order to route access to multiple backend endpoints and so on. However, there are many other use cases one might think of.
+
+For example, I explained in another blog post how to [develop API services using CQRS, API Gateway and Serverless](https://apisix.apache.org/blog/2022/09/23/build-event-driven-api/) where the API Gateway used for resource routing to route all read calls to the product's query service and upsert calls to the product's command service based on HTTP request type.
+
+### Related resources
+
+➔ [API Gateway](https://apisix.apache.org/docs/apisix/terminology/api-gateway/).
+
+➔ [Read book: Enterprise API Management: Design and deliver valuable business APIs](https://www.amazon.com/Enterprise-Management-Luis-Augusto-Weir/dp/1787284433).
+
+### Recommended content 💁
+
+➔ Watch Video Tutorial:
+
+- [Getting Started with Apache APISIX](https://youtu.be/dUOjJkb61so).
+
+- [APIs security with Apache APISIX](https://youtu.be/hMFjhwLMtQ8).
+
+- [Implementing resilient applications with API Gateway (Circuit breaker)](https://youtu.be/aWzo0ysH__c).
+
+➔ Read the blog posts:
+
+- [Implementing resilient applications with API Gateway (Health Check)](https://dev.to/apisix/implementing-resilient-applications-with-api-gateway-health-check-338c).
+
+- [Overview of Apache APISIX API Gateway Plugins](https://dev.to/apisix/overview-of-apache-apisix-api-gateway-plugins-2m8o).
+
+### Community⤵️
Review Comment:
@SylviaBABY Right, I added a list similar to previous posts.
--
This is an automated message from the Apache Git Service.
To respond to the message, please log on to GitHub and use the
URL above to go to the specific comment.
To unsubscribe, e-mail: notifications-unsubscribe@apisix.apache.org
For queries about this service, please contact Infrastructure at:
users@infra.apache.org
[GitHub] [apisix-website] Boburmirzo commented on a diff in pull request #1380: docs: Add new blog post 10 usecases of an API Gateway
Posted by GitBox <gi...@apache.org>.
Boburmirzo commented on code in PR #1380:
URL: https://github.com/apache/apisix-website/pull/1380#discussion_r1006712856
##########
blog/en/blog/2022/10/27/ten-use-cases-api-gateway.md:
##########
@@ -0,0 +1,180 @@
+---
+title: "10 most use cases of an API Gateway in API-Led architecture"
+authors:
+ - name: Bobur Umurzokov
+ title: Author
+ url: https://github.com/Boburmirzo
+ image_url: https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/u/14247607
+keywords:
+- API Gateway
+- Apache APISIX
+- API
+- Architecture
+- Use-cases
+- Microservices
+description: This post elaborates on the 10 most common usages of an API Gateway such as Apache APISIX in architecting API-Led Connectivity.
+tags: [Case Studies]
+image: https://static.apiseven.com/2022/10/27/635a40e58b27a.png
+---
+
+> This post elaborates on the **10 most common usages** of an _API Gateway_ such as [Apache APISIX](https://apisix.apache.org/) in architecting [API-Led Connectivity](https://blogs.mulesoft.com/learn-apis/api-led-connectivity/what-is-api-led-connectivity/). We understand different solutions where you can make use of the API Gateway capabilities to design reliable, high-performance, and simple APIs for other developers.
+
+<!--truncate-->
+
+Here is the summary of 10 patterns that uses the API Gateway (but not all):
+
+1. API Resource routing.
+2. API Content-based routing.
+3. API Geo-routing.
+4. API Aggregator.
+5. API Centralized Authentication.
+6. API Format Conversion.
+7. API Observability.
+8. API Caching.
+9. API Fault handling.
+10. Sidecar API Gateway.
+
+## API-Led Architecture
+
+First of all, let’s revise once again these 3 terms like: **API Gateway**, **API-Led architecture**, and **API-Led Connectivity**.
+
+[API Gateway](https://wikitech.wikimedia.org/wiki/API_Gateway) is a _pattern_ formed by adding a layer between the client and the server that acts as a reverse proxy forwarding request from the client to the server. It allows all clients to access the services they want to access with a single API Gateway layer.
+
+[API-led](https://dzone.com/articles/mulesoft-api-led-connectivity-architectural-and-de) is an _architectural approach_ that puts APIs at the heart of communications between applications and the business capabilities they need to access, in order to consistently deliver seamless functionality across all digital channels.
+
+
+
+**API-led connectivity** refers to _the technique_ of using reusable and well-designed APIs to link data and applications which in turn it is based on **API-Led architecture**. It’s _a modern approach_ that looks at the best ways of reusing APIs to boost your innovation and move quickly in the market. At the most basic level, API-led architecture should address things like:
+
+- Securing APIs from unauthorized access and significant security threats.
+- Ensuring that consuming applications can always find the right API endpoint.
+- Throttling and/or limiting the number of calls made to an API to ensure continuous availability.
+- Supporting capabilities such as API design, testing, continuous integration, life cycle management, monitoring, and operations, to name a few.
+- Error handling and preventing error propagation across the stack.
+- Real-time monitoring of APIs with rich analytics and insight.
+- An approach for implementing scalable and flexible business capabilities, for example, in support of microservices architectures.
+
+Let’s describe in subsequent sections each usage of an API Gateway to address common requirements/challenges that arise when adopting API-led architectures.
+
+---
+
+## API resource routing
+
+The first in the list is the **API resource routing** method which uses an API Gateway to route incoming calls based on unique resource identifiers (URIs). Implementing an API gateway as the single entry point to all services means that API consumers only have to be aware of one URL domain. In this way, it becomes the API gateway's responsibility to route the traffic to the corresponding service endpoints and also enforce any applied policies as it is depicted in the below diagram.
+
+
+
+It reduces complexity on the API consumer side because they do not need to track and consume functionality from multiple HTTP endpoints in case there are many services in the system. Also, no need to implement all cross-cutting concerns, such as authentication/authorization, throttling, and rate limiting separately for each service. Most API Gateways like [Apache APISIX](https://apisix.apache.org/docs/apisix/terminology/api-gateway/) has already these core features.
+
+## API content-based routing
+
+Similarly, **API content-based** routing mechanism also uses an API gateway to route calls based on the content of a request (for example, based on the HTTP header or message body) instead of just the URI.
+
+Take a scenario when database sharding is applied in order to distribute the load across multiple database instances. This technique is typically applied when the overall number of records stored is huge and a single instance struggles to manage the load. Instead, records are spread across multiple database instances. Then, you implement multiple services, one per unique datastore, and adopt an API gateway as the only entry point to all services. You could then configure the API gateway to route calls to the corresponding service based on a key obtained either from the HTTP header or the payload.
+
+
+
+In the above diagram, an API gateway is exposing a single `/customers` resource for multiple customer services, each with a different data store.
+
+## API geo-routing
+
+**API geo-routing** solution routes API calls to the nearest API gateway based on where they originate. In order to prevent latency issues and other unforeseen issues that may occur due to distance (for example, a consuming application from Asia calling an API located in North America), API gateways and other service infrastructure have been deployed in multiple regions across the world as needed. For example, using different sub-domains for each API gateway in each region and letting the consuming application determine the nearest gateway based on application logic. Then, an API gateway provides internal load balancing to make sure that incoming requests are distributed across the available instances of a service.
+
+
+
+As you can see in the preceding diagram, it uses a DNS, traffic management service, and an API Gateway to resolve each subdomain against the region’s load balancer and passes the client request further down to the closest API Gateway.
+
+## API aggregator
+
+This technique performs operations (for example, queries) against multiple services and returns the result to the client service with a single `HTTP request/response` call. Instead of having a client application make several calls to multiple APIs, an API aggregator uses an API Gateway to do this on behalf of the consumer on the server side.
+
+For example, consider a mobile app that makes multiple calls to different APIs to show the data for a single screen. In this case, it increases complexity in the client-side code, over-utilization of network resources, and even poor user experience as the application is more exposed to latency issues. API Gateway can accept as input all information required, does request authentication and validation, understands all data structures from all APIs that it interacts with, and is capable of transforming the response payloads so they can be sent back to the mobile app as a uniform payload needed for the consumer.
+
+
+
+## API Centralized Authentication
+
+In this design, an API Gateway acts as a **centralized authentication gateway**. As an authenticator, API Gateway looks for access credentials in the `HTTP header` - for example, a bearer token, and implements business logic that validates those credentials with an IDP, identity provider such as [Okta](https://www.okta.com/), [Cognito](https://aws.amazon.com/cognito/), [Azure Active Directory](https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/services/active-directory/) or [Ory Hydra](https://www.ory.sh/hydra/)) typically using the [OpenID Connect](https://openid.net/connect/) (OIDC) is an authentication protocol based on the [OAuth 2.0](https://oauth.net/2/) and checking whether they have access or not.
+
+
+
+Centralized authentication with the API Gateway can solve many problems and have some benefits as it completely offloads user management from an application and it improves performance by responding quickly to authentication requests received from client applications.
+
+
Review Comment:
Because, sketchy diagrams I draw new, the rest from old content:) It consumes a lot of time.
--
This is an automated message from the Apache Git Service.
To respond to the message, please log on to GitHub and use the
URL above to go to the specific comment.
To unsubscribe, e-mail: notifications-unsubscribe@apisix.apache.org
For queries about this service, please contact Infrastructure at:
users@infra.apache.org
[GitHub] [apisix-website] Boburmirzo commented on a diff in pull request #1380: docs: Add new blog post 10 usecases of an API Gateway
Posted by GitBox <gi...@apache.org>.
Boburmirzo commented on code in PR #1380:
URL: https://github.com/apache/apisix-website/pull/1380#discussion_r1006703001
##########
blog/en/blog/2022/10/27/ten-use-cases-api-gateway.md:
##########
@@ -0,0 +1,180 @@
+---
+title: "10 most use cases of an API Gateway in API-Led architecture"
+authors:
+ - name: Bobur Umurzokov
+ title: Author
+ url: https://github.com/Boburmirzo
+ image_url: https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/u/14247607
+keywords:
+- API Gateway
+- Apache APISIX
+- API
+- Architecture
+- Use-cases
+- Microservices
+description: This post elaborates on the 10 most common usages of an API Gateway such as Apache APISIX in architecting API-Led Connectivity.
+tags: [Case Studies]
+image: https://static.apiseven.com/2022/10/27/635a40e58b27a.png
+---
+
+> This post elaborates on the **10 most common usages** of an _API Gateway_ such as [Apache APISIX](https://apisix.apache.org/) in architecting [API-Led Connectivity](https://blogs.mulesoft.com/learn-apis/api-led-connectivity/what-is-api-led-connectivity/). We understand different solutions where you can make use of the API Gateway capabilities to design reliable, high-performance, and simple APIs for other developers.
+
+<!--truncate-->
+
+Here is the summary of 10 patterns that uses the API Gateway (but not all):
+
+1. API Resource routing.
+2. API Content-based routing.
+3. API Geo-routing.
+4. API Aggregator.
+5. API Centralized Authentication.
+6. API Format Conversion.
+7. API Observability.
+8. API Caching.
+9. API Fault handling.
+10. Sidecar API Gateway.
+
+## API-Led Architecture
+
+First of all, let’s revise once again these 3 terms like: **API Gateway**, **API-Led architecture**, and **API-Led Connectivity**.
+
+[API Gateway](https://wikitech.wikimedia.org/wiki/API_Gateway) is a _pattern_ formed by adding a layer between the client and the server that acts as a reverse proxy forwarding request from the client to the server. It allows all clients to access the services they want to access with a single API Gateway layer.
+
+[API-led](https://dzone.com/articles/mulesoft-api-led-connectivity-architectural-and-de) is an _architectural approach_ that puts APIs at the heart of communications between applications and the business capabilities they need to access, in order to consistently deliver seamless functionality across all digital channels.
+
+
+
+**API-led connectivity** refers to _the technique_ of using reusable and well-designed APIs to link data and applications which in turn it is based on **API-Led architecture**. It’s _a modern approach_ that looks at the best ways of reusing APIs to boost your innovation and move quickly in the market. At the most basic level, API-led architecture should address things like:
Review Comment:
Removed modern
--
This is an automated message from the Apache Git Service.
To respond to the message, please log on to GitHub and use the
URL above to go to the specific comment.
To unsubscribe, e-mail: notifications-unsubscribe@apisix.apache.org
For queries about this service, please contact Infrastructure at:
users@infra.apache.org
[GitHub] [apisix-website] Boburmirzo commented on a diff in pull request #1380: docs: Add new blog post 10 usecases of an API Gateway
Posted by GitBox <gi...@apache.org>.
Boburmirzo commented on code in PR #1380:
URL: https://github.com/apache/apisix-website/pull/1380#discussion_r1006766505
##########
blog/en/blog/2022/10/27/ten-use-cases-api-gateway.md:
##########
@@ -0,0 +1,180 @@
+---
+title: "10 most use cases of an API Gateway in API-Led architecture"
+authors:
+ - name: Bobur Umurzokov
+ title: Author
+ url: https://github.com/Boburmirzo
+ image_url: https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/u/14247607
+keywords:
+- API Gateway
+- Apache APISIX
+- API
+- Architecture
+- Use-cases
+- Microservices
+description: This post elaborates on the 10 most common usages of an API Gateway such as Apache APISIX in architecting API-Led Connectivity.
+tags: [Case Studies]
+image: https://static.apiseven.com/2022/10/27/635a40e58b27a.png
+---
+
+> This post elaborates on the **10 most common usages** of an _API Gateway_ such as [Apache APISIX](https://apisix.apache.org/) in architecting [API-Led Connectivity](https://blogs.mulesoft.com/learn-apis/api-led-connectivity/what-is-api-led-connectivity/). We understand different solutions where you can make use of the API Gateway capabilities to design reliable, high-performance, and simple APIs for other developers.
+
+<!--truncate-->
+
+Here is the summary of 10 patterns that uses the API Gateway (but not all):
+
+1. API Resource routing.
+2. API Content-based routing.
+3. API Geo-routing.
+4. API Aggregator.
+5. API Centralized Authentication.
+6. API Format Conversion.
+7. API Observability.
+8. API Caching.
+9. API Fault handling.
+10. Sidecar API Gateway.
+
+## API-Led Architecture
+
+First of all, let’s revise once again these 3 terms like: **API Gateway**, **API-Led architecture**, and **API-Led Connectivity**.
+
+[API Gateway](https://wikitech.wikimedia.org/wiki/API_Gateway) is a _pattern_ formed by adding a layer between the client and the server that acts as a reverse proxy forwarding request from the client to the server. It allows all clients to access the services they want to access with a single API Gateway layer.
+
+[API-led](https://dzone.com/articles/mulesoft-api-led-connectivity-architectural-and-de) is an _architectural approach_ that puts APIs at the heart of communications between applications and the business capabilities they need to access, in order to consistently deliver seamless functionality across all digital channels.
+
+
+
+**API-led connectivity** refers to _the technique_ of using reusable and well-designed APIs to link data and applications which in turn it is based on **API-Led architecture**. It’s _a modern approach_ that looks at the best ways of reusing APIs to boost your innovation and move quickly in the market. At the most basic level, API-led architecture should address things like:
+
+- Securing APIs from unauthorized access and significant security threats.
+- Ensuring that consuming applications can always find the right API endpoint.
+- Throttling and/or limiting the number of calls made to an API to ensure continuous availability.
+- Supporting capabilities such as API design, testing, continuous integration, life cycle management, monitoring, and operations, to name a few.
+- Error handling and preventing error propagation across the stack.
+- Real-time monitoring of APIs with rich analytics and insight.
+- An approach for implementing scalable and flexible business capabilities, for example, in support of microservices architectures.
+
+Let’s describe in subsequent sections each usage of an API Gateway to address common requirements/challenges that arise when adopting API-led architectures.
+
+---
+
+## API resource routing
+
+The first in the list is the **API resource routing** method which uses an API Gateway to route incoming calls based on unique resource identifiers (URIs). Implementing an API gateway as the single entry point to all services means that API consumers only have to be aware of one URL domain. In this way, it becomes the API gateway's responsibility to route the traffic to the corresponding service endpoints and also enforce any applied policies as it is depicted in the below diagram.
+
+
+
+It reduces complexity on the API consumer side because they do not need to track and consume functionality from multiple HTTP endpoints in case there are many services in the system. Also, no need to implement all cross-cutting concerns, such as authentication/authorization, throttling, and rate limiting separately for each service. Most API Gateways like [Apache APISIX](https://apisix.apache.org/docs/apisix/terminology/api-gateway/) has already these core features.
+
+## API content-based routing
+
+Similarly, **API content-based** routing mechanism also uses an API gateway to route calls based on the content of a request (for example, based on the HTTP header or message body) instead of just the URI.
+
+Take a scenario when database sharding is applied in order to distribute the load across multiple database instances. This technique is typically applied when the overall number of records stored is huge and a single instance struggles to manage the load. Instead, records are spread across multiple database instances. Then, you implement multiple services, one per unique datastore, and adopt an API gateway as the only entry point to all services. You could then configure the API gateway to route calls to the corresponding service based on a key obtained either from the HTTP header or the payload.
+
+
+
+In the above diagram, an API gateway is exposing a single `/customers` resource for multiple customer services, each with a different data store.
+
+## API geo-routing
+
+**API geo-routing** solution routes API calls to the nearest API gateway based on where they originate. In order to prevent latency issues and other unforeseen issues that may occur due to distance (for example, a consuming application from Asia calling an API located in North America), API gateways and other service infrastructure have been deployed in multiple regions across the world as needed. For example, using different sub-domains for each API gateway in each region and letting the consuming application determine the nearest gateway based on application logic. Then, an API gateway provides internal load balancing to make sure that incoming requests are distributed across the available instances of a service.
+
+
+
+As you can see in the preceding diagram, it uses a DNS, traffic management service, and an API Gateway to resolve each subdomain against the region’s load balancer and passes the client request further down to the closest API Gateway.
+
+## API aggregator
+
+This technique performs operations (for example, queries) against multiple services and returns the result to the client service with a single `HTTP request/response` call. Instead of having a client application make several calls to multiple APIs, an API aggregator uses an API Gateway to do this on behalf of the consumer on the server side.
+
+For example, consider a mobile app that makes multiple calls to different APIs to show the data for a single screen. In this case, it increases complexity in the client-side code, over-utilization of network resources, and even poor user experience as the application is more exposed to latency issues. API Gateway can accept as input all information required, does request authentication and validation, understands all data structures from all APIs that it interacts with, and is capable of transforming the response payloads so they can be sent back to the mobile app as a uniform payload needed for the consumer.
+
+
+
+## API Centralized Authentication
+
+In this design, an API Gateway acts as a **centralized authentication gateway**. As an authenticator, API Gateway looks for access credentials in the `HTTP header` - for example, a bearer token, and implements business logic that validates those credentials with an IDP, identity provider such as [Okta](https://www.okta.com/), [Cognito](https://aws.amazon.com/cognito/), [Azure Active Directory](https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/services/active-directory/) or [Ory Hydra](https://www.ory.sh/hydra/)) typically using the [OpenID Connect](https://openid.net/connect/) (OIDC) is an authentication protocol based on the [OAuth 2.0](https://oauth.net/2/) and checking whether they have access or not.
+
+
+
+Centralized authentication with the API Gateway can solve many problems and have some benefits as it completely offloads user management from an application and it improves performance by responding quickly to authentication requests received from client applications.
+
+
+
+For example, [Apache APISIX](https://apisix.apache.org/) offers a variety of [plugins](https://apisix.apache.org/docs/apisix/plugins/openid-connect/) to enable different methods of API gateway authentication. We looked at some of the most commonly used in this blog post [Centralized Authentication with Apache APISIX Plugins](https://dev.to/apisix/centralized-authentication-with-apache-apisix-plugins-30fo). You can even enable multiple methods for authentication for the given API.
+
+## API Format Conversion
+
+This refers to having the ability to convert payloads from one format to another over the same transport. For example, from XML/SOAP over HTTPS to JSON over HTTPS and vice versa. API Gateways, by default offer capabilities in support of REST API and some specialized API gateways support, in addition to payload conversions, transport conversions such as converting from Message Queuing Telemetry Transport (MQTT) over TCP (a very popular transport in IoT) to JSON over HTTPS.
+
+
+
+For example, Apache APISIX is able to receive an HTTP request, then transcode it and forwards it to a gRPC service, gets the response, and return it back to the client in HTTP format by means of its [gRPC Transcode](https://apisix.apache.org/docs/apisix/plugins/grpc-transcode/) plug-in.
+
+## API Observability
+
+By now, we know that an API gateway offers a central control point for incoming traffic to a variety of destinations but it can also be a central point for observation as well since it is uniquely qualified to know about all the traffic moving between clients and our service networks. There is always the possibility to instrument the API gateways so observability data (structured logs, metrics, and traces) can be collected in order to use specialized monitoring tools.
+
+
+
+For example, Apache APISIX provides [pre-built connectors](https://apisix.apache.org/docs/apisix/plugins/prometheus/) (plug-ins) that you can easily integrate with external monitoring tools. You can leverage these connectors to ingest log data from your API gateways to further derive useful metrics and gain complete visibility into the usage, you can manage performance, and security of your APIs in your environment. There is also a dedicated post on [how to use these observability plugins](https://medium.com/@ApacheAPISIX/api-observability-with-apache-apisix-plugins-34584dc1ce3a).
+
+## API Caching
+
+**API Caching** is yet another level of caching that is usually implemented inside API Gateway. It can reduce the number of calls made to your endpoint and also improve the latency of requests to your API by caching a response from the upstream. If the API Gateway cache has a fresh copy of the requested resource, it uses that copy to satisfy the request directly instead of making a request to the endpoint. If the cached data is not found, the request travels to the intended upstream services (backend services).
+
+
+
+You can read more about [API Gateway Caching with Apache APISIX](https://medium.com/@ApacheAPISIX/api-gateway-caching-for-asp-net-core-web-api-cf24d0e598fc) in the dedicated blog post.
+
+## API Fault handling
+
+It is critical to handle failures in service-to-service calls gracefully. Also, we want to be sure that any resilience mechanisms we have in place such as error handling code, [circuit breaker](https://dev.to/apisix/implementing-resilient-applications-with-api-gateway-circuit-breaker-ggk), [health checks](https://dev.to/apisix/implementing-resilient-applications-with-api-gateway-health-check-338c), [retry](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/architecture/patterns/retry), fallback, redundant instances, and so on. Modern API Gateways support all the above error-handling features including automatic retries and timeouts.
+
+
+
+For example, APISIX acts as an orchestrator that can use this status report to decide how to manage the traffic, load balance to a healthy node, fail-fast due to some cascading failures or simply alerts you when it notices something goes wrong. API Gateway also ensures that routing and other network-level components work together successfully to deliver a request to the API process. It helps you to detect in the early stage and fix issues for your running application much more easily.
+
+## Sidecar API gateway
+
+**Sidecar** implements an API gateway as a container attached to a service in an independent runtime, such as [Kubernetes](https://kubernetes.io/). Sidecar is a pattern that corresponds to a [sidecar](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sidecar) attached to a motorcycle, similarly, it is attached to a parent application and provides supporting features for the application. The sidecar also shares the same lifecycle as the parent application, is created and retired alongside the parent, and introduces additional features such as monitoring, logging, configuration, and networking services. The benefits of adopting this pattern are that each service runtime can configure its own API gateway in the best way. Because the requirement to enable the API gateway functionalities and setups can vary from service to service. At the same time, it separates concerns if an issue occurs in the shared API gateway infrastructure then all services will not be impacted.
Review Comment:
Right, it is too much and maybe I might dedicated blog post for sidecar now I replaced with API Versioning and promoted your content at the same time:))
https://blog.frankel.ch/evolve-apis/
--
This is an automated message from the Apache Git Service.
To respond to the message, please log on to GitHub and use the
URL above to go to the specific comment.
To unsubscribe, e-mail: notifications-unsubscribe@apisix.apache.org
For queries about this service, please contact Infrastructure at:
users@infra.apache.org
[GitHub] [apisix-website] netlify[bot] commented on pull request #1380: docs: Add new blog post 10 usecases of an API Gateway
Posted by GitBox <gi...@apache.org>.
netlify[bot] commented on PR #1380:
URL: https://github.com/apache/apisix-website/pull/1380#issuecomment-1293200806
### <span aria-hidden="true">👷</span> Deploy Preview for *apache-apisix* processing.
| Name | Link |
|---------------------------------|------------------------|
|<span aria-hidden="true">🔨</span> Latest commit | fb2fed17dc542b2bf46b34c6ac909dc395a5936f |
|<span aria-hidden="true">🔍</span> Latest deploy log | https://app.netlify.com/sites/apache-apisix/deploys/635a464f3d6ad9000970fe60 |
--
This is an automated message from the Apache Git Service.
To respond to the message, please log on to GitHub and use the
URL above to go to the specific comment.
To unsubscribe, e-mail: notifications-unsubscribe@apisix.apache.org
For queries about this service, please contact Infrastructure at:
users@infra.apache.org
[GitHub] [apisix-website] Boburmirzo commented on a diff in pull request #1380: docs: Add new blog post 10 usecases of an API Gateway
Posted by GitBox <gi...@apache.org>.
Boburmirzo commented on code in PR #1380:
URL: https://github.com/apache/apisix-website/pull/1380#discussion_r1006708923
##########
blog/en/blog/2022/10/27/ten-use-cases-api-gateway.md:
##########
@@ -0,0 +1,180 @@
+---
Review Comment:
Yes, styles are going to be changed.
--
This is an automated message from the Apache Git Service.
To respond to the message, please log on to GitHub and use the
URL above to go to the specific comment.
To unsubscribe, e-mail: notifications-unsubscribe@apisix.apache.org
For queries about this service, please contact Infrastructure at:
users@infra.apache.org
[GitHub] [apisix-website] Boburmirzo commented on a diff in pull request #1380: docs: Add new blog post 10 usecases of an API Gateway
Posted by GitBox <gi...@apache.org>.
Boburmirzo commented on code in PR #1380:
URL: https://github.com/apache/apisix-website/pull/1380#discussion_r1006777892
##########
blog/en/blog/2022/10/27/ten-use-cases-api-gateway.md:
##########
@@ -0,0 +1,180 @@
+---
+title: "10 most use cases of an API Gateway in API-Led architecture"
+authors:
+ - name: Bobur Umurzokov
+ title: Author
+ url: https://github.com/Boburmirzo
+ image_url: https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/u/14247607
+keywords:
+- API Gateway
+- Apache APISIX
+- API
+- Architecture
+- Use-cases
+- Microservices
+description: This post elaborates on the 10 most common usages of an API Gateway such as Apache APISIX in architecting API-Led Connectivity.
+tags: [Case Studies]
+image: https://static.apiseven.com/2022/10/27/635a40e58b27a.png
+---
+
+> This post elaborates on the **10 most common usages** of an _API Gateway_ such as [Apache APISIX](https://apisix.apache.org/) in architecting [API-Led Connectivity](https://blogs.mulesoft.com/learn-apis/api-led-connectivity/what-is-api-led-connectivity/). We understand different solutions where you can make use of the API Gateway capabilities to design reliable, high-performance, and simple APIs for other developers.
+
+<!--truncate-->
+
+Here is the summary of 10 patterns that uses the API Gateway (but not all):
+
+1. API Resource routing.
+2. API Content-based routing.
+3. API Geo-routing.
+4. API Aggregator.
+5. API Centralized Authentication.
+6. API Format Conversion.
+7. API Observability.
+8. API Caching.
+9. API Fault handling.
+10. Sidecar API Gateway.
+
+## API-Led Architecture
+
+First of all, let’s revise once again these 3 terms like: **API Gateway**, **API-Led architecture**, and **API-Led Connectivity**.
+
+[API Gateway](https://wikitech.wikimedia.org/wiki/API_Gateway) is a _pattern_ formed by adding a layer between the client and the server that acts as a reverse proxy forwarding request from the client to the server. It allows all clients to access the services they want to access with a single API Gateway layer.
+
+[API-led](https://dzone.com/articles/mulesoft-api-led-connectivity-architectural-and-de) is an _architectural approach_ that puts APIs at the heart of communications between applications and the business capabilities they need to access, in order to consistently deliver seamless functionality across all digital channels.
+
+
+
+**API-led connectivity** refers to _the technique_ of using reusable and well-designed APIs to link data and applications which in turn it is based on **API-Led architecture**. It’s _a modern approach_ that looks at the best ways of reusing APIs to boost your innovation and move quickly in the market. At the most basic level, API-led architecture should address things like:
+
+- Securing APIs from unauthorized access and significant security threats.
+- Ensuring that consuming applications can always find the right API endpoint.
+- Throttling and/or limiting the number of calls made to an API to ensure continuous availability.
+- Supporting capabilities such as API design, testing, continuous integration, life cycle management, monitoring, and operations, to name a few.
+- Error handling and preventing error propagation across the stack.
+- Real-time monitoring of APIs with rich analytics and insight.
+- An approach for implementing scalable and flexible business capabilities, for example, in support of microservices architectures.
+
+Let’s describe in subsequent sections each usage of an API Gateway to address common requirements/challenges that arise when adopting API-led architectures.
+
+---
+
+## API resource routing
+
+The first in the list is the **API resource routing** method which uses an API Gateway to route incoming calls based on unique resource identifiers (URIs). Implementing an API gateway as the single entry point to all services means that API consumers only have to be aware of one URL domain. In this way, it becomes the API gateway's responsibility to route the traffic to the corresponding service endpoints and also enforce any applied policies as it is depicted in the below diagram.
+
+
+
+It reduces complexity on the API consumer side because they do not need to track and consume functionality from multiple HTTP endpoints in case there are many services in the system. Also, no need to implement all cross-cutting concerns, such as authentication/authorization, throttling, and rate limiting separately for each service. Most API Gateways like [Apache APISIX](https://apisix.apache.org/docs/apisix/terminology/api-gateway/) has already these core features.
+
+## API content-based routing
+
+Similarly, **API content-based** routing mechanism also uses an API gateway to route calls based on the content of a request (for example, based on the HTTP header or message body) instead of just the URI.
+
+Take a scenario when database sharding is applied in order to distribute the load across multiple database instances. This technique is typically applied when the overall number of records stored is huge and a single instance struggles to manage the load. Instead, records are spread across multiple database instances. Then, you implement multiple services, one per unique datastore, and adopt an API gateway as the only entry point to all services. You could then configure the API gateway to route calls to the corresponding service based on a key obtained either from the HTTP header or the payload.
+
+
+
+In the above diagram, an API gateway is exposing a single `/customers` resource for multiple customer services, each with a different data store.
+
+## API geo-routing
+
+**API geo-routing** solution routes API calls to the nearest API gateway based on where they originate. In order to prevent latency issues and other unforeseen issues that may occur due to distance (for example, a consuming application from Asia calling an API located in North America), API gateways and other service infrastructure have been deployed in multiple regions across the world as needed. For example, using different sub-domains for each API gateway in each region and letting the consuming application determine the nearest gateway based on application logic. Then, an API gateway provides internal load balancing to make sure that incoming requests are distributed across the available instances of a service.
+
+
+
+As you can see in the preceding diagram, it uses a DNS, traffic management service, and an API Gateway to resolve each subdomain against the region’s load balancer and passes the client request further down to the closest API Gateway.
+
+## API aggregator
+
+This technique performs operations (for example, queries) against multiple services and returns the result to the client service with a single `HTTP request/response` call. Instead of having a client application make several calls to multiple APIs, an API aggregator uses an API Gateway to do this on behalf of the consumer on the server side.
+
+For example, consider a mobile app that makes multiple calls to different APIs to show the data for a single screen. In this case, it increases complexity in the client-side code, over-utilization of network resources, and even poor user experience as the application is more exposed to latency issues. API Gateway can accept as input all information required, does request authentication and validation, understands all data structures from all APIs that it interacts with, and is capable of transforming the response payloads so they can be sent back to the mobile app as a uniform payload needed for the consumer.
+
+
+
+## API Centralized Authentication
+
+In this design, an API Gateway acts as a **centralized authentication gateway**. As an authenticator, API Gateway looks for access credentials in the `HTTP header` - for example, a bearer token, and implements business logic that validates those credentials with an IDP, identity provider such as [Okta](https://www.okta.com/), [Cognito](https://aws.amazon.com/cognito/), [Azure Active Directory](https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/services/active-directory/) or [Ory Hydra](https://www.ory.sh/hydra/)) typically using the [OpenID Connect](https://openid.net/connect/) (OIDC) is an authentication protocol based on the [OAuth 2.0](https://oauth.net/2/) and checking whether they have access or not.
+
+
+
+Centralized authentication with the API Gateway can solve many problems and have some benefits as it completely offloads user management from an application and it improves performance by responding quickly to authentication requests received from client applications.
+
+
+
+For example, [Apache APISIX](https://apisix.apache.org/) offers a variety of [plugins](https://apisix.apache.org/docs/apisix/plugins/openid-connect/) to enable different methods of API gateway authentication. We looked at some of the most commonly used in this blog post [Centralized Authentication with Apache APISIX Plugins](https://dev.to/apisix/centralized-authentication-with-apache-apisix-plugins-30fo). You can even enable multiple methods for authentication for the given API.
+
+## API Format Conversion
+
+This refers to having the ability to convert payloads from one format to another over the same transport. For example, from XML/SOAP over HTTPS to JSON over HTTPS and vice versa. API Gateways, by default offer capabilities in support of REST API and some specialized API gateways support, in addition to payload conversions, transport conversions such as converting from Message Queuing Telemetry Transport (MQTT) over TCP (a very popular transport in IoT) to JSON over HTTPS.
+
+
+
+For example, Apache APISIX is able to receive an HTTP request, then transcode it and forwards it to a gRPC service, gets the response, and return it back to the client in HTTP format by means of its [gRPC Transcode](https://apisix.apache.org/docs/apisix/plugins/grpc-transcode/) plug-in.
+
+## API Observability
+
+By now, we know that an API gateway offers a central control point for incoming traffic to a variety of destinations but it can also be a central point for observation as well since it is uniquely qualified to know about all the traffic moving between clients and our service networks. There is always the possibility to instrument the API gateways so observability data (structured logs, metrics, and traces) can be collected in order to use specialized monitoring tools.
+
+
+
+For example, Apache APISIX provides [pre-built connectors](https://apisix.apache.org/docs/apisix/plugins/prometheus/) (plug-ins) that you can easily integrate with external monitoring tools. You can leverage these connectors to ingest log data from your API gateways to further derive useful metrics and gain complete visibility into the usage, you can manage performance, and security of your APIs in your environment. There is also a dedicated post on [how to use these observability plugins](https://medium.com/@ApacheAPISIX/api-observability-with-apache-apisix-plugins-34584dc1ce3a).
+
+## API Caching
+
+**API Caching** is yet another level of caching that is usually implemented inside API Gateway. It can reduce the number of calls made to your endpoint and also improve the latency of requests to your API by caching a response from the upstream. If the API Gateway cache has a fresh copy of the requested resource, it uses that copy to satisfy the request directly instead of making a request to the endpoint. If the cached data is not found, the request travels to the intended upstream services (backend services).
+
+
+
+You can read more about [API Gateway Caching with Apache APISIX](https://medium.com/@ApacheAPISIX/api-gateway-caching-for-asp-net-core-web-api-cf24d0e598fc) in the dedicated blog post.
+
+## API Fault handling
+
+It is critical to handle failures in service-to-service calls gracefully. Also, we want to be sure that any resilience mechanisms we have in place such as error handling code, [circuit breaker](https://dev.to/apisix/implementing-resilient-applications-with-api-gateway-circuit-breaker-ggk), [health checks](https://dev.to/apisix/implementing-resilient-applications-with-api-gateway-health-check-338c), [retry](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/architecture/patterns/retry), fallback, redundant instances, and so on. Modern API Gateways support all the above error-handling features including automatic retries and timeouts.
Review Comment:
Mentioned
--
This is an automated message from the Apache Git Service.
To respond to the message, please log on to GitHub and use the
URL above to go to the specific comment.
To unsubscribe, e-mail: notifications-unsubscribe@apisix.apache.org
For queries about this service, please contact Infrastructure at:
users@infra.apache.org
[GitHub] [apisix-website] Boburmirzo commented on a diff in pull request #1380: docs: Add new blog post 10 usecases of an API Gateway
Posted by GitBox <gi...@apache.org>.
Boburmirzo commented on code in PR #1380:
URL: https://github.com/apache/apisix-website/pull/1380#discussion_r1008806525
##########
blog/en/blog/2022/10/27/ten-use-cases-api-gateway.md:
##########
@@ -0,0 +1,180 @@
+---
Review Comment:
@nfrankel and @SylviaBABY now I updated all pictures that had different styles and we are good to go.
--
This is an automated message from the Apache Git Service.
To respond to the message, please log on to GitHub and use the
URL above to go to the specific comment.
To unsubscribe, e-mail: notifications-unsubscribe@apisix.apache.org
For queries about this service, please contact Infrastructure at:
users@infra.apache.org
[GitHub] [apisix-website] juzhiyuan merged pull request #1380: docs: Add new blog post 10 usecases of an API Gateway
Posted by GitBox <gi...@apache.org>.
juzhiyuan merged PR #1380:
URL: https://github.com/apache/apisix-website/pull/1380
--
This is an automated message from the Apache Git Service.
To respond to the message, please log on to GitHub and use the
URL above to go to the specific comment.
To unsubscribe, e-mail: notifications-unsubscribe@apisix.apache.org
For queries about this service, please contact Infrastructure at:
users@infra.apache.org
[GitHub] [apisix-website] Boburmirzo commented on pull request #1380: docs: Add new blog post 10 usecases of an API Gateway
Posted by GitBox <gi...@apache.org>.
Boburmirzo commented on PR #1380:
URL: https://github.com/apache/apisix-website/pull/1380#issuecomment-1296688437
@SylviaBABY and @hf400159 I need one more round of approvals, please:)
Merged the master branch to get fixed build failure.
--
This is an automated message from the Apache Git Service.
To respond to the message, please log on to GitHub and use the
URL above to go to the specific comment.
To unsubscribe, e-mail: notifications-unsubscribe@apisix.apache.org
For queries about this service, please contact Infrastructure at:
users@infra.apache.org