You are viewing a plain text version of this content. The canonical link for it is here.
Posted to notifications@apisix.apache.org by sy...@apache.org on 2022/09/13 00:53:47 UTC
[apisix-website] branch master updated: docs: add new blog post on using APISIX Ingress controller (#1312)
This is an automated email from the ASF dual-hosted git repository.
sylviasu pushed a commit to branch master
in repository https://gitbox.apache.org/repos/asf/apisix-website.git
The following commit(s) were added to refs/heads/master by this push:
new 9c5e0d8b9e6 docs: add new blog post on using APISIX Ingress controller (#1312)
9c5e0d8b9e6 is described below
commit 9c5e0d8b9e6f0b1411a86c3feb11eea20ae4e15d
Author: Navendu Pottekkat <na...@gmail.com>
AuthorDate: Tue Sep 13 06:23:42 2022 +0530
docs: add new blog post on using APISIX Ingress controller (#1312)
* docs: add new blog post on using APISIX Ingress controller
* apply suggestions from review
* fix canonical URL
Co-authored-by: 琚致远 <ju...@apache.org>
Co-authored-by: Fei Han <97...@users.noreply.github.com>
---
.../2022/09/09/kubernetes-ingress-with-apisix.md | 246 +++++++++++++++++++++
1 file changed, 246 insertions(+)
diff --git a/blog/en/blog/2022/09/09/kubernetes-ingress-with-apisix.md b/blog/en/blog/2022/09/09/kubernetes-ingress-with-apisix.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..65134b08be4
--- /dev/null
+++ b/blog/en/blog/2022/09/09/kubernetes-ingress-with-apisix.md
@@ -0,0 +1,246 @@
+---
+title: "Hands-On: Set Up Ingress on Kubernetes With Apache APISIX Ingress Controller"
+authors:
+ - name: Navendu Pottekkat
+ title: Author
+ url: https://github.com/navendu-pottekkat
+ image_url: https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/u/49474499
+keywords:
+- Ingress controller
+- Kubernetes ingress
+- Apache APISIX
+- APISIX ingress controller
+description: A tutorial on using Ingress in your Kubernetes cluster with Apache APISIX.
+tags: [Ingress, Kubernetes]
+image: https://static.apiseven.com/2022/09/05/6315bd71d6846.png
+---
+
+> A tutorial on using Ingress in your Kubernetes cluster with Apache APISIX.
+
+<!--truncate-->
+
+<head>
+ <link rel="canonical" href="https://navendu.me/posts/hands-on-set-up-ingress-on-kubernetes-with-apache-apisix-ingress-controller/" />
+</head>
+
+In Kubernetes, [Ingress](https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/services-networking/ingress/) is a native object that allows you to access your services externally by defining a set of rules. Using a reverse proxy, an [Ingress controller](https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/services-networking/ingress-controllers/) implements these defined rules and routes external traffic to your services.
+
+
+
+[Apache APISIX](https://apisix.apache.org/) is an open source API gateway (a souped-up reverse proxy) that provides features like authentication, traffic routing, load balancing, canary releases, monitoring, and more. APISIX also supports custom Plugins and integrates with popular open source projects like [Apache SkyWalking](https://apisix.apache.org/docs/apisix/next/plugins/skywalking/) and [Prometheus](https://apisix.apache.org/docs/apisix/next/plugins/prometheus/). To learn more abou [...]
+
+The [Apache APISIX Ingress controller](https://apisix.apache.org/docs/ingress-controller/next/getting-started/) sits between the defined Ingress rules and the APISIX API gateway. It configures the proxy to route traffic based on the defined rules.
+
+
+
+This hands-on tutorial will teach you how to set up the APISIX Ingress controller on your Kubernetes cluster and route traffic to your services.
+
+Before you move on, make sure you:
+
+1. Have access to a Kubernetes cluster. This tutorial uses [minikube](https://minikube.sigs.k8s.io/) for creating a cluster.
+2. Install and configure `kubectl` to communicate with your cluster.
+3. [Install Helm](https://helm.sh/docs/intro/install/) to deploy the APISIX Ingress controller.
+
+## Deploying a Sample Application
+
+We will use a sample HTTP server application ([bare-minimum-api](https://github.com/navendu-pottekkat/bare-minimum-api)) to demonstrate the working of the Ingress controller.
+
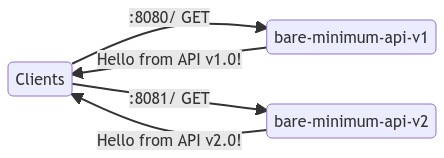
+While running the application, you can set a "version" and a port to listen to. For this example, we will create two "versions" of this application which will return different responses as shown below:
+
+
+
+You can deploy the application on your Kubernetes cluster by running:
+
+```shell
+kubectl run bare-minimum-api-v1 --image navendup/bare-minimum-api --port 8080 -- 8080 v1.0
+kubectl expose pod bare-minimum-api-v1 --port 8080
+```
+
+To test the application outside the cluster, you can use `port-forward`:
+
+```shell
+kubectl port-forward bare-minimum-api-v1 8080:8080
+```
+
+Now, if you open up a new terminal window and run:
+
+```shell
+curl http://127.0.0.1:8080
+```
+
+You will get back a response from the application:
+
+```shell {title="output"}
+Hello from API v1.0!
+```
+
+Similarly, you can deploy another "version" of the application by running:
+
+```shell
+kubectl run bare-minimum-api-v2 --image navendup/bare-minimum-api --port 8081 -- 8081 v2.0
+kubectl expose pod bare-minimum-api-v2 --port 8081
+```
+
+Now, we can deploy APISIX Ingress and expose these applications to external traffic.
+
+## Deploying APISIX Ingress
+
+APISIX and APISIX Ingress controller can be installed using Helm:
+
+```shell
+helm repo add apisix https://charts.apiseven.com
+helm repo add bitnami https://charts.bitnami.com/bitnami
+helm repo update
+kubectl create ns ingress-apisix
+helm install apisix apisix/apisix \
+ --set gateway.type=NodePort \
+ --set ingress-controller.enabled=true \
+ --namespace ingress-apisix \
+ --set ingress-controller.config.apisix.serviceNamespace=ingress-apisix
+kubectl get pods --namespace ingress-apisix
+```
+
+:::note
+
+We are using `NodePort` as the Gateway service type. You can also set it to `LoadBalancer` if your cluster has one.
+
+:::
+
+Helm will create five resources in your cluster:
+
+1. `apisix-gateway`: The data plane that handles external traffic.
+2. `apisix-admin`: Control plane that processes configuration changes.
+3. `apisix-ingress-controller`: The ingress controller.
+4. `apisix-etcd` and 5. `apisix-etcd headless`: To store configuration and handle internal communication.
+
+Once all the pods and services are running, you can test APISIX by accessing the Admin API:
+
+```shell
+kubectl exec -n ingress-apisix deploy/apisix -- curl -s http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes -H 'X-API-Key: edd1c9f034335f136f87ad84b625c8f1'
+```
+
+If you get a response similar to the one shown below, APISIX is up and running:
+
+```json {title="output"}
+{
+ "action": "get",
+ "node": {
+ "key": "/apisix/routes",
+ "dir": true,
+ "nodes": []
+ },
+ "count": 0
+}
+```
+
+## Configuring APISIX Ingress
+
+Once you have verified that the APISIX gateway and Ingress controller is running, you can create [Routes](https://apisix.apache.org/docs/apisix/terminology/route/) to expose the deployed application to external traffic.
+
+This will route traffic between the two application versions based on the client request:
+
+
+
+
+
+To configure Routes, APISIX comes with declarative and easy-to-use [custom resource](https://apisix.apache.org/docs/ingress-controller/next/references/apisix_route_v2beta3/):
+
+```yaml {title="apisix-ingress-manifest.yaml"}
+apiVersion: apisix.apache.org/v2beta3
+kind: ApisixRoute
+metadata:
+ name: api-routes
+spec:
+ http:
+ - name: route-1
+ match:
+ hosts:
+ - local.navendu.me
+ paths:
+ - /v1
+ backends:
+ - serviceName: bare-minimum-api-v1
+ servicePort: 8080
+ - name: route-2
+ match:
+ hosts:
+ - local.navendu.me
+ paths:
+ - /v2
+ backends:
+ - serviceName: bare-minimum-api-v2
+ servicePort: 8081
+```
+
+The APISIX Ingress controller converts this resource to an APISIX gateway configuration.
+
+APISIX also supports configuration using native [Kubernetes Ingress resource](https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/services-networking/ingress/#the-ingress-resource):
+
+```yaml {title="kubernetes-ingress-manifest.yaml"}
+apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
+kind: Ingress
+metadata:
+ name: api-routes
+spec:
+ ingressClassName: apisix
+ rules:
+ - host: local.navendu.me
+ http:
+ paths:
+ - backend:
+ service:
+ name: bare-minimum-api-v1
+ port:
+ number: 8080
+ path: /v1
+ pathType: Exact
+ - backend:
+ service:
+ name: bare-minimum-api-v2
+ port:
+ number: 8081
+ path: /v2
+ pathType: Exact
+```
+
+You can use either to configure APISIX but I prefer the easier APISIX custom resource. We can apply this manifest file to our cluster to create Routes in APISIX:
+
+```shell
+kubectl apply -f apisix-ingress-manifest.yaml
+```
+
+If the Ingress controller is configured correctly, you should see a response indicating that APISIX API gateway has been configured:
+
+```shell {title="output"}
+apisixroute.apisix.apache.org/api-routes created
+```
+
+Now, let's test these Routes.
+
+## Testing the Created Routes
+
+If you were following along using minikube and `NodePort`, you should be able to access APISIX through the Node IP of the service `apisix-gateway`. If the Node IP is not reachable directly (if you are on Darwin, Windows, or WSL), you can create a tunnel to access the service on your machine:
+
+```shell
+minikube service apisix-gateway --url -n ingress-apisix
+```
+
+This will show the URL with which you can access the `apisix-gateway` service.
+
+You can send a `GET` request to this URL and it would be Routed to the appropriate service:
+
+```shell
+curl http://127.0.0.1:51538/v2 -H 'host:local.navendu.me'
+```
+
+```shell {title="output"}
+Hello from API v2.0!
+```
+
+Now you have APISIX routing traffic to your applications! You can try the two configured Routes and see APISIX routing the requests to the appropriate application.
+
+## What's Next?
+
+In this tutorial, you learned to set up APISIX Ingress on your cluster. We tested it out by configuring basic Routes to a sample application.
+
+With APISIX gateway and the Ingress controller, you can also configure Upstreams, Plugins, mTLS, and monitoring. To learn more about APISIX and how you can use these features, visit [apisix.apache.org](https://apisix.apache.org).