You are viewing a plain text version of this content. The canonical link for it is here.
Posted to notifications@apisix.apache.org by GitBox <gi...@apache.org> on 2022/10/19 08:17:29 UTC
[GitHub] [apisix-website] yzeng25 commented on a diff in pull request #1365: docs: Add new blog post APISIX deployment on Scaleway cloud
yzeng25 commented on code in PR #1365:
URL: https://github.com/apache/apisix-website/pull/1365#discussion_r999097395
##########
blog/en/blog/2022/10/19/deploy-apisix-on-scaleway-cloud.md:
##########
@@ -0,0 +1,293 @@
+---
+title: "Deploy and Run Apache APISIX on Scaleway Cloud"
+authors:
+ - name: Bobur Umurzokov
+ title: Author
+ url: https://github.com/Boburmirzo
+ image_url: https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/u/14247607
+keywords:
+- API Gateway
+- Apache APISIX
+- API
+- Scaleway
+- Cloud
+- Deployment
+description: In this post, you will learn how easily deploy and run both Apache APISIX API Gateway and Ingress Controller on Scaleway Cloud Managed Kubernetes to efficiently manage, protect and observe your APIs in the cloud.
+tags: [Case Studies]
+---
+
+> In this post, you will learn how easily deploy and run both [Apache APISIX API Gateway](https://apisix.apache.org/docs/apisix/getting-started/) and [Ingress Controller](https://apisix.apache.org/docs/ingress-controller/getting-started/) on [Scaleway Cloud Managed Kubernetes](https://www.scaleway.com/en/docs/) to efficiently manage, protect and observe your APIs in the cloud.
+
+<!--truncate-->
+
+
+
+Today, more and more developers are looking at how they can bring their existing applications to the cloud—or at how to build new cloud-native applications. Many organizations have significant investments in the migration of mission-critical applications running on-premises to fully supported environments to run these apps in the cloud. This post explains how to deploy and run both [Apache APISIX API Gateway](https://apisix.apache.org/docs/apisix/getting-started/) and [Ingress Controller](https://apisix.apache.org/docs/ingress-controller/getting-started/) on [Scaleway Cloud Managed Kubernetes](https://www.scaleway.com/en/docs/)
+
+Firstly, let’s understand what is Apache APISIX and Scaleway, how you can leverage both solutions to serve your needs. Or you can just skip the intro sections and start with the tutorial.
+
+## What’s Apache APISIX?
+
+[Apache APISIX](https://apisix.apache.org/) is an open-source **API Gateway** under [Apache Software Foundation](https://www.apache.org/) that is lightweight, independently deployable, and scalable that can run anywhere that allows developers to manage API endpoints. You can also leverage APISIX as [Kubernetes Ingress Controller](url) to deliver high performance and get the benefits of stateful load balancing, traffic split, hot reloading, and expansion capabilities by means of its offered diverse plug-ins to satisfy your specific needs. You can read more about the use cases and features offered by Apache APISIX in the [documentation](https://apisix.apache.org/docs/apisix/getting-started/).
+
+
+
+It is also possible to install Apache APISIX by [different methods](https://apisix.apache.org/docs/apisix/installation-guide/) ([Docker](https://www.docker.com/), [Helm](https://helm.sh/), or [RPM](https://rpm.org/)) and run it in the various public cloud providers because of its [cloud-native](https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/dotnet/architecture/cloud-native/definition) behavior.
+
+## What is Scaleway?
+
+[Scaleway](https://www.scaleway.com/en/) is a cloud provider with a variety of services. The public cloud Scaleway elements offer all the important components of a general cloud provider such as [serverless](https://www.scaleway.com/en/serverless-functions/), [containers](https://www.scaleway.com/en/kubernetes-kapsule/), [storage & database](https://www.scaleway.com/en/database/), [virtual machines](https://www.scaleway.com/en/virtual-instances/), [networking](https://www.scaleway.com/en/all-products/#:~:text=Learn%20more-,Network,-Private%20Networks), [IoT hub](https://www.scaleway.com/en/iot-hub/), and many more. You can easily build, deploy and scale your applications in the flexible price model and cost-efficiently.
+
+
+
+Scaleway is the most complete cloud ecosystem trusted by 25000+ businesses in the EU market. It is also playing an active role in improving the open-source ecosystem which already includes many well-known open-source projects such as [NodeJS](https://nodejs.org/en/), [CentOS](https://www.centos.org/), [OpenSuse](https://www.opensuse.org/), and others. You might also want to learn about [the Scaleway Open Source Program here](https://www.scaleway.com/en/about-us/open-source-program/).
+
+## Apache APISIX as an API Management solution in the Scaleway Cloud
+
+Apache APISIX is also a part of this cloud computing partnership program as it is a community project. The main purpose of being a part of the program is to give customers of Scaleway prospect to accelerate their business with an API-first approach by ready-to-use open-source API management solution for building, managing, securing, and observing all internal and external APIs.
+
+We found out that currently, Scaleway does not provide any API management and analysis software in their cloud. As a result, we decided to become partners to connect with thousands of developers from all over the world to get answers and share knowledge, invest in our communities, and give them full control of services with the cloud tools to do what they love. For example, similar to well-known cloud vendors offering API Management solutions like [AWS API Gateway](https://aws.amazon.com/api-gateway/), [Azure API Management](https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/products/api-management/#overview), or [Google Cloud Apigee](https://cloud.google.com/apigee), you can effortlessly get the benefit of APISIX to manage the full API life cycle.
+
+With a small background knowledge of Apache APISIX and Scaleway Cloud, we can jump in to get started guide to bring APISIX and run it with Scaleway’s Kubernetes [Kapsule](https://www.scaleway.com/en/docs/compute/kubernetes/concepts/#kubernetes-kapsule) or [Kosmos](https://www.scaleway.com/en/docs/compute/kubernetes/concepts/#kubernetes-kosmos).
+
+> **Note:** _Kubernetes Kapsule and Kosmos_ are two different cluster types that provide a managed environment to create, configure and run a cluster of preconfigured machines for containerized applications. This allows you to create Kubernetes clusters without the complexity of managing the infrastructure.
+
+## Prerequisites
+
+- For local host environment, you might need to install [Kubectl](https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/tools/) and [Helm](https://helm.sh/docs/intro/install/#from-the-helm-project). It is required to connect to the Kubernetes's cluster.
+- You have an account and are logged into the [Scaleway console](https://console.scaleway.com/).
+- You need create a Kubernetes cluster using the Scaleway Cloud by simply following the [Scaleway’s Kubernetes Quickstart](https://www.scaleway.com/en/docs/compute/kubernetes/quickstart/) guide. You can use the [comprehensive documentation](https://www.scaleway.com/en/docs/) to help you go with console.
+
+## Deploy Apache APISIX and Ingress Controller
+
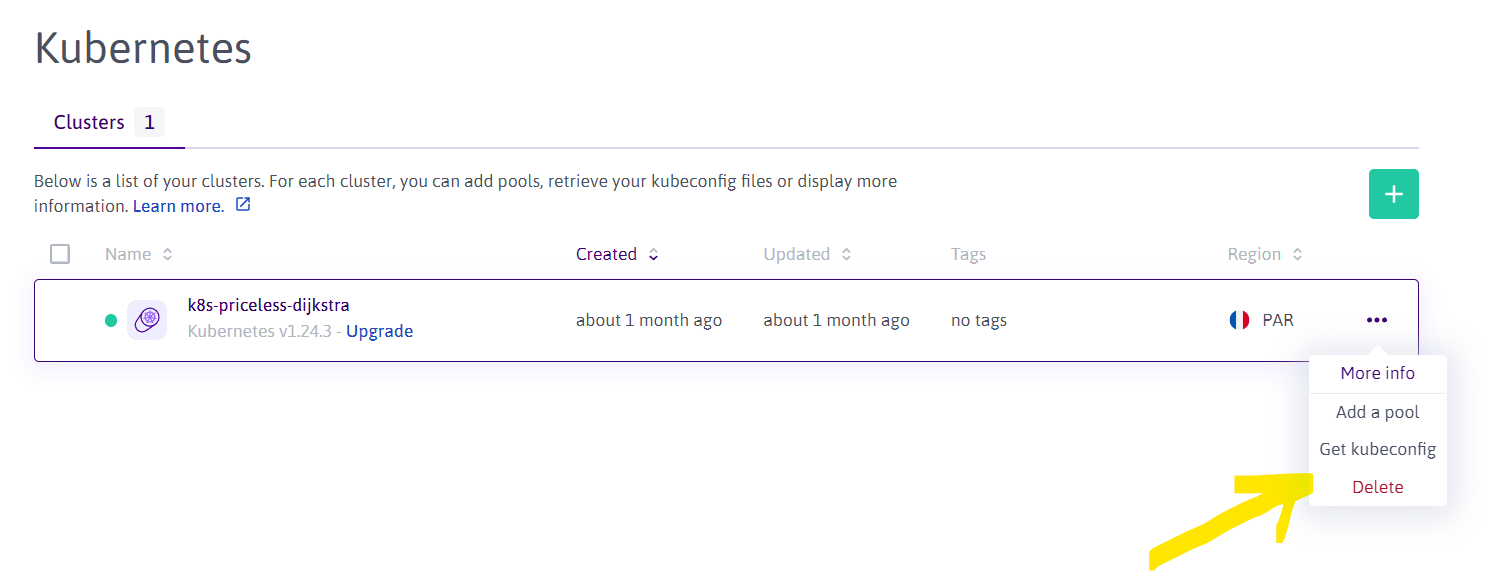
+At this point, I can assume that you created a Kubernetes cluster type of **Kapsule**. Then, you need to open the **Scaleway console**, navigate to the **Kubernetes cluster** you created and download the cluster configuration file `kubeconfig` from the **Kubernetes cluster** and copy it to the local computer's `~/.kube/config` (the default path of kubectl).
+
+> Note: If you have configured the KUBECONFIG environment variable before, `kubectl` will load the KUBECONFIG environment variable first instead of ~/.kube/config. Please note when using.
+
+
+
+### Connect to a cluster with kubectl
+
+Once your cluster is created and the `.kubeconfig` file is downloaded, you can use this with `kubectl`, the Kubernetes command line tool, allowing you to run commands against your Kubernetes clusters. You can use kubectl from a terminal on your local computer to deploy applications, inspect and manage cluster resources, and view logs. See how to [connect to a cluster with kubectl](https://www.scaleway.com/en/docs/compute/kubernetes/how-to/connect-cluster-kubectl/) for more info.
+
+Below you can find two kinds of deployment command examples, one for deploying APISIX and another for Ingress Controller.
+
+### Deploy and run APISIX
+
+To install APISIX via Helm, run:
+
+``` shell
+$ helm repo add apisix https://charts.apiseven.com
+$ helm repo add bitnami https://charts.bitnami.com/bitnami
+$ helm repo update
+$ helm install apisix apisix/apisix --create-namespace --namespace apisix --set gateway.type=LoadBalancer
+```
+
+As an output, you will get the following with the notes:
+
+``` shell
+NAME: apisix
+LAST DEPLOYED: Thu Sep 15 01:14:12 2022
+NAMESPACE: apisix
+STATUS: deployed
+REVISION: 1
+TEST SUITE: None
+NOTES:
+1. Get the application URL by running these commands:
+ NOTE: It may take a few minutes for the LoadBalancer IP to be available.
+ You can watch the status of by running 'kubectl get --namespace apisix svc -w apisix-gateway'
+ export SERVICE_IP=$(kubectl get svc --namespace apisix apisix-gateway --template "{{ range (index .status.loadBalancer.ingress 0) }}{{.}}{{ end }}")
+ echo http://$SERVICE_IP:80
+```
+
+As it is mentioned in the notes, you should run the blow commands to get application IP/URL address:
+
+``` shell
+$ export SERVICE_IP=$(kubectl get svc --namespace apisix apisix-gateway --template "{{ range (index .status.loadBalancer.ingress 0) }}{{.}}{{ end }}")
+$ echo http://$SERVICE_IP:80
+
+http://51.159.10.6:80
+```
+
+You can check anytime the deployment status of APISIX:
+
+``` shell
+$ kubectl get pods -n apisix # All resources are ready
+
+NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
+apisix-656ff547f4-vvcdg 1/1 Running 0 3m9s
+apisix-etcd-0 1/1 Running 0 3m9s
+apisix-etcd-1 1/1 Running 0 3m9s
+apisix-etcd-2 1/1 Running 0 3m9s
+
+$ kubectl get service -n apisix
+
+NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
+apisix-admin ClusterIP 10.33.189.212 <none> 9180/TCP 3m29s
+apisix-etcd ClusterIP 10.43.213.105 <none> 2379/TCP,2380/TCP 3m29s
+apisix-etcd-headless ClusterIP None <none> 2379/TCP,2380/TCP 3m29s
+apisix-gateway LoadBalancer 10.35.46.143 51.159.10.6 80:30345/TCP 3m29s
+
+```
+
+After we make sure that APISIX is upon and running, we can verify it by creating a sample [Upstream](https://apisix.apache.org/docs/apisix/terminology/upstream/) (which targets an external mock service such as `httpbin.org`) and a [Route](https://apisix.apache.org/docs/apisix/terminology/route/).
+
+First, let's apply some changes to our Kubernetes manifest file to have APISIX pod access to the external service (`httpbin.org`). To do so, you can run the following command:
+
+``` shell
+$ kubectl apply -f - <<EOF
+kind: Service
+apiVersion: v1
+metadata:
+ name: httpbin-external
+spec:
+ type: ExternalName
+ externalName: httpbin.org
+EOF
+```
+
+Next, we can create our first test route with an upstream (backend service that is pointing to `httpbin.org`).
+
+> You need to replace `APISIX_POD` with the name of APISIX's pod.
+
+``` shell
+kubectl exec -it ${APISIX_POD} -n apisix -- curl "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes/1" -H "X-API-KEY: edd1c9f034335f136f87ad84b625c8f1" -X PUT -d '
+{
+ "host": "httpbin.org",
+ "uri": "/*",
+ "upstream": {
+ "type": "roundrobin",
+ "nodes": {
+ "httpbin-external.default.svc.cluster.local:80": 1
+ }
+ }
+}'
+```
+
+Then, we can verify access and if the newly created route is functioning correctly by running another final command:
+
+``` shell
+$ curl http://51.159.10.6:80/get -H 'Host: httpbin.org'
+{
+ "headers": {
+ "Accept": "*/*",
+ "Host": "httpbin.org",
+ "User-Agent": "curl/7.68.0",
+ "X-Amzn-Trace-Id": "Root=1-63228c4e-0388e1b61255180620195210",
+ "X-Forwarded-Host": "httpbin.org"
+ }
+}
+```
+
+Here we go, APISIX Admin API is responding to our requests in the Scaleway Cloud and the request is forwarded to the external service.
+
+### Deploy and run APISIX Ingress Controller
+
+Next, we will try to install and verify [Apache APISIX Ingress Controller](https://apisix.apache.org/docs/ingress-controller/getting-started/) is running in the Scaleway Cloud and we do very similar steps as we did for APISIX.
+
+To install APISIX Ingress with helm:
+
+``` shell
+$ helm repo add apisix https://charts.apiseven.com
+$ helm repo add bitnami https://charts.bitnami.com/bitnami
+$ helm repo update
+
+$ kubectl create ns ingress-apisix
+$ helm install apisix apisix/apisix \
+ --set gateway.type=LoadBalancer \
+ --set ingress-controller.enabled=true \
+ --namespace ingress-apisix \
+ --set ingress-controller.config.apisix.serviceNamespace=ingress-apisix
+
+```
+
+Then, check the deployment status:
+
+``` shell
+$ kubectl get pods -n ingress-apisix
+
+NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
+apisix-5bcf68b548-qrsqb 1/1 Running 0 1m
+apisix-etcd-0 1/1 Running 0 1m
+apisix-etcd-1 1/1 Running 0 1m
+apisix-etcd-2 1/1 Running 0 1m
+apisix-ingress-controller-75bd4d9b9b-7xfn5 1/1 Running 0 1m
+
+$ kubectl get svc -n ingress-apisix
+
+apisix-admin ClusterIP 10.36.120.143 <none> 9180/TCP 82m
+apisix-etcd ClusterIP 10.47.39.201 <none> 2379/TCP,2380/TCP 82m
+apisix-etcd-headless ClusterIP None <none> 2379/TCP,2380/TCP 82m
+apisix-gateway LoadBalancer 10.45.241.11 51.159.206.46 80:30197/TCP 82m
+apisix-ingress-controller ClusterIP 10.47.236.40 <none> 80/TCP 82m
+```
+
+Afterward, we can deploy mock server `htttbin` to the default namespace in order to test the ingress controller:
+
+``` shell
+kubectl run httpbin --image kennethreitz/httpbin --port 80
+kubectl expose pod httpbin --port 80
+```
+
+Now we are ready to test ingress by creating a new route the same as below
Review Comment:
```suggestion
Now we are ready to test ingress by creating a new route the same as below:
```
--
This is an automated message from the Apache Git Service.
To respond to the message, please log on to GitHub and use the
URL above to go to the specific comment.
To unsubscribe, e-mail: notifications-unsubscribe@apisix.apache.org
For queries about this service, please contact Infrastructure at:
users@infra.apache.org