You are viewing a plain text version of this content. The canonical link for it is here.
Posted to commits@spark.apache.org by gu...@apache.org on 2023/03/14 06:39:20 UTC
[spark] branch branch-3.4 updated: [SPARK-42496][CONNECT][DOCS] Adding Spark Connect to the Spark 3.4 documentation
This is an automated email from the ASF dual-hosted git repository.
gurwls223 pushed a commit to branch branch-3.4
in repository https://gitbox.apache.org/repos/asf/spark.git
The following commit(s) were added to refs/heads/branch-3.4 by this push:
new e93b59f7421 [SPARK-42496][CONNECT][DOCS] Adding Spark Connect to the Spark 3.4 documentation
e93b59f7421 is described below
commit e93b59f74217cc4c173db50ddb31a4dceda54975
Author: Allan Folting <al...@databricks.com>
AuthorDate: Tue Mar 14 15:38:44 2023 +0900
[SPARK-42496][CONNECT][DOCS] Adding Spark Connect to the Spark 3.4 documentation
### What changes were proposed in this pull request?
Adding a Spark Connect overview page to the Spark 3.4 documentation and a short section on the Spark overview page with a link to it.
### Why are the changes needed?
The first version of Spark Connect is released as part of Spark 3.4.0 and this adds an overview for it to the documentation.
### Does this PR introduce _any_ user-facing change?
Yes, the user facing documentation is updated.
### How was this patch tested?
Built the doc website locally and tested the pages.
SKIP_SCALADOC=1 SKIP_RDOC=1 bundle exec jekyll build
index.html

spark-connect-overview.html
Closes #40324 from allanf-db/spark_connect_docs.
Authored-by: Allan Folting <al...@databricks.com>
Signed-off-by: Hyukjin Kwon <gu...@apache.org>
(cherry picked from commit c7b9b42efdd577cb7ea41752fb6e73444462d0ce)
Signed-off-by: Hyukjin Kwon <gu...@apache.org>
---
docs/img/spark-connect-api.png | Bin 0 -> 808246 bytes
docs/img/spark-connect-communication.png | Bin 0 -> 566977 bytes
docs/index.md | 40 +++--
docs/spark-connect-overview.md | 259 +++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
4 files changed, 285 insertions(+), 14 deletions(-)
diff --git a/docs/img/spark-connect-api.png b/docs/img/spark-connect-api.png
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..02f2017a45d
Binary files /dev/null and b/docs/img/spark-connect-api.png differ
diff --git a/docs/img/spark-connect-communication.png b/docs/img/spark-connect-communication.png
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..f5f04a9f83f
Binary files /dev/null and b/docs/img/spark-connect-communication.png differ
diff --git a/docs/index.md b/docs/index.md
index f6310c41ba7..4f24ad4edce 100644
--- a/docs/index.md
+++ b/docs/index.md
@@ -49,8 +49,19 @@ For Java 11, `-Dio.netty.tryReflectionSetAccessible=true` is required additional
# Running the Examples and Shell
-Spark comes with several sample programs. Scala, Java, Python and R examples are in the
-`examples/src/main` directory. To run one of the Java or Scala sample programs, use
+Spark comes with several sample programs. Python, Scala, Java and R examples are in the
+`examples/src/main` directory.
+
+To run Spark interactively in a Python interpreter, use
+`bin/pyspark`:
+
+ ./bin/pyspark --master "local[2]"
+
+Sample applications are provided in Python. For example:
+
+ ./bin/spark-submit examples/src/main/python/pi.py 10
+
+To run one of the Scala or Java sample programs, use
`bin/run-example <class> [params]` in the top-level Spark directory. (Behind the scenes, this
invokes the more general
[`spark-submit` script](submitting-applications.html) for
@@ -61,31 +72,32 @@ launching applications). For example,
You can also run Spark interactively through a modified version of the Scala shell. This is a
great way to learn the framework.
- ./bin/spark-shell --master local[2]
+ ./bin/spark-shell --master "local[2]"
The `--master` option specifies the
[master URL for a distributed cluster](submitting-applications.html#master-urls), or `local` to run
locally with one thread, or `local[N]` to run locally with N threads. You should start by using
`local` for testing. For a full list of options, run Spark shell with the `--help` option.
-Spark also provides a Python API. To run Spark interactively in a Python interpreter, use
-`bin/pyspark`:
-
- ./bin/pyspark --master local[2]
-
-Example applications are also provided in Python. For example,
-
- ./bin/spark-submit examples/src/main/python/pi.py 10
-
-Spark also provides an [R API](sparkr.html) since 1.4 (only DataFrames APIs included).
+Spark also provides an [R API](sparkr.html) since 1.4 (only DataFrame APIs are included).
To run Spark interactively in an R interpreter, use `bin/sparkR`:
- ./bin/sparkR --master local[2]
+ ./bin/sparkR --master "local[2]"
Example applications are also provided in R. For example,
./bin/spark-submit examples/src/main/r/dataframe.R
+## Running Spark Client Applications Anywhere with Spark Connect
+
+Spark Connect is a new client-server architecture introduced in Spark 3.4 that decouples Spark
+client applications and allows remote connectivity to Spark clusters. The separation between
+client and server allows Spark and its open ecosystem to be leveraged from anywhere, embedded
+in any application. In Spark 3.4, Spark Connect provides DataFrame API coverage for PySpark and
+DataFrame/Dataset API support in Scala.
+
+To learn more about Spark Connect and how to use it, see [Spark Connect Overview](spark-connect-overview.html).
+
# Launching on a Cluster
The Spark [cluster mode overview](cluster-overview.html) explains the key concepts in running on a cluster.
diff --git a/docs/spark-connect-overview.md b/docs/spark-connect-overview.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..e46fb9ad913
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/spark-connect-overview.md
@@ -0,0 +1,259 @@
+---
+layout: global
+title: Spark Connect Overview
+license: |
+ Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
+ contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
+ this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
+ The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
+ (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
+ the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
+
+ http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
+
+ Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
+ distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
+ WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
+ See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
+ limitations under the License.
+---
+**Building client-side Spark applications**
+
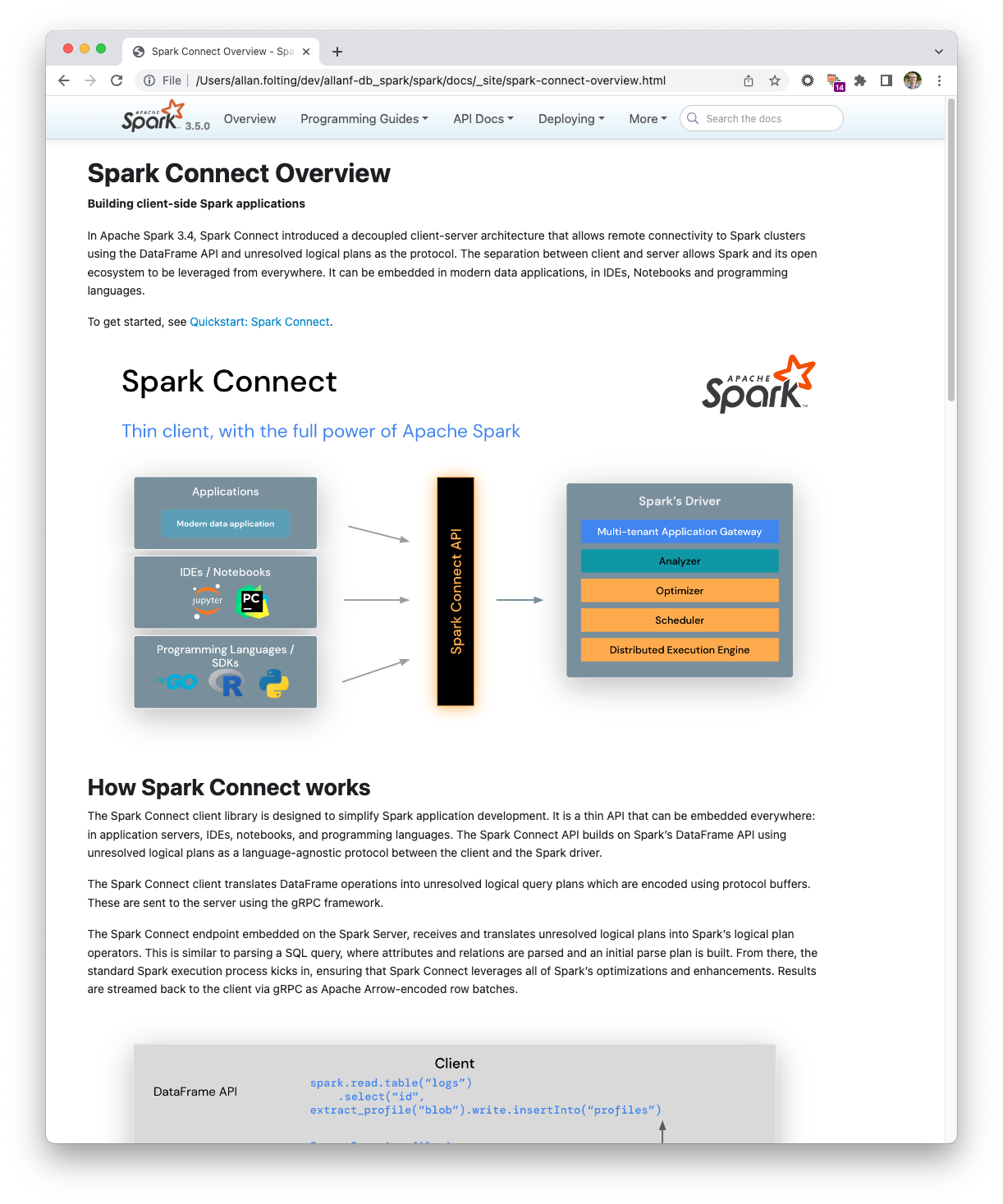
+In Apache Spark 3.4, Spark Connect introduced a decoupled client-server
+architecture that allows remote connectivity to Spark clusters using the
+DataFrame API and unresolved logical plans as the protocol. The separation
+between client and server allows Spark and its open ecosystem to be
+leveraged from everywhere. It can be embedded in modern data applications,
+in IDEs, Notebooks and programming languages.
+
+To get started, see [Quickstart: Spark Connect](api/python/getting_started/quickstart_connect.html).
+
+<p style="text-align: center;">
+ <img src="img/spark-connect-api.png" title="Spark Connect API" alt="Spark Connect API Diagram" />
+</p>
+
+# How Spark Connect works
+
+The Spark Connect client library is designed to simplify Spark application
+development. It is a thin API that can be embedded everywhere: in application
+servers, IDEs, notebooks, and programming languages. The Spark Connect API
+builds on Spark's DataFrame API using unresolved logical plans as a
+language-agnostic protocol between the client and the Spark driver.
+
+The Spark Connect client translates DataFrame operations into unresolved
+logical query plans which are encoded using protocol buffers. These are sent
+to the server using the gRPC framework.
+
+The Spark Connect endpoint embedded on the Spark Server, receives and
+translates unresolved logical plans into Spark's logical plan operators.
+This is similar to parsing a SQL query, where attributes and relations are
+parsed and an initial parse plan is built. From there, the standard Spark
+execution process kicks in, ensuring that Spark Connect leverages all of
+Spark's optimizations and enhancements. Results are streamed back to the
+client via gRPC as Apache Arrow-encoded row batches.
+
+<p style="text-align: center;">
+ <img src="img/spark-connect-communication.png" title="Spark Connect communication" alt="Spark Connect communication" />
+</p>
+
+# Operational benefits of Spark Connect
+
+With this new architecture, Spark Connect mitigates several multi-tenant
+operational issues:
+
+**Stability**: Applications that use too much memory will now only impact their
+own environment as they can run in their own processes. Users can define their
+own dependencies on the client and don't need to worry about potential conflicts
+with the Spark driver.
+
+**Upgradability**: The Spark driver can now seamlessly be upgraded independently
+of applications, e.g. to benefit from performance improvements and security fixes.
+This means applications can be forward-compatible, as long as the server-side RPC
+definitions are designed to be backwards compatible.
+
+**Debuggability and Observability**: Spark Connect enables interactive debugging
+during development directly from your favorite IDE. Similarly, applications can
+be monitored using the application's framework native metrics and logging libraries.
+
+# How to use Spark Connect
+
+Starting with Spark 3.4, Spark Connect is available and supports PySpark and Scala
+applications. We will walk through how to run an Apache Spark server with Spark
+Connect and connect to it from a client application using the Spark Connect client
+library.
+
+## Download and start Spark server with Spark Connect
+
+First, download Spark from the
+[Download Apache Spark](https://spark.apache.org/downloads.html) page. Spark Connect
+was introduced in Apache Spark version 3.4 so make sure you choose 3.4.0 or newer in
+the release drop down at the top of the page. Then choose your package type, typically
+“Pre-built for Apache Hadoop 3.3 and later”, and click the link to download.
+
+Now extract the Spark package you just downloaded on your computer, for example:
+
+{% highlight bash %}
+tar -xvf spark-3.4.0-bin-hadoop3.tgz
+{% endhighlight %}
+
+In a terminal window, go to the `spark` folder in the location where you extracted
+Spark before and run the `start-connect-server.sh` script to start Spark server with
+Spark Connect, like in this example:
+
+{% highlight bash %}
+./sbin/start-connect-server.sh --packages org.apache.spark:spark-connect_2.12:3.4.0
+{% endhighlight %}
+
+Note that we include a Spark Connect package (`spark-connect_2.12:3.4.0`), when starting
+Spark server. This is required to use Spark Connect. Make sure to use the same version
+of the package as the Spark version you downloaded above. In the example here, Spark 3.4.0
+with Scala 2.12.
+
+Now Spark server is running and ready to accept Spark Connect sessions from client
+applications. In the next section we will walk through how to use Spark Connect
+when writing client applications.
+
+## Use Spark Connect in client applications
+
+When creating a Spark session, you can specify that you want to use Spark Connect
+and there are a few ways to do that as outlined below.
+
+If you do not use one of the mechanisms outlined here, your Spark session will
+work just like before, without leveraging Spark Connect, and your application code
+will run on the Spark driver node.
+
+### Set SPARK_REMOTE environment variable
+
+If you set the `SPARK_REMOTE` environment variable on the client machine where your
+Spark client application is running and create a new Spark Session as illustrated
+below, the session will be a Spark Connect session. With this approach, there is
+no code change needed to start using Spark Connect.
+
+In a terminal window, set the `SPARK_REMOTE` environment variable to point to the
+local Spark server you started on your computer above:
+
+{% highlight bash %}
+export SPARK_REMOTE="sc://localhost"
+{% endhighlight %}
+
+And start the Spark shell as usual:
+
+<div class="codetabs">
+
+<div data-lang="python" markdown="1">
+{% highlight bash %}
+./bin/pyspark
+{% endhighlight %}
+
+The PySpark shell is now connected to Spark using Spark Connect as indicated in the welcome
+message.
+</div>
+
+</div>
+
+And if you write your own program, create a Spark session as shown in this example:
+
+<div class="codetabs">
+
+<div data-lang="python" markdown="1">
+{% highlight python %}
+from pyspark.sql import SparkSession
+spark = SparkSession.builder.getOrCreate()
+{% endhighlight %}
+</div>
+
+</div>
+
+Which will create a Spark Connect session from your application by reading the
+`SPARK_REMOTE` environment variable we set above.
+
+### Specify Spark Connect when creating Spark session
+
+You can also specify that you want to use Spark Connect explicitly when you
+create a Spark session.
+
+For example, you can launch the PySpark shell with Spark Connect as
+illustrated here.
+
+<div class="codetabs">
+
+<div data-lang="python" markdown="1">
+To launch the PySpark shell with Spark Connect, simply include the `remote`
+parameter and specify the location of your Spark server. We are using `localhost`
+in this example to connect to the local Spark server we started above.
+
+{% highlight bash %}
+./bin/pyspark --remote "sc://localhost"
+{% endhighlight %}
+
+And you will notice that the PySpark shell welcome message tells you that
+you have connected to Spark using Spark Connect.
+
+Now you can run PySpark code in the shell to see Spark Connect in action:
+
+{% highlight python %}
+>>> columns = ["id","name"]
+>>> data = [(1,"Sarah"),(2,"Maria")]
+>>> df = spark.createDataFrame(data).toDF(*columns)
+>>> df.show()
++---+-----+
+| id| name|
++---+-----+
+| 1|Sarah|
+| 2|Maria|
++---+-----+
+
+>>>
+{% endhighlight %}
+</div>
+
+</div>
+
+Or, when writing your own code, include the `remote` function with a reference to
+your Spark server when you create a Spark session, as in this example:
+
+<div class="codetabs">
+
+<div data-lang="python" markdown="1">
+{% highlight python %}
+from pyspark.sql import SparkSession
+spark = SparkSession.builder.remote("sc://localhost").getOrCreate()
+{% endhighlight %}
+</div>
+
+<div data-lang="scala" markdown="1">
+{% highlight scala %}
+import org.apache.spark.sql.SparkSession
+val spark = SparkSession.builder().remote("sc://localhost").build()
+{% endhighlight %}
+</div>
+
+</div>
+
+# Client application authentication
+
+While Spark Connect does not have built-in authentication, it is designed to
+work seamlessly with your existing authentication infrastructure. Its gRPC
+HTTP/2 interface allows for the use of authenticating proxies, which makes
+it possible to secure Spark Connect without having to implement authentication
+logic in Spark directly.
+
+# What is supported in Spark 3.4
+
+**PySpark**: In Spark 3.4, Spark Connect supports most PySpark APIs, including
+[DataFrame](api/python/reference/pyspark.sql/dataframe.html),
+[Functions](api/python/reference/pyspark.sql/functions.html), and
+[Column](api/python/reference/pyspark.sql/column.html). However,
+some APIs such as [SparkContext](api/python/reference/api/pyspark.SparkContext.html)
+and [RDD](api/python/reference/api/pyspark.RDD.html) are not supported.
+You can check which APIs are currently
+supported in the [API reference](api/python/reference/index.html) documentation.
+Supported APIs are labeled "Supports Spark Connect" so you can check whether the
+APIs you are using are available before migrating existing code to Spark Connect.
+
+**Scala**: In Spark 3.4, Spark Connect supports most Scala APIs, including
+[Dataset](api/scala/org/apache/spark/sql/Dataset.html),
+[functions](api/scala/org/apache/spark/sql/functions$.html), and
+[Column](api/scala/org/apache/spark/sql/Column.html).
+
+Support for more APIs is planned for upcoming Spark releases.
\ No newline at end of file
---------------------------------------------------------------------
To unsubscribe, e-mail: commits-unsubscribe@spark.apache.org
For additional commands, e-mail: commits-help@spark.apache.org